北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1167-1171. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.018
恶性肿瘤患儿完全植入式静脉输液港手术并发症
- 北京大学第一医院小儿外科,北京 100034
Surgical complications of totally implantable venous access port in children with malignant tumors
Hui LI,Yang-xu GAO,Shu-lei WANG,Hong-xin YAO*( )
)
- Department of Pediatric Surgery, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
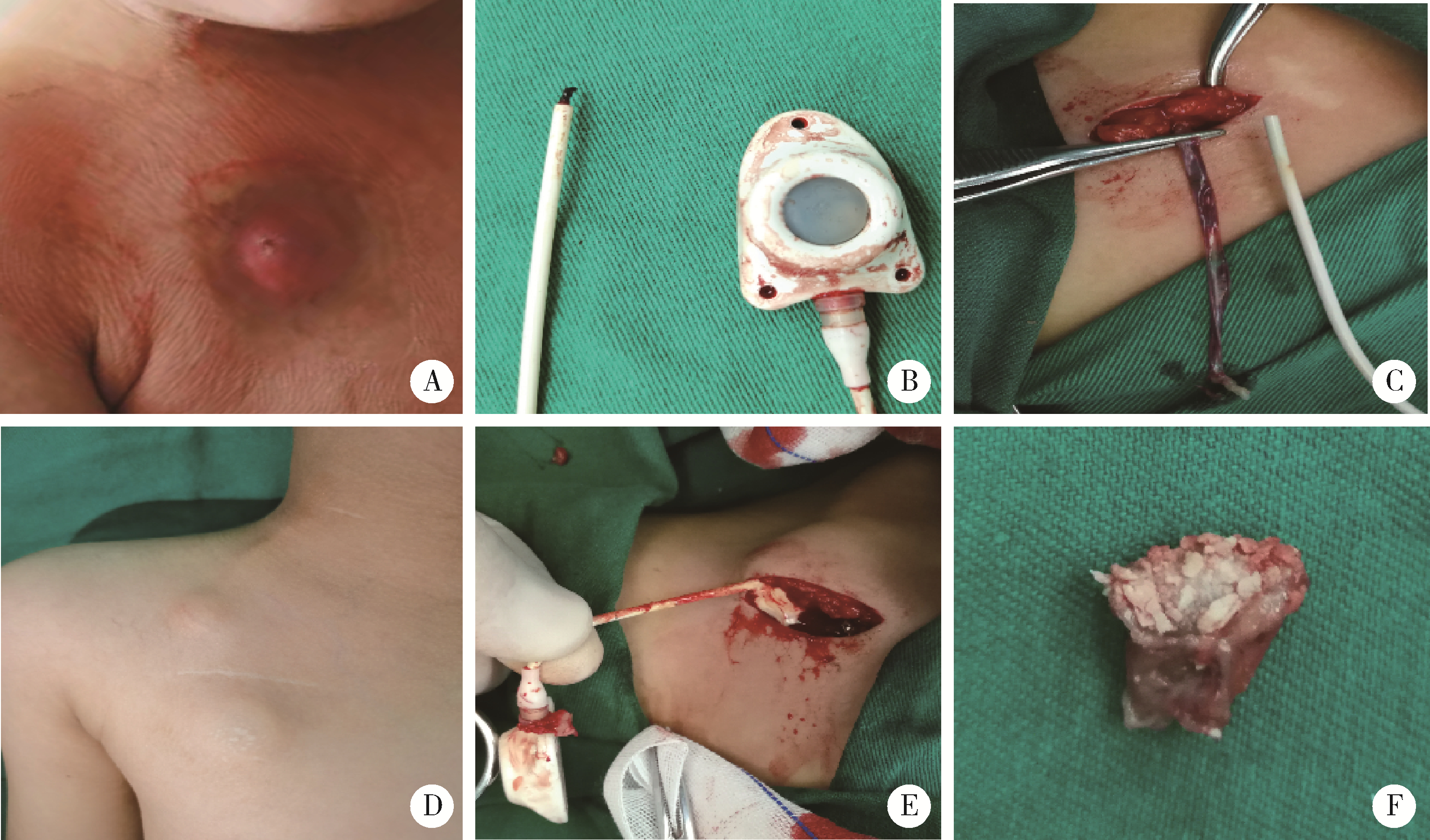
目的: 总结完全植入式静脉输液港(totally implantable venous access port,TIVAP)在恶性肿瘤患儿中应用的手术经验,探讨其手术并发症的应对方法。方法: 回顾性分析北京大学第一医院小儿外科2017年1月至2019年12月期间165例接受TIVAP植入术的恶性肿瘤患儿病例资料,记录并统计TIVAP植入的手术过程、并发症及并发症处理情况。结果: 本组患儿按手术方式不同分为颈外静脉切开组(n=27)和颈内静脉穿刺组(n=138),后者又分为超声引导穿刺组(n=95)和盲穿刺组(n=43)。颈外静脉切开组无穿刺并发症发生,其平均置管成功所用时间和导管进入上腔静脉所用顺管次数均多于颈内静脉穿刺组[(9.26±1.85) min vs. (5.76±1.56) min,(1.93±0.87)次vs. 1次],差异有统计学意义。超声引导颈内静脉穿刺组平均置管成功所用时间、一次穿刺成功率、平均穿刺次数和穿刺并发症发生率均优于盲穿刺组[(5.36±1.12) min vs. (6.67±1.99) min,93.68%(89/95) vs. 74.42%(32/43),(1.06±0.24)次vs. (1.29±0.55)次,2.11%(2/95) vs. 11.63%(5/43)],差异有统计学意义。本组总并发症发生率12.12%(20/165),其中气胸1例,误穿动脉1例,局部血肿5例,输液港相关性感染4例(输液港局部感染2例、导管相关性血流感染2例),港座表面皮下组织变菲薄2例,港座翻转1例,输液不畅4例(导管弯折1例、导管堵塞3例),皮下管路周围排异物聚集2例,未发生导管断裂、脱落和导管夹闭综合征等并发症。结论: TIVAP能为恶性肿瘤患儿提供安全有效的输液通道,颈外静脉切开和超声引导颈内静脉穿刺是小儿TIVAP植入的可靠术式。手术医师应对TIVAP并发症有充分的认识,采取措施减少并发症的发生,正确处置已发生的并发症。
中图分类号:
- R726
| 1 |
Zhang P , Du J , Fan CS , et al. Utility of totally implantable venous access ports in patients with breast cancer[J]. Breast J, 2020, 26 (2): 333- 334.
doi: 10.1111/tbj.13595 |
| 2 |
Xu HP , Chen R , Jiang CJ , et al. Implanting totally implantable venous access ports in the upper arm is feasible and safe for patients with early breast cancer[J]. J Vasc Access, 2020, 21 (5): 609- 614.
doi: 10.1177/1129729819894461 |
| 3 |
余磊, 张英妹, 黄种文, 等. 经颈静脉及锁骨下静脉输液港植入术并发症的比较分析[J]. 当代医学, 2021, 27 (3): 112- 114.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2021.03.044 |
| 4 |
李颖, 姜浩, 韩哲洙, 等. 颈内静脉与锁骨下静脉植入输液港并发症发生率的对比分析[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2020, 36 (9): 1496- 1499.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2020.09.035 |
| 5 |
Sundaram J , Agarwal P , Ramasundaram M , et al. Implantable venous access devices in pediatric malignancies: Institutional expe-rience in a developing nation[J]. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg, 2020, 25 (5): 286- 290.
doi: 10.4103/jiaps.JIAPS_121_19 |
| 6 |
Zhang KC , Chen L , Chinese Research Hospital Association Digestive Tumor Committee , et al. Chinese expert consensus and practice guideline of totally implantable access port for digestive tract carcinomas[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26 (25): 3517- 3527.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i25.3517 |
| 7 |
中国医师协会介入医师分会. 植入式给药装置介入专家共识[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2019, 99 (7): 484- 490.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2019.07.002 |
| 8 | 周涛, 唐甜甜, 耿翠芝, 等. 植入式静脉输液港植入手术2007例分析[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2014, 34 (4): 348- 350. |
| 9 |
Caterina G , Maria A , Alessandro C , et al. Totally implantable venous access devices in children with medical complexity: Preliminary data from a tertiary care hospital[J]. J Vasc Access, 2017, 18 (5): 426- 429.
doi: 10.5301/jva.5000727 |
| 10 |
Philomena CD , Shiyam K , Annupam K , et al. Complications and management of totally implantable central venous access ports in cancer patients at a university hospital in Oman[J]. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J, 2021, 21 (1): e103- e109.
doi: 10.18295/squmj.2021.21.01.014 |
| 11 | 黄一敏, 徐伟珏, 吴一波, 等. 小儿完全植入式静脉输液港导管相关性血流感染的诊治——附4例报道[J]. 临床小儿外科杂志, 2020, 19 (10): 939- 942. |
| 12 |
Taveira MRV , Lima LS , Araújo CC , et al. Risk factors for central line-associated bloodstream infection in pediatric oncology patients with a totally implantable venous access port: A cohort study[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2017, 64 (2): 336- 342.
doi: 10.1002/pbc.26225 |
| 13 |
Choksi A , Finnegan K , Etezadi V . Does systemic antibiotic prophylaxis prior to the placement of totally implantable venous access devices reduce early infection? A retrospective study of 1 485 cases at a large academic institution[J]. Am J Infect Control, 2020, 48 (1): 95- 99.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2019.06.028 |
| 14 | 周荻, 葛峰, 缪长虹, 等. 复旦大学附属中山医院完全植入式静脉输液港植入与维护规范(v1.2020)[J]. 中国临床医学, 2020, 27 (4): 697- 703. |
| 15 |
余超, 葛坤元, 蒋晓东, 等. 3种不同途径植入静脉输液港的临床应用比较[J]. 复旦学报(医学版), 2021, 48 (2): 229- 234.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2021.02.013 |
| 16 |
Ding XY , Ding F , Wang YG , et al. Shanghai expert consensus on totally implantable access ports 2019[J]. J Intervent Med, 2019, 2 (4): 141- 145.
doi: 10.1016/j.jimed.2019.10.008 |
| 17 |
Chou PL , Fu JY , Cheng CH , et al. Current port maintenance strategies are insufficient: View based on actual presentations of implanted ports[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98 (44): e17757.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017757 |
| [1] | 刘京,陆爱东,左英熹,吴珺,黄志卓,贾月萍,丁明明,张乐萍,秦炯. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病合并癫痫发作75例临床特征和预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [2] | 崔雅茜,杜军保,张清友,廖莹,刘平,王瑜丽,齐建光,闫辉,徐文瑞,刘雪芹,孙燕,孙楚凡,张春雨,陈永红,金红芳. 儿童直立不耐受和坐位不耐受的疾病谱及治疗方式十年回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 954-960. |
| [3] | 马涛,李艳辉,陈曼曼,马莹,高迪,陈力,马奇,张奕,刘婕妤,王鑫鑫,董彦会,马军. 青春期启动提前与儿童肥胖类型的关联研究: 基于横断面调查和队列调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 961-970. |
| [4] | 杜燕燕,王健,贺兰,季丽娜,徐樨巍. 儿童川崎病合并轻微脑炎/脑病伴可逆性胼胝体压部病变综合征1例并文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 756-761. |
| [5] | 刘云飞,党佳佳,钟盼亮,马宁,师嫡,宋逸. 1990—2019年中国5~24岁人群伤害死亡率分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 498-504. |
| [6] | 钱婧,魏友加,程毅菁,张奕,彭博,朱春梅. 儿童坏死性肺炎临床特征及危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 541-547. |
| [7] | 闫辉,逄璐,李雪迎,杨文双,蒋世菊,刘平,闫存玲. 单中心就诊2~18岁儿童胆固醇水平异常发生率及病因分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 217-221. |
| [8] | 张宏,董继元,王建军,范临夏,曲强,刘洋. 兰州市臭氧对儿童哮喘的短期影响及其季节性差异[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 227-235. |
| [9] | 冯莎蔚,国慧,王勇,赵一姣,刘鹤. 乳牙数字化参考牙冠模型的初步构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 327-334. |
| [10] | 李伟浩,李伟,张学民,李清乐,焦洋,张韬,蒋京军,张小明. 去分支杂交手术和传统手术治疗胸腹主动脉瘤的结果比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 177-181. |
| [11] | 王子靖,李在玲. 有幽门螺杆菌感染家族史儿童胃部菌群的特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1115-1121. |
| [12] | 刘雅菲,宋琳琳,邢茂炜,蔡立新,王东信. 全身麻醉下小儿开颅术术中心脏前负荷动态指标的一致性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 946-951. |
| [13] | 陈曼曼,杨招庚,苏彬彬,李艳辉,高迪,马莹,马涛,董彦会,马军. 中山市儿童青少年青春期身高生长突增规律[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 506-510. |
| [14] | 杨雪,孙伟,王哲,姬爱平,白洁. 儿童和青少年牙外伤急诊患者临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 384-389. |
| [15] | 张子一,夏斌,徐明明,李毅萍,唐瞻贵,陈泳清. 湖南韶山地区儿童口腔卫生干预效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 913-918. |
|