北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 756-761. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.04.028
儿童川崎病合并轻微脑炎/脑病伴可逆性胼胝体压部病变综合征1例并文献复习
- 1. 清华大学附属北京清华长庚医院儿科,清华大学临床医学院,北京 102218
2. 首都医科大学附属北京儿童医院消化内科,国家儿童医学中心,北京 100045
Kawasaki disease complicated with mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion: A case report and literature review
Yan-yan DU1,Jian WANG1,Lan HE1,Li-na JI1,*( ),Xi-wei XU1,2
),Xi-wei XU1,2
- 1. Department of Pediatrics, Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital Affiliated to Tsinghua University, School of Clinical Medicine of Tsinghua University, Beijing 102218, China
2. Department of Gastroenterology, Beijing Children' s Hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University & National Center for Children' s Health, Beijing 100045, China
摘要:
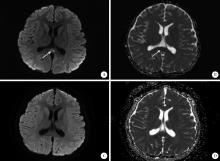
报道1例川崎病合并轻微脑炎/脑病伴可逆性胼胝体压部病变综合征(mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion,MERS)患儿的临床诊疗经过,并回顾相关文献报道,总结疾病特点,提高对该病的认识。本例患者为7岁余男孩,持续高热6 d,伴草莓舌、双眼球结膜充血、全身大片红斑样充血样皮疹和颈部淋巴结肿大,符合川崎病诊断标准。丙种球蛋白(2 g/kg)静脉滴注24 h后患儿仍有发热,且出现头痛、嗜睡表现,头颅磁共振成像(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)显示胼胝体压部局限性梭形肿胀,T1稍低、T2稍高异常信号,扩散加权成像(diffusion-weighted images,DWI)呈明显高信号,表观扩散系数(apparent diffusion coefficient,ADC)图呈明显低信号,提示MERS,予甲泼尼龙2 mg/(kg·d)静脉滴注,数小时后患儿热退,头痛、嗜睡症状消失。1周后复查头颅MRI正常,出院时没有神经系统异常和冠状动脉扩张。共检索到符合条件的外文文献12篇,未检索到中文文献,共报道17例川崎病合并MERS患儿,中位年龄6.5岁(1~14岁),其中5岁以上儿童11例,合并冠状动脉扩张者4例。所有患儿均有不同程度的意识障碍、幻视、惊厥等神经系统症状,头颅MRI符合MERS影像学改变,经积极治疗, 所有患儿的神经系统症状完全消失,其中13例患儿复查了头颅MRI,影像学改变均恢复正常,所有患儿均未遗留神经系统后遗症。川崎病合并MERS的病例报道非常少见,并发MERS的川崎病多发生在5岁以上年长儿童,头颅MRI检查有助于早期诊断,及时积极治疗可以使MERS病情短期内逆转,不留神经系统后遗症。
中图分类号:
- R729
| 1 |
Newburger JW , Takahashi M , Gerber MA , et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: A statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association[J]. Pediatrics, 2004, 114 (6): 1708- 1733.
doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-2182 |
| 2 |
Kurokawa Y , Masuda H , Kobayashi T , et al. Effective therapy with infliximab for clinically mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion in an infant with Kawasaki disease[J]. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi, 2017, 40 (3): 190- 195.
doi: 10.2177/jsci.40.190 |
| 3 |
Kobayashi T , Inoue Y , Takeuchi K , et al. Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in patients with Kawasaki disease[J]. Circulation, 2006, 113 (22): 2606- 2612.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.592865 |
| 4 |
Itamura S , Kamada M , Nakagawa N , et al. Kawasaki disease complicated with reversible splenial lesion and acute myocarditis[J]. Pediatr Cardiol, 2011, 32 (5): 696- 699.
doi: 10.1007/s00246-011-9937-4 |
| 5 |
Sato T , Ushiroda Y , Oyama T , et al. Kawasaki disease-associated MERS: Pathological insights from SPECT findings[J]. Brain Dev, 2012, 34 (7): 605- 608.
doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2011.09.015 |
| 6 | Takanashi J , Shirai K , Sugawara Y , et al. Kawasaki disease complicated by mild encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion (MERS)[J]. J Neurol Sci, 2012, 315 (1/2): 167- 169. |
| 7 | Takahashi KI , Homma S , Suzuki K , et al. A case of Kawasaki disease complicated by clinically mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion (MERS)[J]. J Tokyo Wom Med Univ, 2017, 87 (Suppl 1): 118- 124. |
| 8 | Tsukamoto Y , Majima H , Inukai S . A girl of Kawasaki disease associated with MERS after diagnosis of febrile seizure[J]. J Jpn Soc Pediatr Radiol, 2021, 37 (1): 113- 118. |
| 9 | 松村雄, 阿久津裕子, 倉信大, ほか. 川崎病に合併した脳症の症例報告[J]. 心臓, 2014, 46 (12): 1648- 1649. |
| 10 | 八木文子, 中田桂, 川上睦美, ほか. Mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion (MERS)2型の2例[J]. 臨床放射線, 2018, 63 (8): 911- 918. |
| 11 | 森秀洋, 澤田真理子, 佐藤一寿, ほか. 可逆性脳梁膨大部病変を有する軽症脳炎·脳症を合併した川崎病に対する血漿交換療法[J]. 日本小児科学会雑誌, 2020, 124 (10): 1514- 1519. |
| 12 |
Yoshihara S , Fujita Y , Miyamoto K , et al. Kawasaki disease with mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with reversible splenial lesion in a 2-year-old girl[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2021, 88 (7): 718.
doi: 10.1007/s12098-021-03779-5 |
| 13 |
Kashiwagi M , Tanabe T , Shimakawa S , et al. Clinico-radiological spectrum of reversible splenial lesions in children[J]. Brain Dev, 2014, 36 (4): 330- 336.
doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2013.05.007 |
| 14 |
Ka A , Britton P , Troedson C , et al. Mild encephalopathy with reversible splenial lesion: An important differential of encephalitis[J]. Eur J Paediatr Neurol, 2015, 19 (3): 377- 382.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2015.01.011 |
| 15 |
Tada H , Takanashi J , Barkovich AJ , et al. Clinically mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion[J]. Neurology, 2004, 63 (10): 1854- 1858.
doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000144274.12174.CB |
| 16 |
Takanashi J . Two newly proposed infectious encephalitis/encephalopathy syndromes[J]. Brain Dev, 2009, 31 (7): 521- 528.
doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2009.02.012 |
| 17 | Takanashi J , Imamura A , Hayakawa F , et al. Differences in the time course of splenial and white matter lesions in clinically mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion (MERS)[J]. J Neurol Sci, 2010, 292 (1/2): 24- 27. |
| 18 |
Starkey J , Kobayashi N , Numaguchi Y , et al. Cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum that show restricted difusion: Mechanisms, causes, and manifestations[J]. Radiographics, 2017, 37 (2): 562- 576.
doi: 10.1148/rg.2017160085 |
| 19 |
Takanashi J , Tada H , Maeda M , et al. Encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion is associated with hyponatremia[J]. Brain Dev, 2009, 31 (3): 217- 220.
doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2008.04.002 |
| 20 |
Watanabe T , Abe Y , Sato S , et al. Hyponatremia in Kawasaki disease[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2006, 21 (6): 778- 781.
doi: 10.1007/s00467-006-0086-6 |
| 21 |
Rife E , Gedalia A . Kawasaki Disease: An Update[J]. Curr Rheumatol Rep, 2020, 22 (10): 75.
doi: 10.1007/s11926-020-00941-4 |
| 22 |
Terai M , Honda T , Yasukawa K , et al. Prognostic impact of vascular leakage in acute Kawasaki disease[J]. Circulation, 2003, 108 (3): 325- 330.
doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000079166.93475.5F |
| 23 |
Miyata R , Tanuma N , Hayashi M , et al. Oxidative stress in patients with clinically mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion (MERS)[J]. Brain Dev, 2012, 34 (2): 124- 127.
doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2011.04.004 |
| 24 |
Ichiyama T , Nishikawa M , Hayashi T , et al. Cerebral hypoperfusion during acute Kawasaki disease[J]. Stroke, 1998, 29 (7): 1320- 1321.
doi: 10.1161/01.STR.29.7.1320 |
| 25 |
Hikita T , Kaminaga T , Wakita S , et al. Regional cerebral blood flow abnormalities in patients with kawasaki disease[J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2011, 36 (8): 643- 649.
doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e318217adfc |
| 26 | 多田弘子, 高梨潤一. 可逆性脳梁膨大部病変を有する軽症脳炎脳症―up-to-date[J]. 日本小児科学会雑誌, 2019, 123 (5): 814- 823. |
| [1] | 赵双云, 邹思雨, 李雪莹, 沈丽娟, 周虹. 中文版口腔健康素养量表简版(HeLD-14)在学龄前儿童家长中应用的信度和效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 828-832. |
| [2] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [3] | 岳芷涵,韩娜,鲍筝,吕瑾莨,周天一,计岳龙,王辉,刘珏,王海俊. 儿童早期体重指数轨迹与超重风险关联的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 390-396. |
| [4] | 费秀文,刘斯,汪波,董爱梅. 成人及儿童组织坏死性淋巴结炎临床特征及治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 533-540. |
| [5] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [6] | 闫晓晋,刘云飞,马宁,党佳佳,张京舒,钟盼亮,胡佩瑾,宋逸,马军. 《中国儿童发展纲要(2011-2020年)》实施期间中小学生营养不良率变化及其政策效应分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 593-599. |
| [7] | 弭小艺,侯杉杉,付子苑,周末,李昕璇,孟召学,蒋华芳,周虹. 中文版童年不良经历问卷在学龄前儿童父母中应用的信效度评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 408-414. |
| [8] | 崔孟杰,马奇,陈曼曼,马涛,王鑫鑫,刘婕妤,张奕,陈力,蒋家诺,袁雯,郭桐君,董彦会,马军,星一. 不同生长模式与7~17岁儿童青少年代谢综合征的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [9] | 党佳佳,蔡珊,钟盼亮,王雅琪,刘云飞,师嫡,陈子玥,张依航,胡佩瑾,李晶,马军,宋逸. 室外夜间人工光暴露与中国9~18岁儿童青少年超重肥胖的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [10] | 陈敬,肖伍才,单蕊,宋洁云,刘峥. DRD2基因rs2587552多态性对儿童肥胖干预效果的影响:一项前瞻性、平行对照试验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 436-441. |
| [11] | 李辉,高阳旭,王书磊,姚红新. 恶性肿瘤患儿完全植入式静脉输液港手术并发症[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
| [12] | 刘京,陆爱东,左英熹,吴珺,黄志卓,贾月萍,丁明明,张乐萍,秦炯. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病合并癫痫发作75例临床特征和预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [13] | 崔雅茜,杜军保,张清友,廖莹,刘平,王瑜丽,齐建光,闫辉,徐文瑞,刘雪芹,孙燕,孙楚凡,张春雨,陈永红,金红芳. 儿童直立不耐受和坐位不耐受的疾病谱及治疗方式十年回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 954-960. |
| [14] | 马涛,李艳辉,陈曼曼,马莹,高迪,陈力,马奇,张奕,刘婕妤,王鑫鑫,董彦会,马军. 青春期启动提前与儿童肥胖类型的关联研究: 基于横断面调查和队列调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 961-970. |
| [15] | 刘云飞,党佳佳,钟盼亮,马宁,师嫡,宋逸. 1990—2019年中国5~24岁人群伤害死亡率分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 498-504. |
|
||