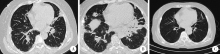
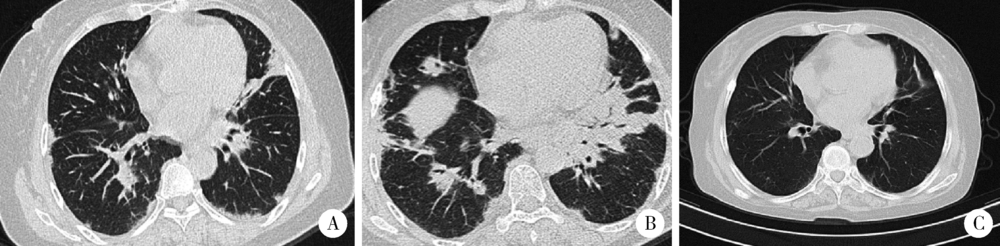
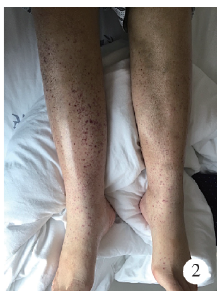
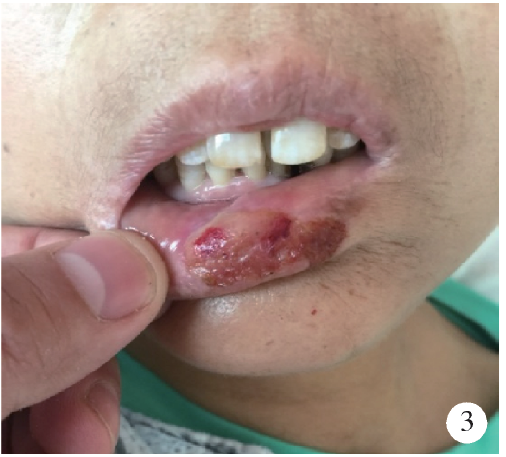
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1173-1177. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.035
Previous Articles Next Articles
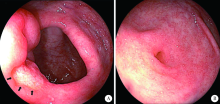
Dermatomyositis combined with IgA vasculitis: A case report
Jing XU1,Jing XU2,He LI3,Jie TANG4,Jian-long SHU4,Jing ZHANG1,Lian-jie SHI1,Sheng-guang LI1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
2. Department of Nephrology, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
3. Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
4. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Guangxi International Zhuang Medicine Hospital, Nanning 530201, China
CLC Number:
- R593.26
| [1] | Russo RAG, Katsicas MM, Dávila M , et al. Cholestasis in juve-nile dermatomyositis: report of three cases[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2001,44(5):1139-1142. |
| [2] | Ueda H, Miyazaki Y, Tsuboi N , et al. Clinical and pathological characteristics of elderly Japanese patients with IgA Vasculitis with nephritis: a case series[J]. Intern Med, 2019,58(1):31-38. |
| [3] | Tan J, Tang Y, Xu Y , et al. The clinicopathological characteristics of Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis with presentation of nephrotic syndrome [J]. Kidney Blood Press Res, 2019,44(4):754-764. |
| [4] | Chua JS, Zandbergen M, Wolterbeek R , et al. Complement-mediated microangiopathy in IgA nephropathy and IgA vasculitis with nephritis[J]. Mod Pathol, 2019,32(8):1147-1157. |
| [5] | Lin Q, Li X . Children with Henoch-Schonlein purpura with low complement levels: follow-up for >6 years[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2017,32(7):1279. |
| [6] | Yu JH, Lee KB, Lee JE , et al. A case of elderly-onset crescentic Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis with hypocomplementemia and positive MPO-ANCA[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2012,27(8):957-960. |
| [7] | Lin Q, Min Y, Li Y , et al. Henoch-Schonlein purpura with hypocomplementemia[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2012,27(5):801-806. |
| [8] | Motoyama O, Iitaka K . Henoch-Schonlein purpura with hypocomplementemia in children[J]. Pediatr Int, 2005,47(1):39-42. |
| [9] | Garcia-Fuentes M, Martin A, Chantler C , et al. Serum complement components in Henoch-Schonlein purpura[J]. Arch Dis Child, 1978,53(5):417-419. |
| [10] | Zhang Y, Huang X . Gastrointestinal involvement in Henoch-Schonlein purpura[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2008,43(9):1038-1043. |
| [11] | Sasaki K, Nukuda Y, Masuda T , et al. Endoscopically and histologically documented gastrointestinal lesions in an adult patient with Henoch-Schonlein purpura[J]. Endoscopy, 1994,26(7):629-630. |
| [12] | Basu R . Perforation of the bowel in Henoch-Schonlein purpura[J]. Arch Dis Child, 1959,34:342-343. |
| [13] | Emanuel B, Lieberman AD, Rosen S . Intussusception due to Henoch-Schonlein purpura. Case reports and review of the literature[J]. Ill Med J, 1962,122:162-167. |
| [14] | Nakamura A, Fuchigami T, Inamo Y . Protein-losing enteropathy associated with Henoch-Schonlein purpura[J]. Pediatr Rep, 2010,2(2):e20. |
| [15] | Louie CY, Gomez AJ, Sibley RK , et al. Histologic features of gastrointestinal tract biopsies in IgA vasculitis (Henoch-Schonlein purpura)[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2018,42(4):529-533. |
| [16] | Han Y, Jin SY, Kim DW , et al. Endoscopic and microscopic findings of gastrointestinal tract in Henoch-Schonlein purpura: Single institute experience with review of literature[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019,98(20):e15643. |
| [17] | Akkari I, Mrabet S, Ben Jazia E . Gastrointestinal biopsy in Henoch-Schonlein purpura: A great diagnostic contribution[J]. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med, 2017,4(9):000662. |
| [18] | Yen T, Huang J, Chen C . Unexpected IgA nephropathy during the treatment of a young woman with idiopathic dermatomyositis: case report and review of the literature[J]. J Nephrol, 2003,16(1):148-153. |
| [19] | 舒晓明, 卢昕, 王国春 . 中国人多发性肌炎/皮肌炎合并肾脏损害的临床特点(附文献复习)[J]. 中日友好医院学报, 2017,31(2):67-70. |
| [20] |
钱莹, 任红, 陈晓农 , 等. 多发性肌炎和皮肌炎的肾脏损害分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2011,31(4):451-454.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2011.04.015 |
| [21] | Georgaki-Angelaki E, Kostaridou S, Lourida A , et al. Abrupt and durable remission of Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis with cyclosporine A[J]. NDT Plus, 2008,1(5):300-302. |
| [1] | Dongwu LIU, Jie CHEN, Mingli GAO, Jing YU. Rheumatoid arthritis with Castleman-like histopathology in lymph nodes: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [2] | Yun-fei SHI,Hao-jie WANG,Wei-ping LIU,Lan MI,Meng-ping LONG,Yan-fei LIU,Yu-mei LAI,Li-xin ZHOU,Xin-ting DIAO,Xiang-hong LI. Analysis of clinicopathological and molecular abnormalities of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [3] | Qi SHEN,Yi-xiao LIU,Qun HE. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of kidney: Clinicopathology and prognosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 276-282. |
| [4] | Wei-hua HOU,Shu-jie SONG,Zhong-yue SHI,Mu-lan JIN. Clinicopathological features of Helicobacter pylori-negative early gastric cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 292-298. |
| [5] | Xue-mei HA,Yong-zheng YAO,Li-hua SUN,Chun-yang XIN,Yan XIONG. Solid placental transmogrification of the lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [6] | Bo-han NING,Qing-xia ZHANG,Hui YANG,Ying DONG. Endometrioid adenocarcinoma with proliferated stromal cells, hyalinization and cord-like formations: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [7] | Qian SU,Xin PENG,Chuan-xiang ZHOU,Guang-yan YU. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in oral and maxillofacial regions: An analysis of 369 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 13-21. |
| [8] | Xiao-yan XING,Jun-xiao ZHANG,Feng-yun-zhi ZHU,Yi-fan WANG,Xin-yao ZHOU,Yu-hui LI. Clinical analysis of 5 cases of dermatomyositis complicated with macrophage activation syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1214-1218. |
| [9] | Er-shu BO,Peng HONG,Yu ZHANG,Shao-hui DENG,Li-yuan GE,Min LU,Nan LI,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathological features and prognostic analysis of papillary renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 615-620. |
| [10] | LI Bing-yu,TANG Zu-nan,HU Lei-hao,ZHANG Wen-bo,YU Yao,YU Guang-yan,PENG Xin. Clinicopathologic analysis of micro and mini parotid gland tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 335-339. |
| [11] | XUE Jiang,ZHANG Jian-yun,SHI Rui-rui,XIE Xiao-yan,BAI Jia-ying,LI Tie-jun. Clinicopathological analysis of 105 patients with fibrous dysplasia of cranio-maxillofacial region [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 54-61. |
| [12] | ZHANG Pu-li,YANG Hong-xia,ZHANG Li-ning,GE Yong-peng,PENG Qing-lin,WANG Guo-chun,LU Xin. Value of serum YKL-40 in the diagnosis of anti-MDA5-positive patients with dermatomyositis complicated with severe pulmonary injury [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1055-1060. |
| [13] | WEI Hui,Luo-zeng ##,Ci-dan-yang-zong ##,Bai-ma-yang-jin ##. Analysis of clinical characteristics of Henoch-Schonlein purpura patients from different altitudes in plateau areas [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1072-1077. |
| [14] | Mei-ge LIU,Pu FANG,Yan WANG,Lu CONG,Yang-yi FAN,Yuan YUAN,Yan XU,Jun ZHANG,Dao-jun HONG. Clinical, pathological and genetic characteristics of 8 patients with distal hereditary motor neuropathy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 957-963. |
| [15] | Yu-zhou GAN,Yu-hui LI,Li-hua ZHANG,Lin MA,Wen-wen HE,Yue-bo JIN,Yuan AN,Zhan-guo LI,Hua YE. Comparison of clinical and immunological features between clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis and typical dermatomyositis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1001-1008. |
|
||