Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 636-640. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
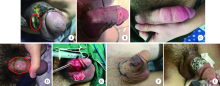
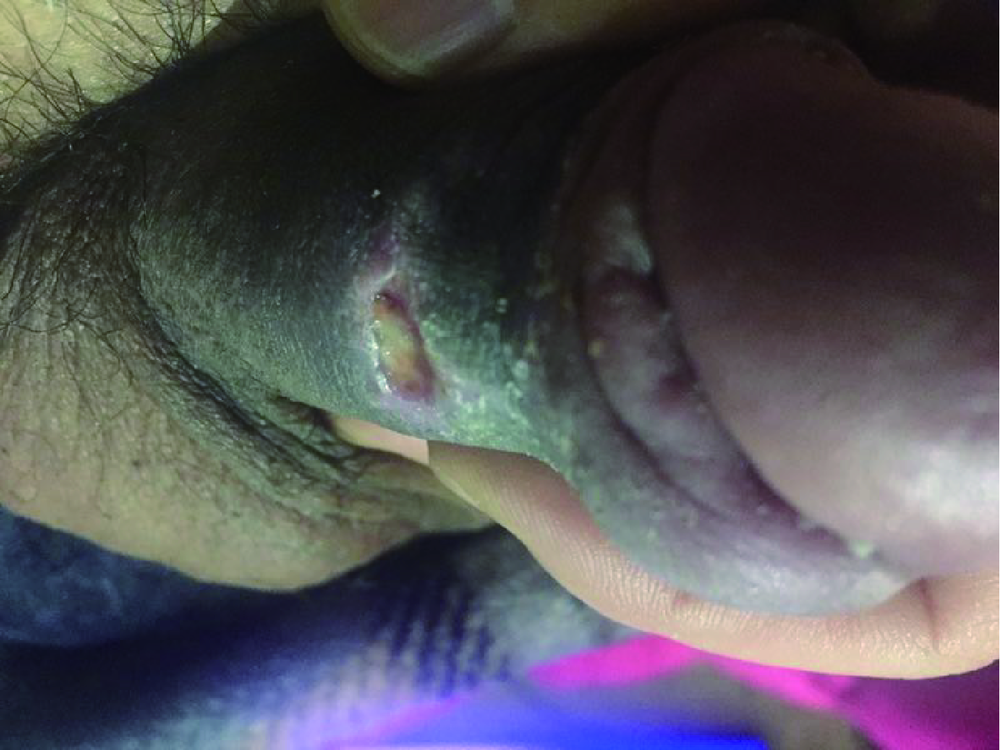
Complications and management for penile augmentation with acellular dermal matrix
Ting-min XU,Xiao-wei ZHANG,Guo-xi ZHANG,Wen-jun BAI,Qing LI,Tao XU( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R697.1
| [1] | Evangelos S, Charalambos C, Dimitrios B , et al. Augmentation phalloplasty surgery for penile dysmorphophobia in young adults: considerations regarding patient selection, outcome evaluation and techniques applied[J]. Eur Urol, 2005,48(1):121-128. |
| [2] | 麦凯欣, 朱辉 . 阴茎增粗术的研究进展[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志, 2009,20(9):558-561. |
| [3] | Whitehead E. Allograft dermal matrix graft (Alloderm ®) for pericavernosal penile widening in normal men [C]. Abstract pre-sented at: First World Congress on Aesthetic Medicine, 2004. |
| [4] | 杨文博, 张晓威, 兰轲 . 脱细胞异体真皮补片联合阴茎增粗术对早泄的作用与安全性[J]. 中国性科学, 2018,27(7):18-20. |
| [5] | Zhang X, Wu Y, Zhang M , et al. Acellular dermal matrix in premature ejaculation: A preliminary study[J]. Medicine, 2018,97(45):e13135. |
| [6] | Livesey SA, Herndon DN, Hollyoak MA , et al. Transplanted acellular allograft dermal matrix. Potential as a template for the reconstruction of viable dermis[J]. Transplantation, 1995,60(1):1-9. |
| [7] | Chen RN, Ho HO, Tsai YT , et al. Process development of an acellular dermal matrix (ADM) for biomedical applications[J]. Biomaterials, 2004,25(13):2679-2686. |
| [8] | 陈一宁, 但卫华, 但年华 . 脱细胞真皮基质的改性及应用概述[J]. 材料导报, 2018,32(13):2311-2319. |
| [9] | 林健, 郝金瑞, 金杰 , 等. 人同种异体真皮脱细胞基质在尿道重建中的临床应用[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2005,85(15):1057-1059. |
| [10] | 符津山, 周治彦, 许思怡 . 骨髓间充质干细胞联合脱细胞真皮基质修复尿道损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(13):2075-2080. |
| [11] | 殷鹏程, 黄万顺, 姚明文 , 等. 4种阴茎增粗术治疗阴茎细小158例疗效分析[J]. 浙江医学, 2016,38(23):1948-1949. |
| [12] | 吴小蔚, 简麒超, 董玉林 , 等. 阴茎延长同期行脱细胞异体真皮基质补片双平面植入阴茎增粗术[J]. 中华医学美学美容杂志, 2011,17(5):336-339. |
| [13] | Tealab AA, Maarouf AM, Habous M , et al. The use of an acellular collagen matrix in penile augmentation: A pilot study in Saudi Arabia[J]. Arab Journal of Urology, 2013,11(2):169-173. |
| [14] | Jung GW . Penile girth enhancement with allograft, penile augmentation[M]. Germany: Springer, 2016: 83-92. |
| [15] | Alter G, Jordan G . Penile elongation and girth enhancement[J]. AUA Update Series, 2007,26:229-237. |
| [16] | Bruno JJ 2 nd , Senderoff DM, Fracchia JA , et al. Reconstruction of penile wounds following complications of AlloDerm-based augmentation phalloplasty[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2007,119(1):1e-4e. |
| [17] | 李战松 . 脱细胞异体真皮基质医用组织补片在阴茎增粗成形中的应用[J]. 中国性科学, 2013,22(10):59-61. |
| [18] | Chu CH, Shieh SJ . Reconstruction of circumferential skin defect of the penile shaft using a bipedicle scrotal flap[J]. Dermatol Surg, 2012,38(2):266-270. |
| [19] | 陶谏, 任永安, 柏龙文 . 阴囊双蒂袋状皮瓣套入法一期修复阴茎皮肤缺损一例[J]. 中华整形外科杂志, 2001,17(3):143. |
| [20] | 王祥, 刘德贵, 石敏 , 等. 阴囊双蒂皮瓣修复包皮环切术后包皮过短[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 1994(6):448. |
| [21] | 陈媛媛, 陆鑫锋, 赵亮 , 等. 阴囊双蒂皮瓣联合皮片移植治疗男性外阴大面积乳房外Paget病[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志, 2012,45(12):904-905. |
| [22] | Weber DM, Landolt MA, Gobet R , et al. The penile perception score: an instrument enabling evaluation by surgeons and patient self-assessment after hypospadias repair[J]. J Urol, 2013,189(1):189-193. |
| [1] | Li WAN, Zhoucang ZHANG, Jiaxiang DING, Mei WANG. Venous air embolism following removal of central venous catheters: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 938-941. |
| [2] | Su-huan XU,Bei-bei WANG,Qiu-ying PANG,Li-jun ZHONG,Yan-ming DING,Yan-bo HUANG,Xin-yan CHE. Effect of equal temperature bladder irrigation in patients with transurethral resection of prostate: A meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 676-683. |
| [3] | Hui LI,Yang-xu GAO,Shu-lei WANG,Hong-xin YAO. Surgical complications of totally implantable venous access port in children with malignant tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
| [4] | Hai-long HE,Qing LI,Tao XU,Xiao-wei ZHANG. Treatment of adult-acquired buried penis with suprapubic liposuction combined with modified Devine operation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 741-745. |
| [5] | Bo YU,Yang-yu ZHAO,Zhe ZHANG,Yong-qing WANG. Infective endocarditis in pregnancy: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| [6] | LI Wei-hao,LI Wei,ZHANG Xue-min,LI Qing-le,JIAO Yang,ZHANG Tao,JIANG Jing-jun,ZHANG Xiao-ming. Comparison of the outcomes between open and hybrid approaches in the treatment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms repair [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 177-181. |
| [7] | Wen-min DONG,Ming-rui WANG,Hao HU,Qi WANG,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU. Initial clinical experience and follow-up outcomes of treatment for ureteroileal anastomotic stricture with Allium coated metal ureteral stent [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 637-641. |
| [8] | Jian GAO,Li-bao HU,Chen CHEN,Xin ZHI,Tao XU. Interventional treatment of hemorrhage after percutaneous nephrolithotomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 667-671. |
| [9] | Chun-long ZHANG,He LI,Qing LI,Wen-jun BAI,Tao XU,Xiao-wei ZHANG. Decision regret analysis among Chinese patients receiving penile girth enhancement with acellular dermal matrix [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 678-683. |
| [10] | Kai MA,Xing-ke QU,Qing-quan XU,Liu-lin XIONG,Xiong-jun YE,Li-zhe AN,Wei-nan CHEN,Xiao-bo HUANG. Endoscopic treatment for ureterovesical junction stenosis in patients with kidney transplantation: 13 cases report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1155-1158. |
| [11] | Zhong-cheng XIN,Bi-cheng YANG,Meng LI,Yi-ming YUAN,Wan-shou CUI,Yuan TANG,Dong FANG,Wei-dong SONG. Appllication of human acellular dermal matrix in surgical treatment of genitourinary disease [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 778-782. |
| [12] | Chen LIANG,Wei-yu ZHANG,Hao HU,Qi WANG,Zhi-wei FANG,Ke-xin XU. Comparison of effectiveness and complications between two different methods of augmentation cystoplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 293-297. |
| [13] | Jia-xuan XU,Hong-zhi WANG,Jun DONG,Xiao-jie CHEN,Yong YANG,Ren-xiong CHEN,Guo-dong WANG. Analysis of risk factors for acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome after esophagectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(6): 1057-1062. |
| [14] | WANG Bo-jie, GUO Chao, LI Chun-jing, MU Dong-liang. Prevalance of peri-anesthesia allergy and its related risk factor: a retrospective survey from 2012-2017 [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 193-199. |
| [15] | LI Xu, LI Feng-long, LU Yi, ZHU Yi-ming, GUO Si-yi, LI Yi-jun, JIANG Chun-yan. Clinical study on locking plate for the treatment of non-osteoporotic complex proximal humeral fractures [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 855-860. |
|
||