Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 190-195. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
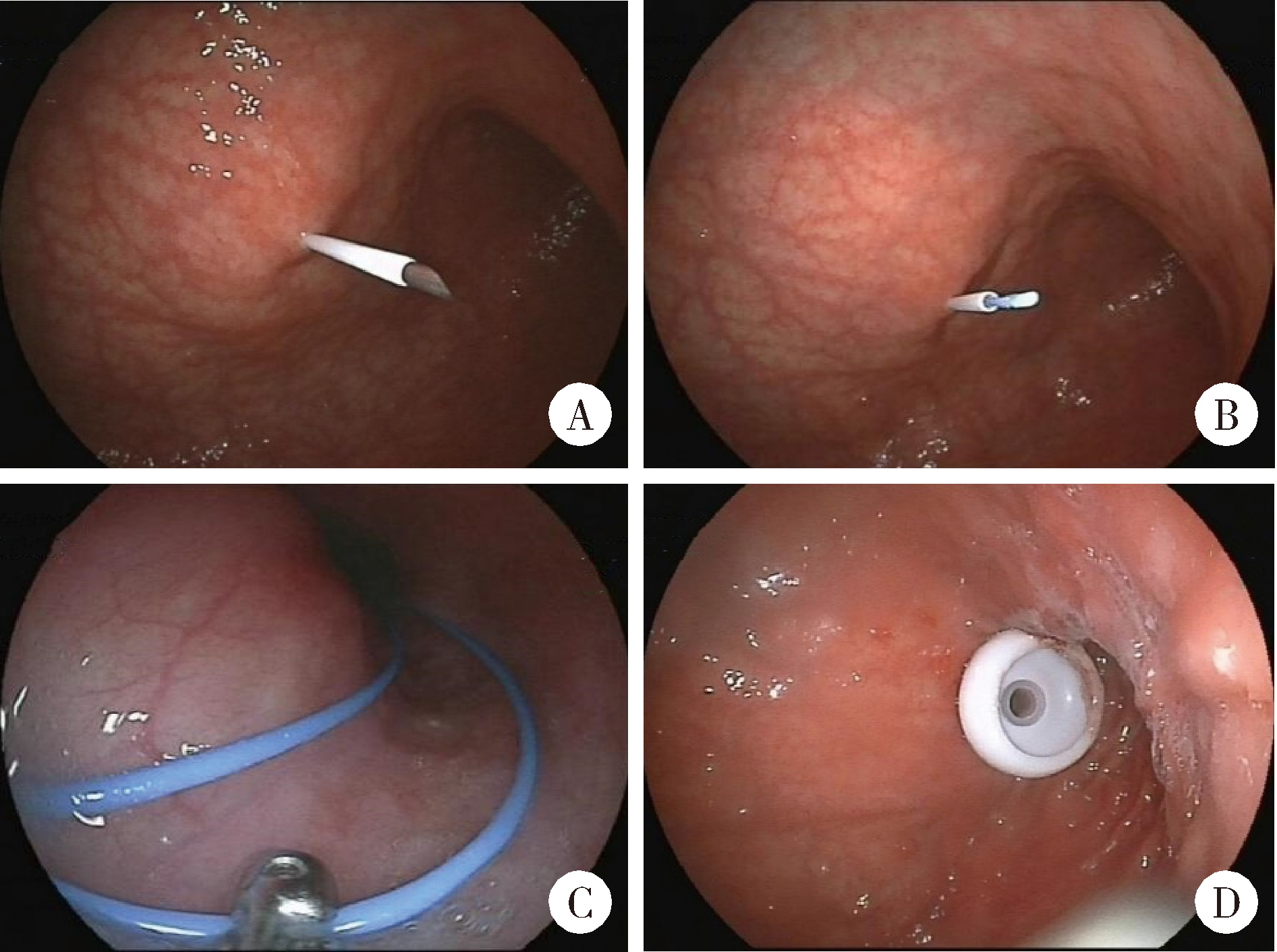
Analysis of early complications and risk factors in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
Xueli TIAN1, Zhiqiang SONG1, Yonghui HUANG2,*( ), Wei YAO1
), Wei YAO1
- 1. Department of Gastroenterology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Gastroenterology, Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital, Beijing 102218, China
CLC Number:
- R744.8
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| [1] | Xiaolin WANG, Shaoyi GUO, Dazhao CHEN, Xijie WEN, Yong HUA, Liang ZHANG, Qin ZHANG. A follow-up study on total hip arthroplasty in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus combined with osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(6): 1081-1088. |
| [2] | Chao ZUO, Guoli WANG, Kunlin YANG, Xinyan CHE, Yisen MENG, Kai ZHANG. Comparison of efficacy and safety of transurethral thulium fiber laser enucleation of prostate in patients with different prostate volumes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(4): 711-716. |
| [3] | Zhao ZHAO, Weiyu ZHANG, Wenbo YANG, Yongjie ZHANG, Xiaopeng ZHANG, Huiying ZHAO, Gang ZHOU, Qiang WANG. Kidney transplantation in low-age, low-weight children: A report of two cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(4): 803-807. |
| [4] | Fei WANG, Xinyue ZHANG, Muqing LIU, Enbo WANG, Denghui DUAN. Clinical application and three-dimensional finite element analysis of along-axis extraction method in mandibular mesial and horizontally impacted third molar surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(1): 106-112. |
| [5] | Liwei WANG, Bingchuan LIU, Yinyin QU, Changyi WU, Yun TIAN. Clinical application of multidisciplinary team in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic refractory wounds [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(1): 185-191. |
| [6] | Fangfei XIE, Hong QIAO, Boya LI, Cui YUAN, Fang WANG, Yu SUN, Shuangling LI. Severe malnutrition during pregnancy complicated with acute pyelonephritis causing sepsis, refractory septic shock and multiple organ failure: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(1): 202-207. |
| [7] | Li WAN, Zhoucang ZHANG, Jiaxiang DING, Mei WANG. Venous air embolism following removal of central venous catheters: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 938-941. |
| [8] | Su-huan XU,Bei-bei WANG,Qiu-ying PANG,Li-jun ZHONG,Yan-ming DING,Yan-bo HUANG,Xin-yan CHE. Effect of equal temperature bladder irrigation in patients with transurethral resection of prostate: A meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 676-683. |
| [9] | Shan YE,Ping-ping JIN,Nan ZHANG,Hai-bo WU,Lin SHI,Qiang ZHAO,Kun YANG,Hui-shu YUAN,Dong-sheng FAN. Cortical thickness and cognitive impairment in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1158-1162. |
| [10] | Hui LI,Yang-xu GAO,Shu-lei WANG,Hong-xin YAO. Surgical complications of totally implantable venous access port in children with malignant tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
| [11] | Bo YU,Yang-yu ZHAO,Zhe ZHANG,Yong-qing WANG. Infective endocarditis in pregnancy: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| [12] | LI Wei-hao,LI Wei,ZHANG Xue-min,LI Qing-le,JIAO Yang,ZHANG Tao,JIANG Jing-jun,ZHANG Xiao-ming. Comparison of the outcomes between open and hybrid approaches in the treatment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms repair [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 177-181. |
| [13] | Wen-min DONG,Ming-rui WANG,Hao HU,Qi WANG,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU. Initial clinical experience and follow-up outcomes of treatment for ureteroileal anastomotic stricture with Allium coated metal ureteral stent [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 637-641. |
| [14] | Jian GAO,Li-bao HU,Chen CHEN,Xin ZHI,Tao XU. Interventional treatment of hemorrhage after percutaneous nephrolithotomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 667-671. |
| [15] | Kai MA,Xing-ke QU,Qing-quan XU,Liu-lin XIONG,Xiong-jun YE,Li-zhe AN,Wei-nan CHEN,Xiao-bo HUANG. Endoscopic treatment for ureterovesical junction stenosis in patients with kidney transplantation: 13 cases report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1155-1158. |
|
||