Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 518-522. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.03.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
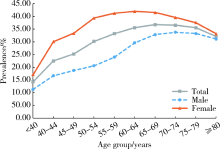
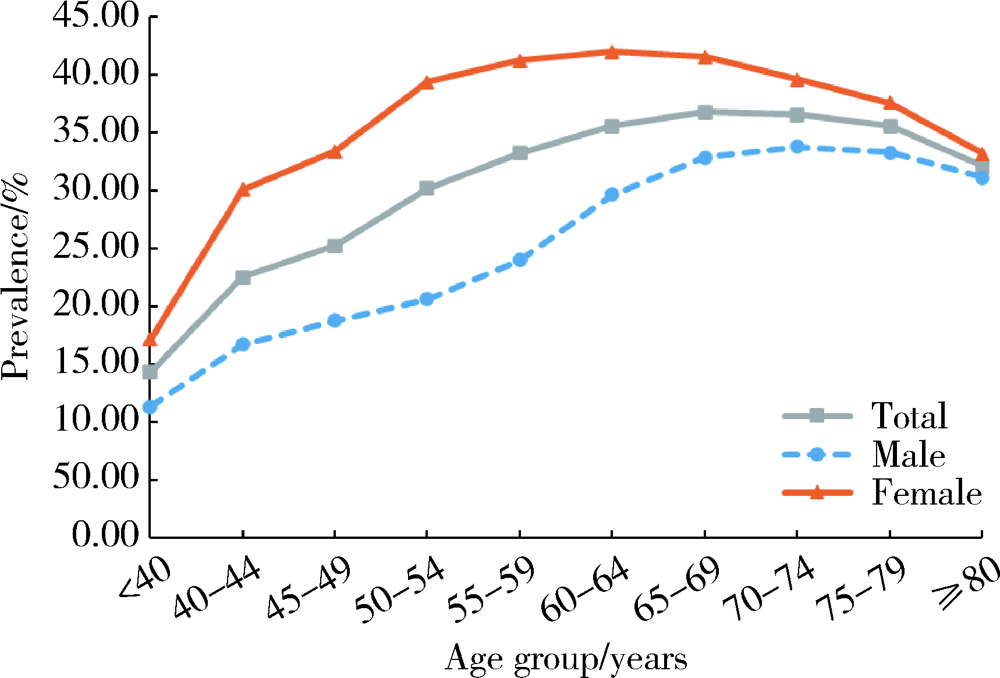
Prevalence and risk factors of osteoarthritis in patients with type 2 diabetes in Beijing, China from 2015 to 2017
WU Jun-hui1,CHEN Hong-bo1,2,WU Yi-qun1,WU Yao1,WANG Zi-jing1,WU Tao1,WANG Meng-ying1,WANG Si-yue1,WANG Xiao-wen1,WANG Jia-ting1,YU Huan1,HU Yong-hua1,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Geriatric Nursing and Rehabilitation, Peking University School of Nursing, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R181.3
| [1] |
Hunter DJ, Bierma-Zeinstra S. Osteoarthritis[J]. Lancet, 2019,393(10182):1745-1759.
doi: S0140-6736(19)30417-9 pmid: 31034380 |
| [2] |
Hunter DJ, Schofield D, Callander E. The individual and socio-economic impact of osteoarthritis[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2014,10(7):437-441.
doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.44 pmid: 24662640 |
| [3] |
Neogi T. The epidemiology and impact of pain in osteoarthritis[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2013,21(9):1145-1153.
doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2013.03.018 |
| [4] | 王华军, 陈均源, 罗斯敏, 等. 糖尿病与骨关节炎相关性的Meta分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 25(11):994-998. |
| [5] |
Veronese N, Cooper C, Reginster JY, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2019,49(1):9-19.
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.01.005 |
| [6] | Asfandiyarova NS, Nizov AA, Nekhaeva TI, et al. Osteoarthrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Terapevticheski Arkhiv, 2013,85(5):44. |
| [7] | 刘爱武, 王秋萍, 杜娜, 等. 住院患者2型糖尿病与膝骨关节炎流行病学的研究[J]. 中国社区医师, 2019,35(9):165-169. |
| [8] | 曾雁冰, 袁志鹏, 方亚. 中国老年人就医行为及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2020,37(2):199-205. |
| [9] |
Liu Y, Zhang HF, Liang NX. Prevalence and associated factors of knee osteoarthritis in a rural Chinese adult population: An epidemiological survey[J]. BMC Public Health, 2015,16(1):94.
doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-2782-x |
| [10] |
Lee SG, Kim SJ. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis, risk factors, and quality of life: the Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey[J]. Int J Rheum Dis, 2017,20(7):809-817.
doi: 10.1111/apl.2017.20.issue-7 |
| [11] |
Nieves-Plaza M, Castro-Santana LE, Font YM, et al. Association of hand or knee osteoarthritis with diabetes mellitus in a population of Hispanics from Puerto Rico[J]. J Clin Rheumatol, 2013,19(1):1-6.
doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e31827cd578 pmid: 23319016 |
| [12] |
Prieto-Alhambra D, Judge A, Javaid MK, et al. Incidence and risk factors for clinically diagnosed knee, hip and hand osteoarthritis: Influences of age, gender and osteoarthritis affecting other joints[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2014,73(9):1659-1664.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203355 |
| [13] |
Rosa SC, Goncalves J, Judas F, et al. Impaired glucose trans-porter-1 degradation and increased glucose transport and oxidative stress in response to high glucose in chondrocytes from osteo-arthritic versus normal human cartilage[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2009,11(3):R80.
doi: 10.1186/ar2713 |
| [14] |
Courties A, Sellam J. Osteoarthritis and type 2 diabetes mellitus: What are the links?[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2016,122:198-206.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2016.10.021 |
| [15] |
Findlay DM. Vascular pathology and osteoarthritis[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2007,46(12):1763-1768.
pmid: 17693442 |
| [16] |
Johnson EO, Soultanis K, Soucacos PN. Vascular anatomy and microcirculation of skeletal zones vulnerable to osteonecrosis: Vascularization of the femoral head[J]. Orthop Clin North Am, 2004,35(3):285-291.
doi: 10.1016/j.ocl.2004.03.002 |
| [1] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [2] | Hongguang LI,Weihua HAN,Xun WU,Jiling FENG,Gang LI,Juanhong MENG. Preliminarily study of arthrocentesis combined with liquid phase concentrated growth factor injection in the treatment of unilateral temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 338-344. |
| [3] | Yong-wei LIN,Ya-lin ZHOU,Run-long ZHAO,Ya-jun XU,Yan-ping LIU. Analysis on the iron status and associated factors during the first trimester of pregnancy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 600-605. |
| [4] | Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Yan XU,Zhuo-hua LIN,You-jing SUN,Li-gang CUI. Comparative study of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of asymptomatic anterosuperior acetabular labrum tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [5] | Hao WU,Li-ping PAN,Heng LIU,Hong-bin WANG,Tai-guo NING,Yong-ping CAO. Effect of posterior tibial slope on the short-term outcome in mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 877-882. |
| [6] | KE Yan,ZHANG Qiang,MA Yun-qing,LI Ru-jun,TAO Ke,GUI Xian-ge,LI Ke-peng,ZHANG Hong,LIN Jian-hao. Short-term outcomes of total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of Tönnis grade 3 hip osteoarthritis in patients with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 175-182. |
| [7] | Yan GENG,Zhi-bo SONG,Xiao-hui ZHANG,Xue-rong DENG,Yu WANG,Zhuo-li ZHANG. Depression and anxiety in patients with psoriatic arthritis: Prevalence and associated factors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1048-1055. |
| [8] | Si-wei DENG,Ze-yi CHEN,Zhi-ke LIU,Jian WANG,Lin ZHUO,Shuang-qing GAO,Jia-kuo YU,Si-yan ZHAN. Epidemiological study of bone and joint injury based on urban medical insurance database [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 527-534. |
| [9] | Lu XU,Lu CHEN,Dong-sheng FAN,Jing-nan FENG,Li-li LIU,Si-yan ZHAN,Sheng-feng WANG. Calculation of the prevalence of progressive muscular atrophy among adults in China based on urban medical insurance data from 15 provinces [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 521-526. |
| [10] | Xiao-ying ZHANG,Jia-jing PENG,Chuan-hui LIU,Xiao-yan CAI,Jiang-lin ZHANG,Yi-fang MEI,Hong-tao JIN,Xiao-fei WANG,Hong MO,Zhan-guo LI. A multi-center cross-sectional survey of medicine application in patients with osteoarthritis in China [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(6): 1044-1048. |
| [11] | WANG Dan-dan, GAN Ye-hua, MA Xu-chen, MENG Juan-hong. Association between ADAMTS14 gene polymorphism and the temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis in Chinese Han females [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 279-283. |
| [12] | SHI Hui-feng, ZHANG Jing-xu, ZHANG Rong, WANG Xiao-li. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders in children aged 0-6 years in China: a meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 798-806. |
| [13] | LI Zhi-chang, JIANG Long, ZHANG Shu, QIN Xue-ying, Daniel K. White PT,HOU Yun-fei, ZHOU Zhi-wei, LIN Jian-hao. Evaluation of physical function for the end-stage osteoarthritis patient waiting for the total knee replacement [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(2): 257-262. |
| [14] | LI Wei, JIANG Chun-yan, WANG Zhan-wei, XIAO De-ming. Intraarticular injection of bevacizumab in treatment of osteoarthritis: a laboratory research on a rabbit model [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(2): 203-209. |
| [15] | PAN Li-ping, CAO Yong-ping, WEN Li-cheng, CHAI Wei-bing, DU Jun-bao, JIN Hong-fang, LIU Jia, YANG Xin, MENG Zhi-chao, LIU Heng, CUI Yun-peng, WANG Rui, WU Hao, ZHOU Xing-tong, LI Xiang. Hydrogen sulfide in cartilage and its inhibitory effect on matrix metalloproteinase 13 expression in chondrocytes induced by interlukin-1β [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(2): 194-201. |
|
||