北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1172-1177. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.019
外侧锁定接骨板治疗股骨远端骨折术后翻修的相关影响因素
侯国进,周方*( ),田耘,姬洪全,张志山,郭琰,吕扬,杨钟玮
),田耘,姬洪全,张志山,郭琰,吕扬,杨钟玮
- 北京大学第三医院骨科,北京 100191
Related factors of revision of distal femoral fractures treated with lateral locking plate
Guo-jin HOU,Fang ZHOU*( ),Yun TIAN,Hong-quan JI,Zhi-shan ZHANG,Yan GUO,yang LV,Zhong-wei YANG
),Yun TIAN,Hong-quan JI,Zhi-shan ZHANG,Yan GUO,yang LV,Zhong-wei YANG
- Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
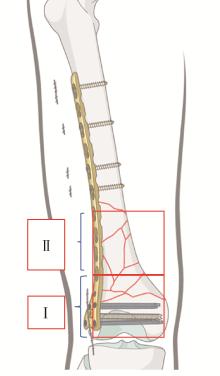
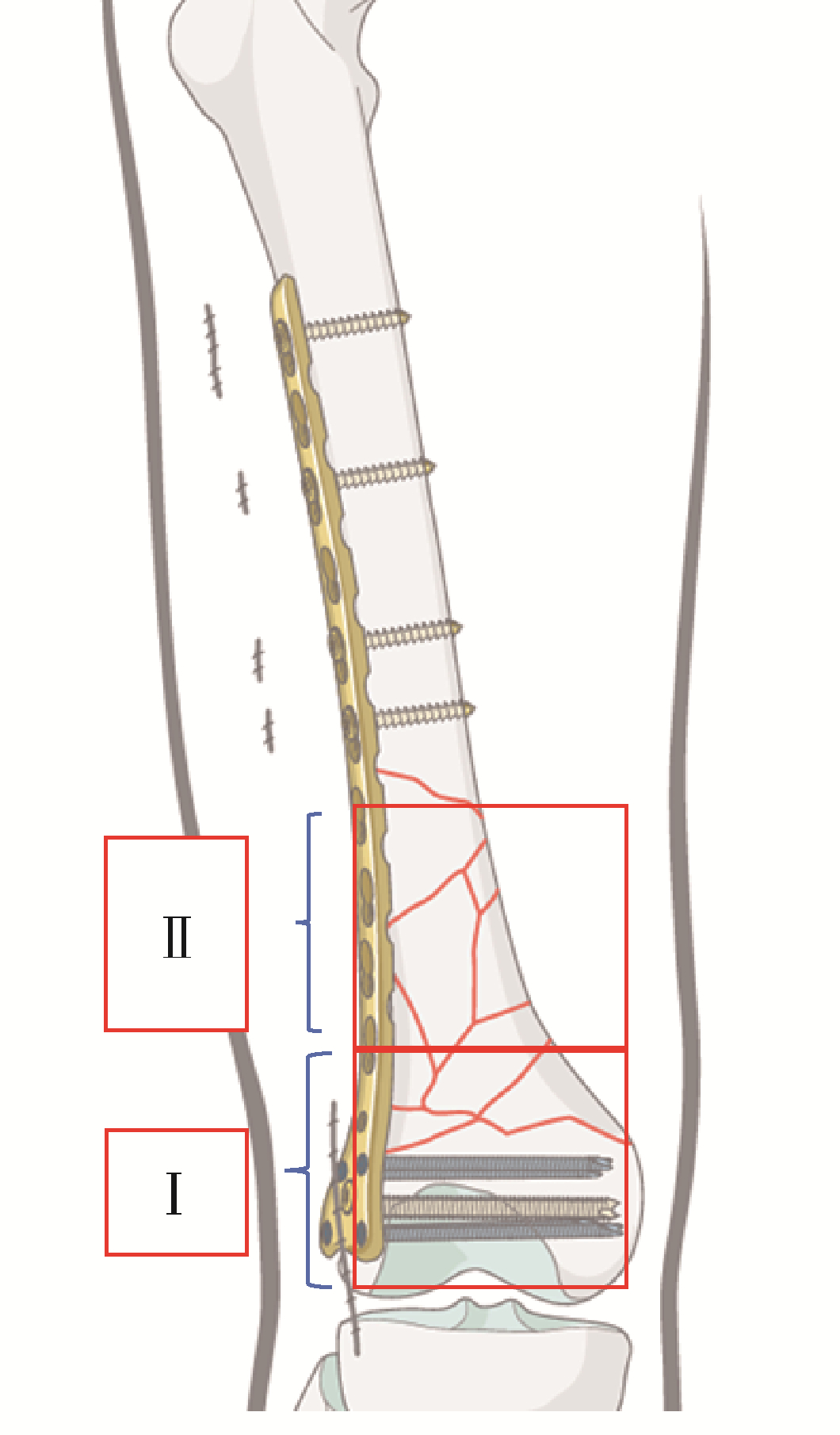
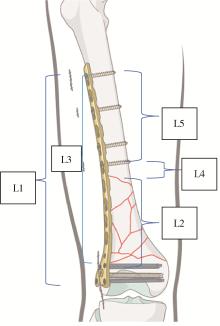
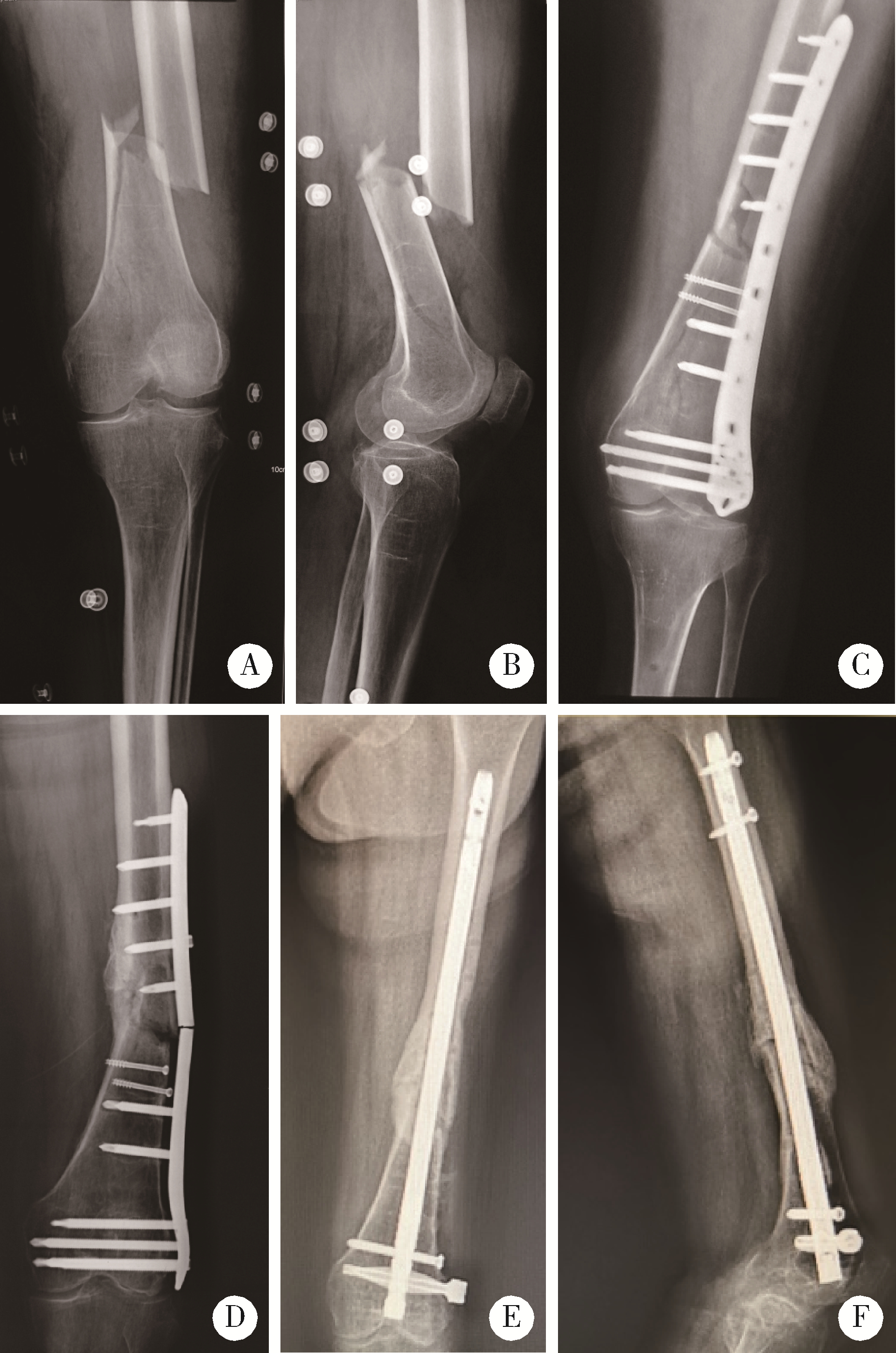
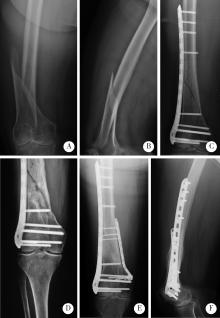
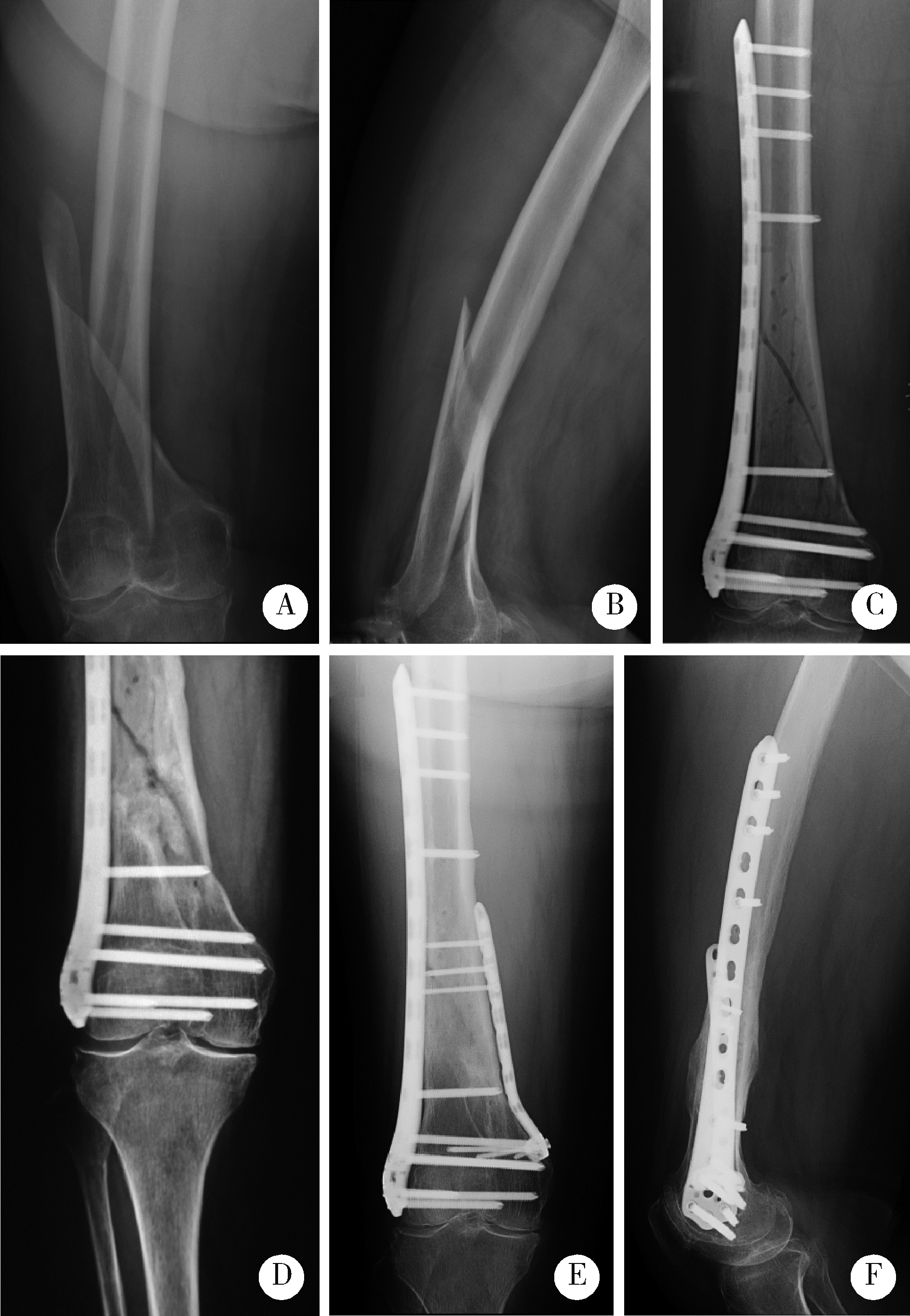
目的: 分析外侧锁定接骨板治疗股骨远端骨折术后因骨折不愈合或内固定断裂需要进行翻修手术的相关因素。方法: 回顾性分析了北京大学第三医院2005年3月至2019年3月诊治的股骨远端骨折患者的临床资料,共有130例患者纳入该研究,翻修组12例,未翻修组118例。利用SPSS 17.0软件对患者的一般情况[性别、年龄、体重指数(body mass index,BMI)、合并基础疾病、吸烟史]、损伤相关因素(受伤原因、开放或闭合性损伤、骨折AO/OTA分型、骨折累及区域分布)、手术相关因素(手术时间、复位质量、是否出现术后感染)及内固定结构等临床资料进行单因素比较及Logistic回归分析。结果: 130例纳入该研究的患者中12例进行了翻修手术,翻修率为9.2%。单因素分析发现年龄、BMI、骨折AO/OTA分型、骨折累及区域、手术时间、复位质量、接骨板长度/骨折区长度及髁螺钉上方的接骨板长度/骨折区长度在翻修组和未翻修组的差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);Logistic回归分析发现骨折AO/OTA分型中A3型骨折、骨折累及髁上区域、手术时间、复位质量和髁螺钉上方的接骨板长度/骨折区长度是外侧锁定接骨板治疗股骨远端骨折术后翻修的相关因素(P<0.05)。A3型骨折干骺端内侧皮质粉碎破坏其内侧支撑能力、骨折累及髁上皮质骨区域、骨折复位不良导致外侧接骨板承受的弯曲应力增加、长时间手术操作造成骨折端血运破坏、接骨板的长度不足造成应力集中等因素可能是外侧锁定接骨板术后翻修的危险因素。对于外侧锁定接骨板治疗失败的股骨远端骨折患者,辅助使用内侧微创接骨板固定+自体骨移植、更换髓内钉等是临床常用的治疗策略。结论: 骨折AO/OTA分型中A3型骨折、骨折累及髁上区域、复位质量不良、长手术时间及髁螺钉上方的接骨板长度/骨折区长度不足是影响外侧锁定接骨板治疗股骨远端骨折术后翻修的相关因素;个性化的选择合理的接骨板及手术策略是降低外侧锁定接骨板治疗股骨远端骨折术后的翻修率的关键。
中图分类号:
- R683.4
| 1 |
Court-Brown CM , Caesar B . Epidemiology of adult fractures: A review[J]. Injury, 2006, 37 (8): 691- 697.
doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2006.04.130 |
| 2 | Martinet O , Cordey J , Harder Y , et al. The epidemiology of fractures of the distal femur[J]. Injury, 2000, 31 (3): 62- 63. |
| 3 |
Hoffmann MF , Jones CB , Sietsema DL , et al. Clinical outcomes of locked plating of distal femoral fractures in a retrospective cohort[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2013, 8 (1): 43.
doi: 10.1186/1749-799X-8-43 |
| 4 | Consortium SF . LCP versus LISS in the treatment of open and closed distal femur fractures: does it make a difference?[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2016, 30 (6): e212- e216. |
| 5 | Henderson CE , Kuhl LL , Fitzpatrick DC , et al. Locking plates for distal femur fractures: Is there a problem with fracture healing?[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2011, 25 (Suppl 1): 8- 14. |
| 6 |
Rodriguez EK , Boulton C , Weaver MJ , et al. Predictive factors of distal femoral fracture nonunion after lateral locked plating: A retrospective multicenter case-control study of 283 fractures[J]. Injury, 2014, 45 (3): 554- 559.
doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2013.10.042 |
| 7 |
MoreLand JR , Bassett LW , Hanker GJ . Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1987, 69 (5): 745- 749.
doi: 10.2106/00004623-198769050-00016 |
| 8 | 李景学, 孙鼎元. 骨关节X线诊断学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1992: 176. |
| 9 |
Syed AA , Agarwal M , Giannoudis PV , et al. Distal femoral fractures: Long-term outcome following stabilisation with the LISS[J]. Injury, 2004, 35 (6): 599- 607.
doi: 10.1016/S0020-1383(03)00247-X |
| 10 | Kregor PJ , Stannard JA , Zlowodzki M , et al. Treatment of distal femur fractures using the less invasive stabilization system[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2014, 18 (8): 509- 520. |
| 11 |
Lujan T , Henderson CE , Madey SM , et al. Locked plating of distal femur fractures leads to inconsistent and asymmetric callus formation[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2010, 24 (3): 156- 162.
doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181be6720 |
| 12 |
Ebraheim NA , Liu J , Hashmi SZ , et al. High complication rate in locking plate fixation of lower periprosthetic distal femur fractures in patients with total knee arthroplasties[J]. J Arthroplasty, 2012, 27 (5): 809- 813.
doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2011.08.007 |
| 13 |
Hak DJ , Toker S , Yi C , et al. The influence of fracture fixation biomechanics on fracture healing[J]. Orthopedics, 2010, 33 (10): 752- 755.
doi: 10.3928/01477447-20100826-20 |
| 14 | Fulkerson E , Egol KA , Kubiak EN , et al. Fixation of diaphyseal fractures with a segmental defect: A biomechanical comparison of locked and conventional plating techniques[J]. Trauma, 2006, 60 (4): 830- 835. |
| 15 |
Ricci WM , Streubel PN , Morshed S , et al. Risk factors for failure of locked plate fixation of distal femur fractures: an analysis of 335 cases[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2014, 28 (2): 83- 89.
doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e31829e6dd0 |
| 16 |
Steinberg EL , Elis J , Steinberg Y , et al. A double-plating approach to distal femur fracture: A clinical study[J]. Injury, 2017, 48 (10): 2260- 2265.
doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2017.07.025 |
| 17 | Jagodzinski M , Krettek C . Effect of mechanical stability on fracture healing: An update[J]. Injury, 2007, 38 (Suppl 1): 3- 10. |
| 18 | Peschiera V , Staletti L , Cavanna M , et al. Predicting the failure in distal femur fractures[J]. Injury, 2018, 49 (Suppl 3): 2- 7. |
| 19 |
Tan SL , Balogh ZJ . Indications and limitations of locked plating[J]. Injury, 2009, 40 (7): 683- 691.
doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2009.01.003 |
| 20 | 宁鹏, 赵铭, 张月东. 下肢骨折锁定加压钢板内固定失败的Logistic回归分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2014, 22 (24): 2238- 2243. |
| 21 |
Elkins J , Marsh JL , Lujan T , et al. Motion predicts clinical callus formation: Construct-specific finite element analysis of supracondylar femoral fractures[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2016, 98 (4): 276- 284.
doi: 10.2106/JBJS.O.00684 |
| 22 | 程建岗, 袁志, 刘建, 等. 锁定接骨板动力化治疗股骨远端骨折经锁定接骨板内固定术后骨不连的效果[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2019, 40 (1): 57- 59. |
| [1] | 黄莹,吴志远,周行红,蔡志刚,张杰. 股前外侧皮瓣修复上颌骨缺损术后面部软组织对称性感观分级[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [2] | 熊士凯,史尉利,王安鸿,谢兴,郭秦炜. 腓骨远端撕脱骨折的影像学诊断:踝关节X线与CT三维重建的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 156-159. |
| [3] | 罗靓,霍文岗,张钦,李春. 类风湿关节炎合并角膜溃疡的临床特点和相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1032-1036. |
| [4] | 郑佳鹏,肖棋,邓辉云,吴清泉,翟文亮,林达生. 外侧半月板腘肌腱区损伤的关节镜下分型和处理[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 891-895. |
| [5] | 许志锋,凌云鹏,崔仲奇,赵鸿,宫一辰,傅元豪,杨航,万峰. 经左胸前外侧微创冠脉搭桥治疗冠心病多支病变[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 863-869. |
| [6] | 王顺吉,章文博,于尧,谢晓艳,杨宏宇,彭歆. 术前虚拟设计在股前外侧皮瓣修复口腔颌面部缺损中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 119-123. |
| [7] | 车新艳,吴士良,陈宇珂,黄燕波,杨洋. 女性医务人员尿失禁及其对生活质量影响的现况调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 706-710. |
| [8] | 李森磊,杨先腾,田晓滨,孙立. 直接前入路和前外侧入路全髋关节置换术后的早期功能恢复对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 268-272. |
| [9] | 徐杰,庄伟达,李新炜,俞国雨,林院,罗奋棋,肖毓华. 直接前入路和后外侧保留梨状肌入路全髋关节置换术的疗效对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2): 214-220. |
| [10] | 张永进,李甲,綦珂,薛晨晨,徐卫东. 全髋关节置换术中直接前方入路与后外侧入路的疗效及安全性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2): 201-205. |
| [11] | 白露,张文涛,黄伟,张新涛,江长青,李伟. 踝关节外侧韧带的解剖学观测及其临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(5): 679-683. |
|
||