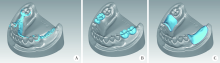
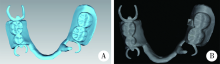
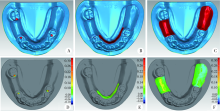
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 335-339. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.02.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluation of one-piece polyetheretherketone removable partial denture fabricated by computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing
Xin-xin LI1,Yu-shu LIU1,Yu-chun SUN2,Hu CHEN2,Hong-qiang YE1,∆( ),Yong-sheng ZHOU1,∆(
),Yong-sheng ZHOU1,∆( )
)
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology,Beijing 100081, China;
2. Center for Digital Dentistry,Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology,Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R783.3
| [1] |
Williams RJ, Bibb R, Rafik T . A technique for fabricating patterns for removable partial denture frameworks using digitized casts and electronic surveying[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2004,91(1):85-88.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2003.10.002 |
| [2] | Han J, Wang Y, Lu P . A preliminary report of designing removable partial denture frameworks using a specifically developed software package[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2010,23(4):370-375. |
| [3] | Panayotov IV, Orti V, Cuisinier F , et al. Polyetheretherketone (peek) for medical applications[J]. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 2016,27(7):118. |
| [4] |
Najeeb S, Zafar MS, Khurshid Z , et al. Applications of polyetheretherketone (peek) in oral implantology and prosthodontics[J]. J Prosthodont Res, 2016,60(1):12-19.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpor.2015.10.001 |
| [5] | Costa-Palau S, Torrents-Nicolas J, Brufau-de Barbera M , et al. Use of polyetheretherketone in the fabrication of a maxillary obturator prosjournal: a clinical report[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2013,112(3):680-682. |
| [6] | Zoidis P, Papathanasiou I, Polyzois G . The use of a modified polyetheretherketone (peek) as an alternative framework material for removable dental prostheses. A clinical report[J]. J Pros-thodont, 2015,25(7):580-584. |
| [7] |
Tannous F, Steiner M, Shahin R , et al. Retentive forces and fatigue resistance of thermoplastic resin clasps[J]. Dent Mater, 2012,28(3):273-278.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2011.10.016 |
| [8] |
Frank RP, Brudvik JS, Leroux B , et al. Relationship between the standards of removable partial denture construction, clinical acceptability, and patient satisfaction[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2000,83(5):521-527.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-3913(00)70008-4 |
| [9] |
Stern MA, Brudvik JS, Frank RP . Clinical evaluation of removable partial denture rest seat adaptation[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 1985,53(5):658-662.
doi: 10.1016/0022-3913(85)90015-0 |
| [10] |
Dunham D, Brudvik JS, Morris WJ , et al. A clinical investigation of the fit of removable partial dental prosjournal clasp assemblies[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2006,95(4):323-326.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2006.02.001 |
| [11] |
Ye H, Ning J, Li M , et al. Preliminary clinical application of removable partial denture frameworks fabricated using computer-aided design and rapid prototyping techniques[J]. Int J Pros-thodont, 2017,30(4):348-353.
doi: 10.11607/ijp.5270 |
| [12] | Luthardt RG, Bornemann G, Lemelson S , et al. An innovative method for evaluation of the 3-D internal fit of CAD/CAM crowns fabricated after direct optical versus indirect laser scan digitizing[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2004,17(6):680-685. |
| [13] |
Rantanen T, Eerikäinen E . Accuracy of the palatal plate of removable partial dentures, and influence of laboratory[J]. Dent Mater, 1986,2(1):28-31.
doi: 10.1016/S0109-5641(86)80066-5 |
| [1] | Xinyu XU,Ling WU,Fengqi SONG,Zili LI,Yi ZHANG,Xiaojing LIU. Mandibular condyle localization in orthognathic surgery based on mandibular movement trajectory and its preliminary accuracy verification [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [2] | Sui LI,Wenjie MA,Shimin WANG,Qian DING,Yao SUN,Lei ZHANG. Trueness of different digital design methods for incisal guidance of maxillary anterior implant-supported single crowns [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [3] | FENG Sha-wei,GUO Hui,WANG Yong,ZHAO Yi-jiao,LIU He. Initial establishment of digital reference standardized crown models of the primary teeth [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 327-334. |
| [4] | LI Yi,WONG Lai U,LIU Xiao-qiang,ZHOU Ti,LYU Ji-zhe,TAN Jian-guo. Marginal features of CAD/CAM laminate veneers with different materials and thicknesses [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 140-145. |
| [5] | QIU Shu-ting,ZHU Yu-jia,WANG Shi-min,WANG Fei-long,YE Hong-qiang,ZHAO Yi-jiao,LIU Yun-song,WANG Yong,ZHOU Yong-sheng. Preliminary clinical application verification of complete digital workflow of design lips symmetry reference plane based on posed smile [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 193-199. |
| [6] | WANG Li-xin , XU Xiao, NI Yao-feng, SUN Hai-tao, YU Ri-yue, WEI Shi-cheng. In vivo study of liposome-modified polyetheretherketone implant on bacteriostasis and osseointegration [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 758-763. |
| [7] | XU Xiao-xiang,CAO Ye,ZHAO Yi-jiao,JIA Lu,XIE Qiu-fei. In vitro evaluation of the application of digital individual tooth tray in the impression making of mandibular full-arch crown abutments [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 54-61. |
| [8] | YUE Zhao-guo,ZHANG Hai-dong,YANG Jing-wen,HOU Jian-xia. Comparison of residual cement between CAD/CAM customized abutments and stock abutments via digital measurement in vitro [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 69-75. |
| [9] | LI Zheng,LIU Yu-shu,WANG Shi-min,ZHANG Rui,JIA Lu,YE Hong-qiang,HU Wen-jie,ZHAO Wen-yan,LIU Yun-song,ZHOU Yong-sheng. Application of biocopy function of temporary crown occlusal morphology in patients with severe attrition [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 62-68. |
| [10] | FANG Shuo-bo,YANG Guang-ju,KANG Yan-feng,SUN Yu-chun,XIE Qiu-fei. Method and accuracy of determining the jaw position of repositioning splint with the aid of digital technique [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 76-82. |
| [11] | Lang YOU,Ke-hui DENG,Wei-wei LI,Yi-jiao ZHAO,Yu-chun SUN,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Visual sensitivity threshold of lateral view of nasolabial Angle changes in edentulous jaw patients [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2020, 52(1): 107-112. |
| [12] | Shuo CHEN,Yang HE,Jin-gang AN,Yi ZHANG. Application of computer-aided virtual mandibular position in the simultaneous treatment of children with temporomandibular joint ankylosis and jaw deformity [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(5): 954-958. |
| [13] | Kuan-paul WANG,Hong-qiang YE,Hu CHEN,Yong WANG,Yu-chun SUN,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Establishment and preliminary clinical evaluation of edentulous custom trays designed and fabricated by chair-side CAD and 3D printing systems [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 349-355. |
| [14] | Shi-min WANG,Zheng LI,Guan-bo WANG,Hong-qiang YE,Yun-song LIU,Dai TONG,Wen-hui GAO,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Preliminary clinical application of complete digital workflow of design and manufacturing occlusal splint for sleep bruxism [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 105-110. |
| [15] | PENG Li, WANG Zu-hua, SUN Yu-chun, QU Wei,HAN Yang, LIANG Yu-hong. Computer aided design and three-dimensional printing forapicoectomy guide template [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 905-910. |
|
||