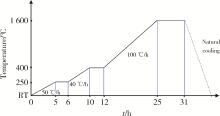
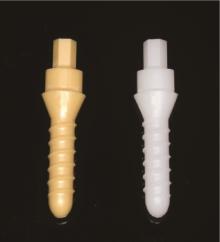
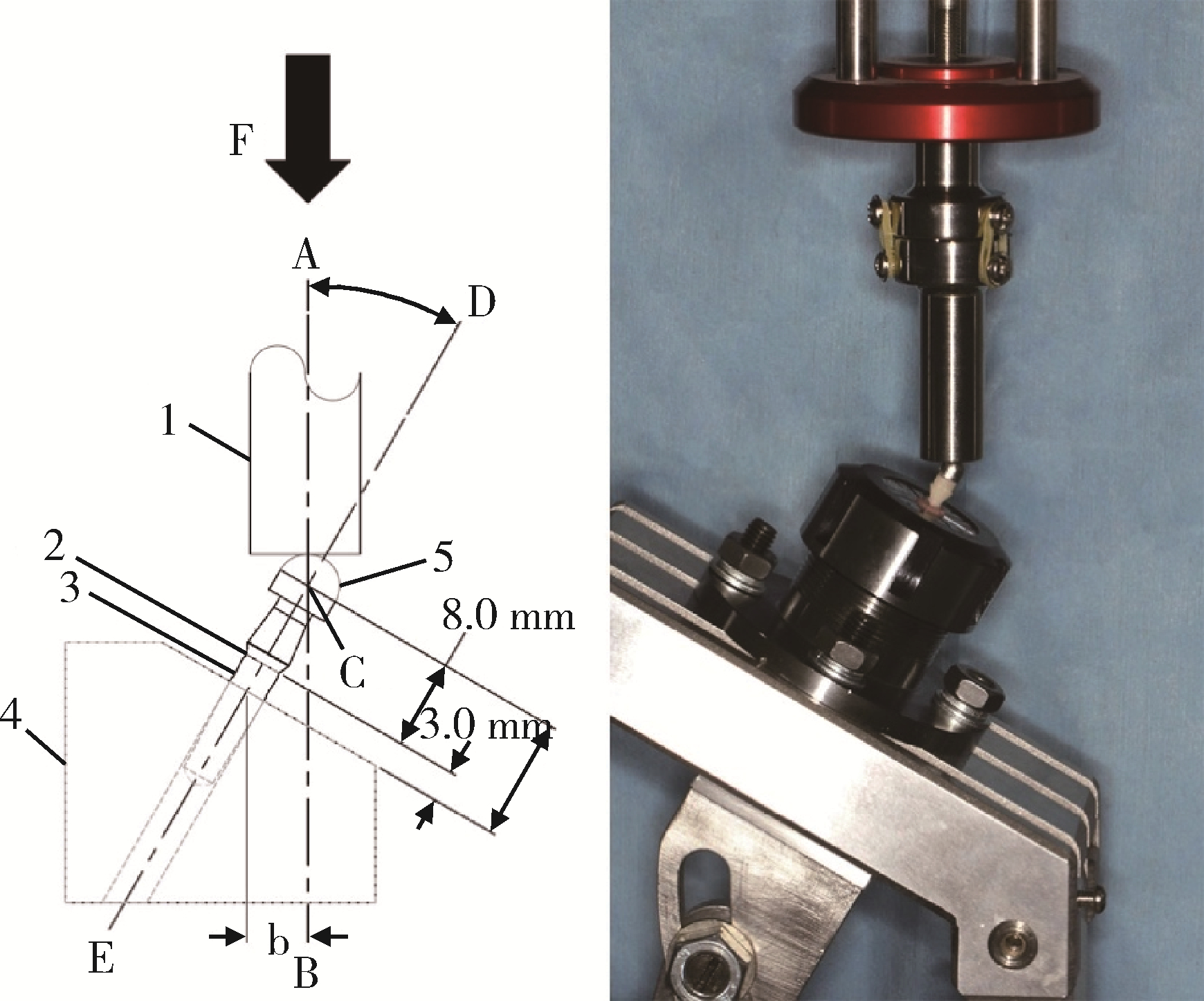
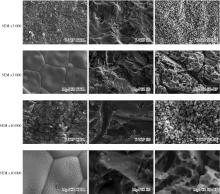
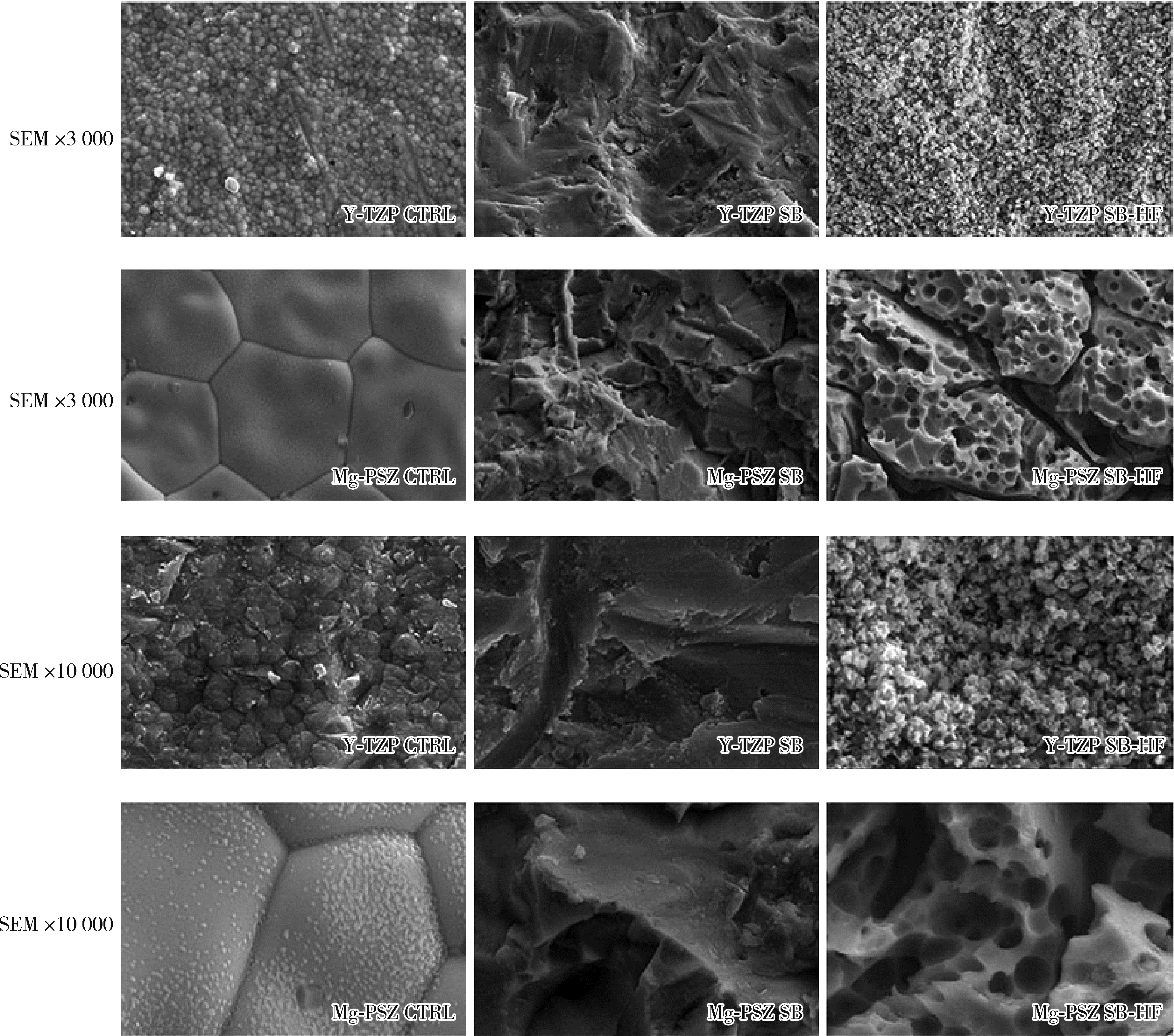
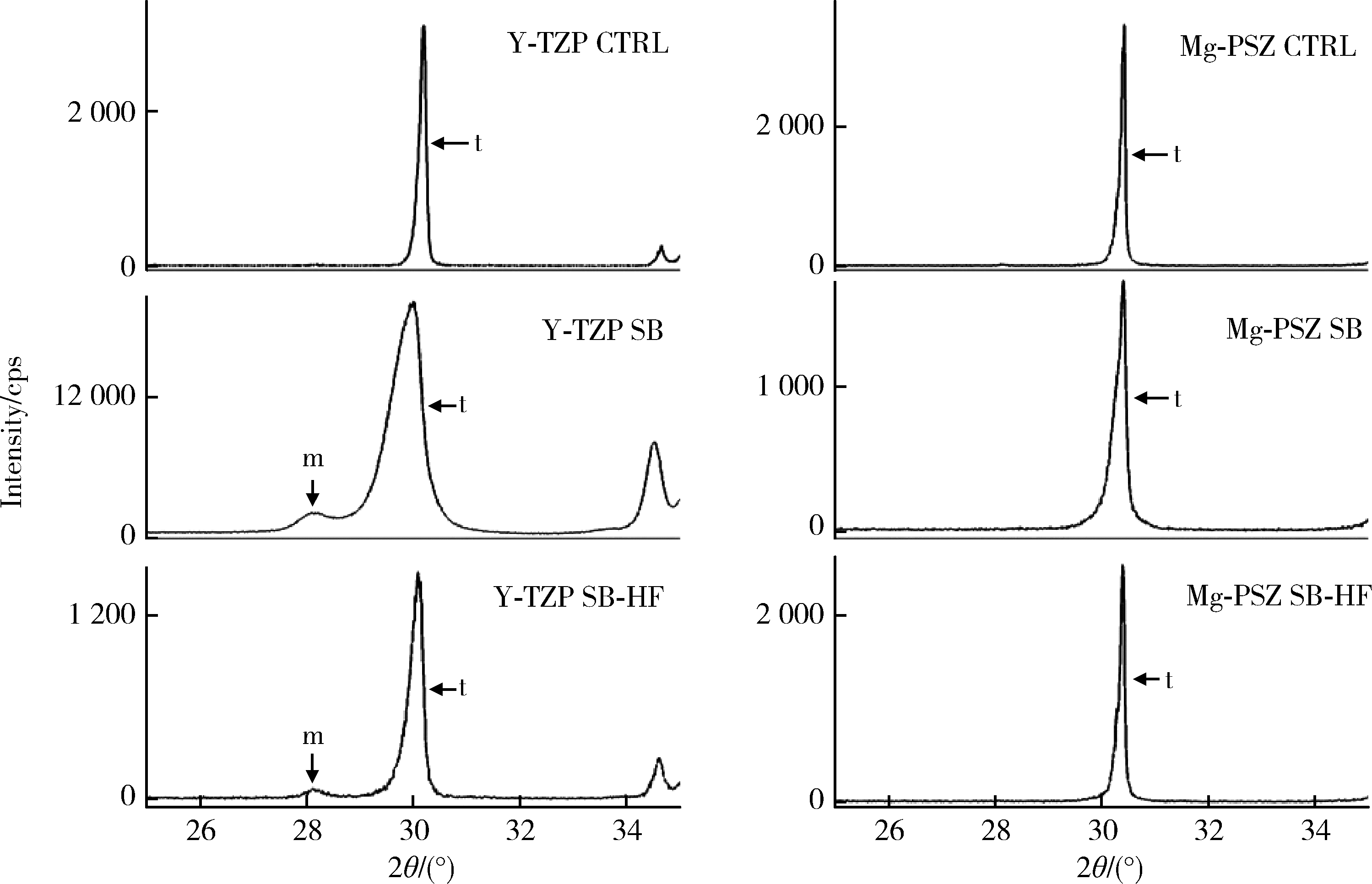
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 721-728. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.04.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of surface treatment on the phase and fracture strength of yttria- and magnesia-stabilized zirconia implants
Qian DING1,Wen-jin LI1,Feng-bo SUN2,Jing-hua GU3,Yuan-hua LIN2,Lei ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Proshodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R783.1
| 1 |
Elnayef B , Lazaro A , Suarez-Lopez DAF , et al. Zirconia implants as an alternative to titanium: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2017, 32 (3): e125- e134.
doi: 10.11607/jomi.5223 |
| 2 |
Roehling S , Astasov-Frauenhoffer M , Hauser-Gerspach I , et al. In vitro biofilm formation on titanium and zirconia implant surfaces[J]. J Periodontol, 2017, 88 (3): 298- 307.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2016.160245 |
| 3 |
Kubasiewicz-Ross P , Hadzik J , Dominiak M . Osseointegration of zirconia implants with 3 varying surface textures and a titanium implant: A histological and micro-CT study[J]. Adv Clin Exp Med, 2018, 27 (9): 1173- 1179.
doi: 10.17219/acem/69246 |
| 4 |
Hanawa T . Zirconia versus titanium in dentistry: A review[J]. Dent Mater J, 2020, 39 (1): 24- 36.
doi: 10.4012/dmj.2019-172 |
| 5 |
Denry I , Kelly JR . State of the art of zirconia for dental applications[J]. Dent Mater, 2008, 24 (3): 299- 307.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2007.05.007 |
| 6 | Toraya H , Yoshimura M , Somiya S . Calibration curve for quantitative analysis of the monoclinic-tetragonal ZrO2 system by X-ray diffraction[J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 1984, 67 (6): 119- 121. |
| 7 | Wennerberg A , Albrektsson T . Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: A systematic review[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2009, 20 (Suppl 4): 172- 184. |
| 8 | Albrektsson T , Wennerberg A . On osseointegration in relation to implant surfaces[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2019, 21 (Suppl 1): 4- 7. |
| 9 |
Pieralli S , Kohal RJ , Lopez HE , et al. Osseointegration of zirconia dental implants in animal investigations: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Dent Mater, 2018, 34 (2): 171- 182.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2017.10.008 |
| 10 |
Soon G , Pingguan-Murphy B , Akbar SA . Modulation of osteoblast behavior on nanopatterned yttria-stabilized zirconia surfaces[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2017, 68, 26- 31.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.01.028 |
| 11 |
Casucci A , Osorio E , Osorio R , et al. Influence of different surface treatments on surface zirconia frameworks[J]. J Dent, 2009, 37 (11): 891- 897.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2009.06.013 |
| 12 |
Smielak B , Klimek L . Effect of hydrofluoric acid concentration and etching duration on select surface roughness parameters for zirconia[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2015, 113 (6): 596- 602.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2015.01.001 |
| 13 | Bergemann C , Duske K , Nebe JB , et al. Microstructured zirconia surfaces modulate osteogenic marker genes in human primary osteoblasts[J]. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 2015, 26 (1): 5350. |
| 14 |
Flamant Q , Marro FG , Rovira J , et al. Hydrofluoric acid etching of dental zirconia. Part 1: Etching mechanism and surface characterization[J]. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2016, 36 (1): 121- 134.
doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.09.021 |
| 15 |
Furuya K , Takemoto S , Yamashita S , et al. Low-temperature degradation of high-strength Y-TZP (yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal)[J]. Dent Mater J, 2020, 39 (4): 577- 586.
doi: 10.4012/dmj.2019-090 |
| 16 | 王晓春, 张希艳. 材料现代分析与测试技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2009: 82. |
| 17 | Warren BE . X-Ray Diffraction[M]. New York: Dover Publications Inc., 1990: 251- 254. |
| 18 | Roy ME , Whiteside LA , Katerberg BJ , et al. Phase transformation, roughness, and microhardness of artificially aged yttria- and magnesia-stabilized zirconia femoral heads[J]. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2007, 83 (4): 1096- 1102. |
| 19 |
Zucuni CP , Dapieve KS , Rippe MP , et al. Influence of finishing/polishing on the fatigue strength, surface topography, and roughness of an yttrium-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystals subjected to grinding[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2019, 93, 222- 229.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.02.013 |
| 20 |
Amaral M , Cesar PF , Bottino MA , et al. Fatigue behavior of Y-TZP ceramic after surface treatments[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2016, 57, 149- 156.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2015.11.042 |
| 21 |
Aurelio IL , Marchionatti AM , Montagner AF , et al. Does air particle abrasion affect the flexural strength and phase transformation of Y-TZP? A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Dent Mater, 2016, 32 (6): 827- 845.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2016.03.021 |
| 22 | Karakoca S , Yilmaz H . Influence of surface treatments on surface roughness, phase transformation, and biaxial flexural strength of Y-TZP ceramics[J]. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater, 2009, 91 (2): 930- 937. |
| 23 |
Egilmez F , Ergun G , Cekic-Nagas I , et al. Factors affecting the mechanical behavior of Y-TZP[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2014, 37, 78- 87.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2014.05.013 |
| 24 |
Sanon C , Chevalier J , Douillard T , et al. A new testing protocol for zirconia dental implants[J]. Dent Mater, 2015, 31 (1): 15- 25.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2014.09.002 |
| 25 |
Ding Q , Zhang L , Bao R , et al. Effects of different surface treatments on the cyclic fatigue strength of one-piece CAD/CAM zirconia implants[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2018, 84, 249- 257.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.05.002 |
| 26 |
Sanon C , Chevalier J , Douillard T , et al. Low temperature degradation and reliability of one-piece ceramic oral implants with a porous surface[J]. Dent Mater, 2013, 29 (4): 389- 397.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2013.01.007 |
| 27 | 牛月月, 王春燕, 舒静媛, 等. 氧化锆基纳米羟基磷灰石功能梯度材料的制备及力学检测[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24 (10): 1528- 1533. |
| 28 |
Bermúdez-Reyes B , Del Refugio Lara-Banda M , Reyes-Zarate E , et al. Effect on growth and osteoblast mineralization of hydroxyapatite-zirconia (HA-ZrO2) obtained by a new low temperature system[J]. Biomed Mater, 2018, 13 (3): 035001.
doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/aaa3a4 |
| [1] | Congwei WANG,Min GAO,Yao YU,Wenbo ZHANG,Xin PENG. Clinical analysis of denture rehabilitation after mandibular fibula free-flap reconstruction [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [2] | Fei SUN,Jian LIU,Si-qi LI,Yi-ping WEI,Wen-jie HU,Cui WANG. Profiles and differences of submucosal microbial in peri-implantitis and health implants: A cross-sectional study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 30-37. |
| [3] | Wei-wei LI,Hu CHEN,Yong WANG,Yu-chun SUN. Research on friction and wear behaviors of silicon-lithium spray coating on zirconia ceramics [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 94-100. |
| [4] | LI Yi,YU Hua-jie,QIU Li-xin. Clinical classification and treatment decision of implant fracture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 126-133. |
| [5] | WANG Zheng,DING Qian,GAO Yuan,MA Quan-quan,ZHANG Lei,GE Xi-yuan,SUN Yu-chun,XIE Qiu-fei. Effect of porous zirconia ceramics on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 31-39. |
| [6] | LI Wen-jin,DING Qian,YUAN Fu-song,Sun Feng-bo,ZHENG Jian-qiao,BAO Rui,Zhang Lei. Effects of femtosecond laser treatment on surface characteristics and flexural strength of zirconia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 770-775. |
| [7] | YANG Xin,LI Rong,YE Hong-qiang,CHEN Hu,WANG Yong,ZHOU Yong-sheng,SUN Yu-chun. Evaluation of fracture strength of two kinds of zirconia all-ceramic crowns with different edge compensation angles [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 402-405. |
| [8] | LI Peng,PIAO Mu-zi,HU Hong-cheng,WANG Yong,ZHAO Yi-jiao,SHEN Xiao-jing. Radiography study on osteotome sinus floor elevation with placed implant simultaneously with no graft augmentation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 95-101. |
| [9] | Zhong ZHANG,Huan-xin MENG,Jie HAN,Li ZHANG,Dong SHI. Effect of vertical soft tissue thickness on clinical manifestation of peri-implant tissue in patients with periodontitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 332-338. |
| [10] | Chun-ping LIN,Song-he LU,Jun-xin ZHU,Hong-cheng HU,Zhao-guo YUE,Zhi-hui TANG. Influence of thread shapes of custom-made root-analogue implants on stress distribution of peri-implant bone: A three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1130-1137. |
| [11] | Qian WANG,Dan LI,Zhi-hui TANG. Sinus floor elevation and simultaneous dental implantation: A long term retrospective study of sinus bone gain [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(5): 925-930. |
| [12] | Miao ZHENG,Ling-lu ZHAN,Zhi-qiang LIU,He-ping LI,Jian-guo TAN. Effect of different plasma treated zirconia on the adhensive behaviour of human gingival fibroblasts [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 315-320. |
| [13] | Xiao-qian LIU,Qiu-wen CHEN,Hai-lan FENG,Bing WANG,Jian QU,Zhen SUN,Mo-di HENG,Shao-xia PAN. Oral hygiene maintenance of locator attachments implant overdentures in edentulous population: A longitudinal study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 136-144. |
| [14] | Zhi-yong△ ZHANG,Tian MENG,Quan CHEN,Wen-shu LIU,Yu-huan CHEN. Retrospective analysis of early dental implant failure [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(6): 1088-1091. |
| [15] | ZHOU Tuan-feng, WANG Xin-zhi . Clinical observation of the restoration of computer aided designed and manufactured one-piece zirconia posts and cores: a 5-year prospective follow-up study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 680-684. |
|
||