北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 711-716. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.013
前列腺体积不同的患者经尿道光纤铥激光前列腺剜除术的有效性及安全性比较
左超1,2,*, 王国立1,*, 杨昆霖1, 车新艳1, 孟一森1,*( ), 张凯1,*(
), 张凯1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第一医院泌尿外科, 北京 100034
2. 北京市密云区医院泌尿外科, 北京 101500
Comparison of efficacy and safety of transurethral thulium fiber laser enucleation of prostate in patients with different prostate volumes
Chao ZUO1,2, Guoli WANG1, Kunlin YANG1, Xinyan CHE1, Yisen MENG1,*( ), Kai ZHANG1,*(
), Kai ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Urology, Beijing Miyun District Hospital, Beijing 101500, China
摘要:
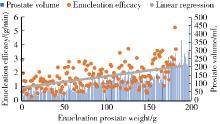
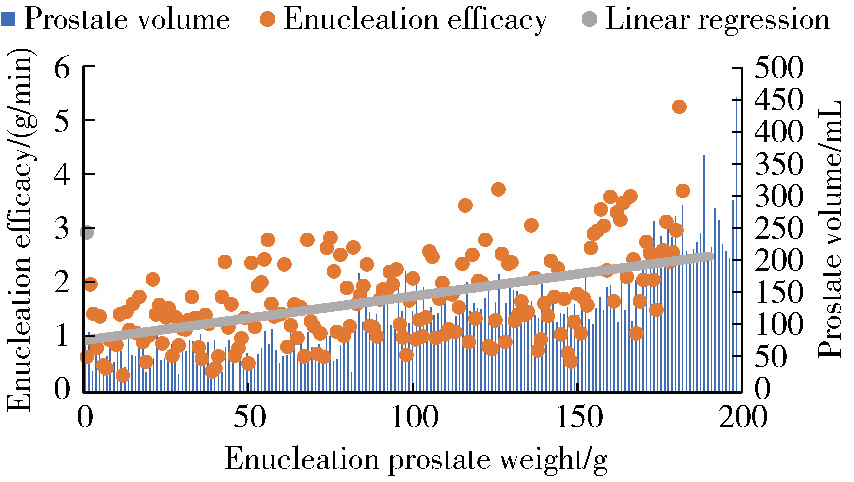
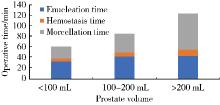
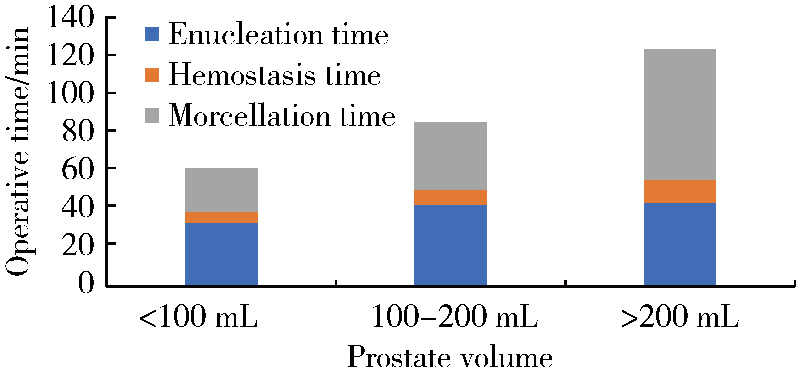
目的: 评估采用光纤铥激光前列腺剜除术(thulium fiber laser enucleation of the prostate,ThuFLEP)治疗超大体积(>200 mL)前列腺的有效性和安全性。方法: 回顾性分析2022年1月至2024年5月,于北京大学第一医院由同一泌尿外科医师进行手术的485例良性前列腺增生(benign prostatic hyperplasia, BPH)患者的临床资料,患者均采用光纤铥激光,根据前列腺总体积(total volume of the prostate,TPV)将患者分为三组:A组TPV < 100 mL、B组100 mL≤TPV < 200 mL、C组TPV≥200 mL。三组患者的年龄[(69.38±7.79)岁、(69.64±8.69)岁、(70.32±7.44)岁]、国际前列腺症状评分(International Prostate Symptom Score,IPSS)[(22.7±1.9)分、(22.8±2.7)分、(25.8±3.7)分]、最大尿流率(maximum urinary flow rate,Qmax)[(7.9±2.7) mL/s、(9.3±4.3) mL/s、(9.9±3.3) mL/s]差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);三组患者的前列腺体积[(103.49±46.19) mL、(75.73±30.69) mL、(273.49±49.19) mL]、前列腺特异性抗原(prostate specific antigen, PSA)[3.52 (1.05, 8.76) μg/L、6.78 (1.61, 7.45) μg/L、8.52 (5.05, 12.76) μg/L]差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。结果: 所有患者的手术均顺利完成,三组患者的剜除时间[30.0 (21.2, 44.5) min、41.6 (31.2, 52.5) min、45.1 (35.2, 50.0) min]、住院时间[(6.06±1.21) d、(6.15±1.50) d、(7.71±1.74) d]差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);而三组患者的术后留置导尿管时间[(4.0±1.4) d、(4.0±1.3) d、(6.6±1.1) d]、手术时间[61 (42, 89) min、82 (62, 105) min、115 (96, 142) min]、剜除效率[1.29 (0.71, 1.56) g/min、1.67 (1.23, 2.15) g/min、2.74 (2.20, 3.34) g/min]、血红蛋白下降值[12 (7, 19) g/L、17 (11, 24) g/L、27 (19, 35) g/L]差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。线性回归分析显示,剜除效率与剜除重量之间存在较强的正向线性相关(r=0.880,P < 0.001),剜除效率随着前列腺体积增加而提高。术后三组患者之间的IPSS[(6.6±1.7)分、(6.2±1.4)分、(4.6±1.1)分]、Qmax[(18.9±3.1) mL/s、(16.8±3.8) mL/s、(22.9±7.1) mL/s]差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术后的IPSS、Qmax与术前比较差异均有统计学意义,但术后C组Qmax的提高明显高于其他两组(P < 0.05)。术后并发症以Clavien-Dindo并发症系统评分为标准,分为Clavien-Dindo Ⅰ (尿潴留、持续性血尿)、Clavien-Dindo Ⅱ (腺体残余、泌尿系感染、输血)和Clavien-Dindo Ⅲ (尿道狭窄、膀胱颈挛缩、出血并再次手术),三组患者术后均随访3个月,Clavien-Dindo的并发症发生率分别为5.2% (13例)、6.7% (12例)和12.1% (7例),组间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),其中,泌尿系感染、输血及出血并再次手术的组间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),其他并发症的组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论: 前列腺体积越大,输血及再次手术的风险增高,剜除效率随着前列腺体积的增加而提高,光纤铥激光前列腺剜除术治疗超大体积的BPH安全、有效。
中图分类号:
- R697.3
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
左超, 杨昆霖, 车新艳, 等. "U"形整叶法经尿道光纤铥激光前列腺剜切术治疗良性前列腺增生的疗效和安全性[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2024, 45 (7): 515- 520.
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
中华医学会泌尿外科学分会激光学组, 微创学组, 尿控学组. 经尿道激光前列腺剜除术热点问题中国专家共识[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2024, 45 (7): 489- 496.
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
左超, 杨昆霖, 李志存, 等. "双沟双环法"经尿道铥激光前列腺剜除术单一术者学习曲线分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2023, 103 (20): 1563- 1567.
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| [1] | 赵兆, 张维宇, 杨文博, 张勇杰, 张晓鹏, 赵慧颖, 周刚, 王强. 低龄、低体重儿童肾移植2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 803-807. |
| [2] | 刘宁, 满立波, 何峰, 黄广林, 翟建坡. 良性前列腺增生患者排尿中断症状与尿动力学指标的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(2): 328-333. |
| [3] | 许素环,王蓓蓓,庞秋颖,钟丽君,丁炎明,黄燕波,车新艳. 等体温膀胱冲洗对经尿道前列腺电切术患者干预效果的meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 676-683. |
| [4] | 李辉,高阳旭,王书磊,姚红新. 恶性肿瘤患儿完全植入式静脉输液港手术并发症[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
| [5] | 李伟浩,李伟,张学民,李清乐,焦洋,张韬,蒋京军,张小明. 去分支杂交手术和传统手术治疗胸腹主动脉瘤的结果比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 177-181. |
| [6] | 董文敏,王明瑞,胡浩,王起,许克新,徐涛. Allium覆膜金属输尿管支架长期留置治疗输尿管-回肠吻合口狭窄的初期临床经验及随访结果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 637-641. |
| [7] | 高健,胡立宝,陈尘,郅新,徐涛. 经皮肾镜去石术后出血的介入治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 667-671. |
| [8] | 马凯,曲星珂,许清泉,熊六林,叶雄俊,安立哲,陈伟男,黄晓波. 肾移植术后移植肾输尿管膀胱吻合口狭窄的腔内治疗:13例报道[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1155-1158. |
| [9] | 刘可,张帆,肖春雷,夏海缀,郝一昌,毕海,赵磊,刘余庆,卢剑,马潞林. 低功率钬激光“七步两叶法”前列腺剜除术治疗良性前列腺增生[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1159-1164. |
| [10] | 徐稼轩,王宏志,董军,陈小杰,杨勇,陈仁雄,王国栋. 食管癌术后急性肺损伤/急性呼吸窘迫综合征的危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1057-1062. |
| [11] | 李旭, 李奉龙, 鲁谊, 朱以明, 郭斯翊, 李屹钧, 姜春岩. 锁定钢板治疗非骨质疏松性复杂肱骨近端骨折的中期临床及影像学随访研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 855-860. |
| [12] | 黄珺君,张红,章巍,王玺,龚玉红,王广发. 支气管镜下介入治疗早期并发症的独立危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(6): 1006-1011. |
| [13] | 葛娜,关明,李茜,李率,王恩博. 可弯曲喉罩在颌面外科日间手术的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(6): 1010-1014. |
| [14] | 刘坤,徐宗源,孟峻嵩,傅广波,顾硕,顾民. 术前营养风险对根治性全膀胱切除术后并发症发生率的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 800-803. |
| [15] | 刘宁, 黄广林, 满立波, 何峰, 王海东, 王海, 李贵忠, 王建伟. 缩短钬激光前列腺剜除术学习曲线的方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 720-723. |
|
||