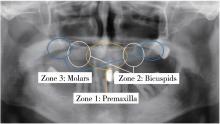
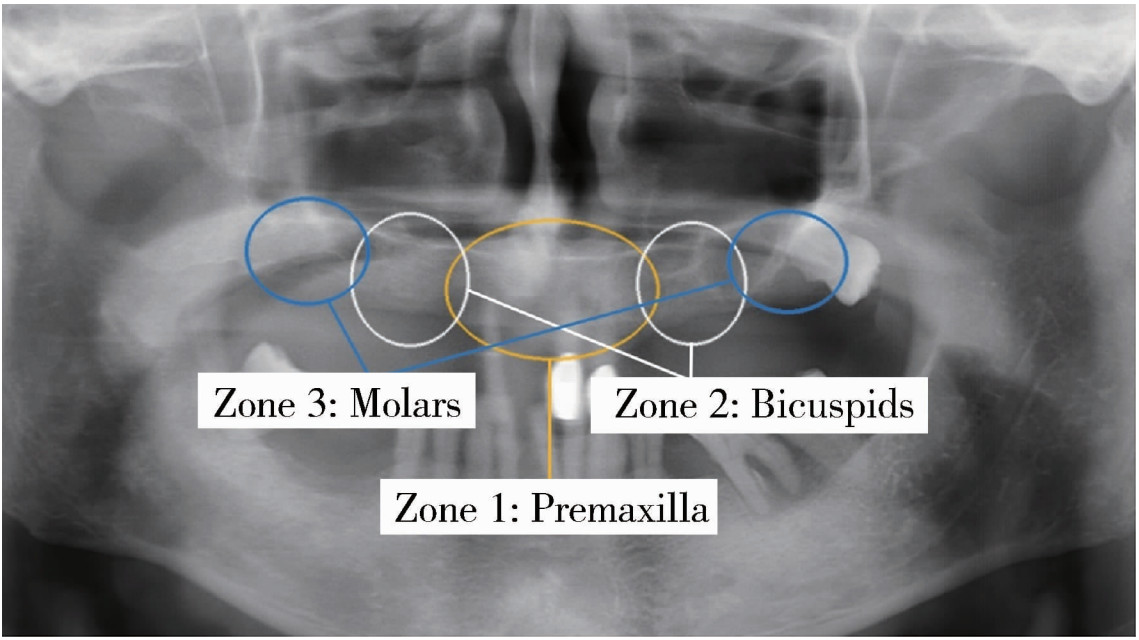
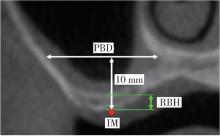
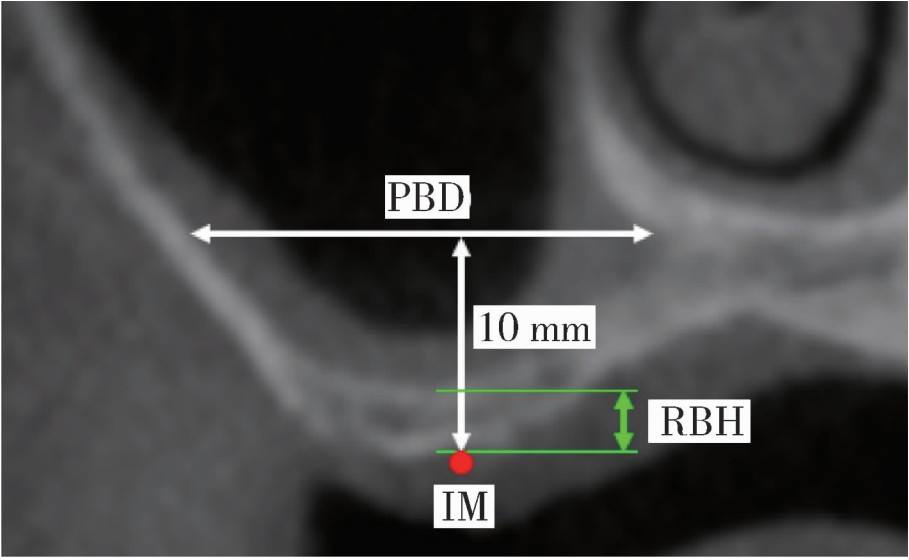
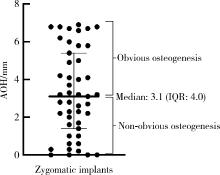
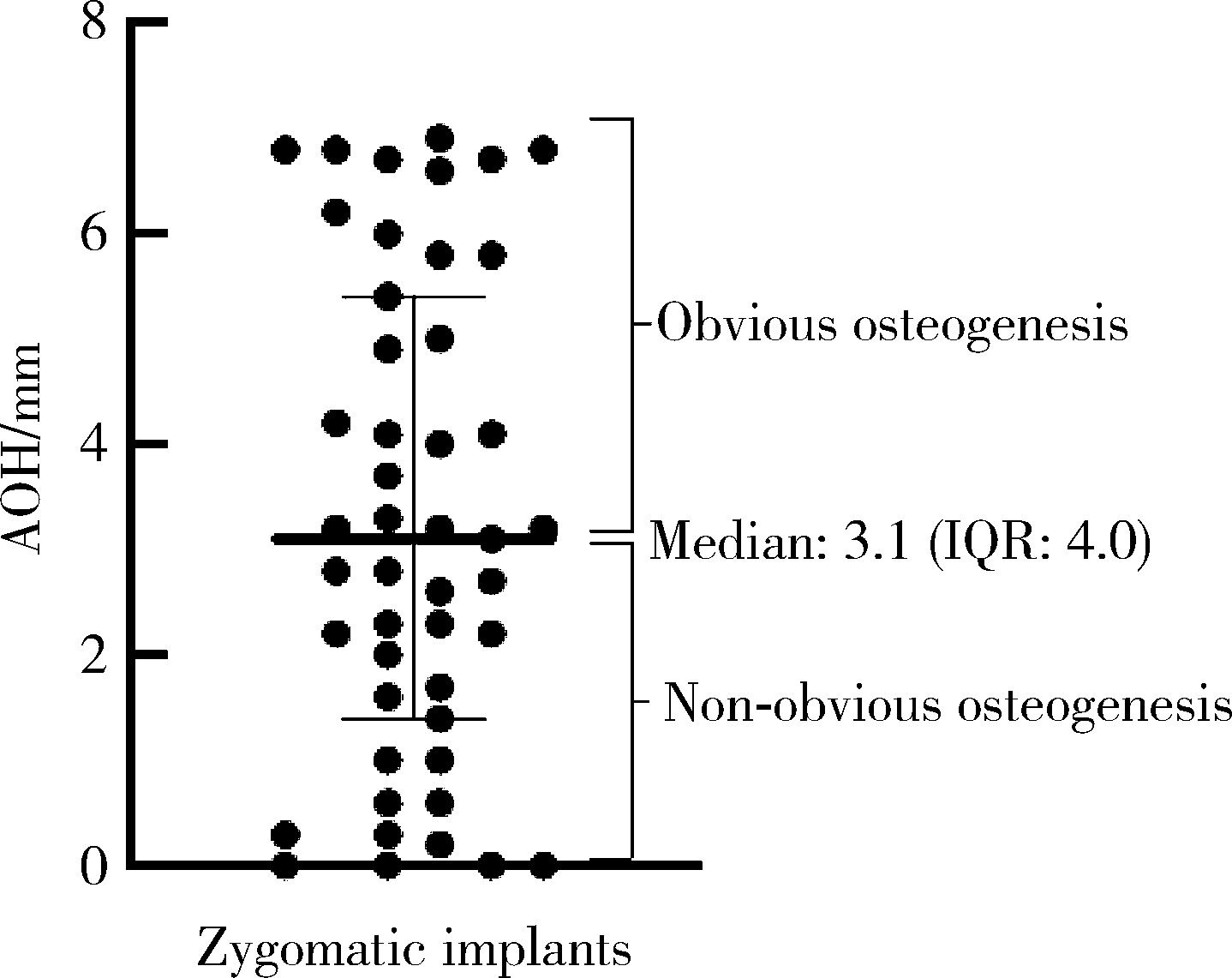
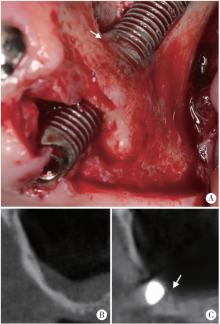
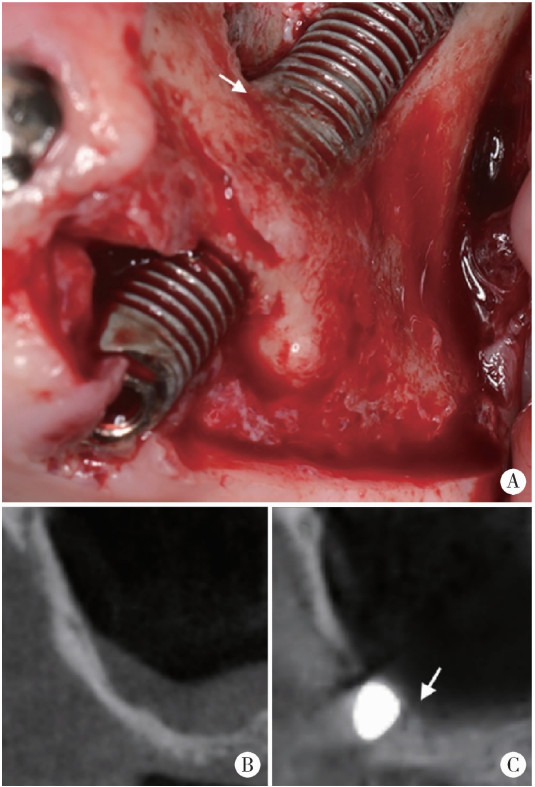
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 967-974. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Imaging study of osteogenesis in maxillary sinus segment of zygomatic implants
Ziyang YU1, Houzuo GUO1, Xi JIANG1, Weihua HAN2, Ye LIN1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Implantology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digi-tal Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Stomatology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College & Chinese Academy of Medical Science, Beijing 100730, China
CLC Number:
- R782.12
| 1 |
Tavelli C, Tedesco A. Survival and complication rate of zygomatic implants: A systematic review[J/OL]. J Oral Implantol (2022-12-06) [2023-01-24]. doi: 10.1563/aaid-joi-D-22-00008.
|
| 2 |
doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.1995.060405.x |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.14027 |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
周国辉. 穿颧骨植体在无牙上颌的应用[J]. 中国口腔种植学杂志, 2009, 14 (2): 28- 29.
|
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2012.12.006 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2015.01.009 |
| 10 |
林柏均, 吕鸣樾, 袁泉. 影响经牙槽嵴顶上颌窦底提升术成骨效果的解剖因素分析[J]. 口腔医学, 2022, 42 (3): 193- 199.
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2007.06.687 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.11607/jomi.7488 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.090686 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.02034.x |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.12477 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.1111/cid.12606 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.13891 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2021.03.016 |
| 20 |
doi: 10.1007/s00784-020-03432-z |
| 21 |
doi: 10.1111/jre.12402 |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
doi: 10.1111/cid.12218 |
| 25 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2007.01372.x |
| 26 |
林野. 上颌窦植骨与种植[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2020: 205.
|
| 27 |
doi: 10.1097/ID.0000000000000554 |
| 28 |
doi: 10.1111/cid.12298 |
| 29 |
郑小菲, 莫安春, 朱娟芳, 等. 上颌窦解剖因素对经牙槽嵴顶上颌窦底提升术成骨效果的影响[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38 (6): 652- 656.
|
| [1] | Yulan WANG, Hao ZENG, Yufeng ZHANG. Current situation and exploration of clinical transformation of plasmatrix in oral implantology [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(5): 836-840. |
| [2] | Fangru LIN, Zhihui TANG. Correlation analysis of peri-implant health after single-tooth dental implant [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(2): 347-353. |
| [3] | Juan WANG, Lixin QIU, Huajie YU. Influence of emergence profile designs on the peri-implant tissue in the mandibular molar: A randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(1): 65-72. |
| [4] | Congwei WANG,Min GAO,Yao YU,Wenbo ZHANG,Xin PENG. Clinical analysis of denture rehabilitation after mandibular fibula free-flap reconstruction [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [5] | Qian DING,Wen-jin LI,Feng-bo SUN,Jing-hua GU,Yuan-hua LIN,Lei ZHANG. Effects of surface treatment on the phase and fracture strength of yttria- and magnesia-stabilized zirconia implants [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 721-728. |
| [6] | Fei SUN,Jian LIU,Si-qi LI,Yi-ping WEI,Wen-jie HU,Cui WANG. Profiles and differences of submucosal microbial in peri-implantitis and health implants: A cross-sectional study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 30-37. |
| [7] | LAN Lin,HE Yang,AN Jin-gang,ZHANG Yi. Relationship between prognosis and different surgical treatments of zygomatic defects: A retrospective study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 356-362. |
| [8] | LI Yi,YU Hua-jie,QIU Li-xin. Clinical classification and treatment decision of implant fracture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 126-133. |
| [9] | DU Wen-yu,YANG Jing-wen,JIANG Ting. Early constant observation of the effect of deferoxamine mesylate on improvement of vascularized bone regeneration in SD rat skull critical size defect model [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1171-1177. |
| [10] | WANG Jing-qi,WANG Xiao. In vivo study of strontium-doped calcium phosphate cement for biological properties [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 378-383. |
| [11] | ZHANG Sheng-nan,AN Na,OUYANG Xiang-ying,LIU Ying-jun,WANG Xue-kui. Role of growth arrest-specific protein 6 in migration and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 9-15. |
| [12] | LI Peng,PIAO Mu-zi,HU Hong-cheng,WANG Yong,ZHAO Yi-jiao,SHEN Xiao-jing. Radiography study on osteotome sinus floor elevation with placed implant simultaneously with no graft augmentation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 95-101. |
| [13] | Mei WANG, Bo-wen LI, Si-wen WANG, Yu-hua LIU. Preparation and osteogenic effect study of small intestinal submucosa sponge [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(5): 952-958. |
| [14] | Zhong ZHANG,Huan-xin MENG,Jie HAN,Li ZHANG,Dong SHI. Effect of vertical soft tissue thickness on clinical manifestation of peri-implant tissue in patients with periodontitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 332-338. |
| [15] | Chun-ping LIN,Song-he LU,Jun-xin ZHU,Hong-cheng HU,Zhao-guo YUE,Zhi-hui TANG. Influence of thread shapes of custom-made root-analogue implants on stress distribution of peri-implant bone: A three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1130-1137. |
|
||