Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 105-110. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.01.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
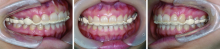
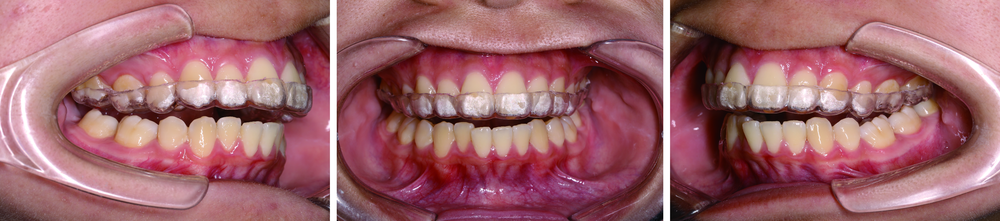
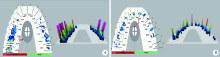
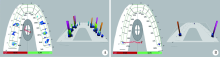
Preliminary clinical application of complete digital workflow of design and manufacturing occlusal splint for sleep bruxism
Shi-min WANG1,Zheng LI1,Guan-bo WANG1,Hong-qiang YE1,Yun-song LIU1,△( ),Dai TONG1,2,Wen-hui GAO2,Yong-sheng ZHOU1
),Dai TONG1,2,Wen-hui GAO2,Yong-sheng ZHOU1
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Beijing 100081, China
2. Dental Laboratory, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R783.2
| [1] | American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International classification of sleep disorder: Diagnostic and coding manual[M]. Chicago, Illinois: American Academy of Sleep Medicine, 2005: 189-192. |
| [2] |
Karakis D, Dogan A, Bek B . Evaluation of the effect of two diffe-rent occlusal splints on maximum occlusal force in patients with sleep bruxism: A pilot study[J]. J Adv Prosthodont, 2014,6(2):103-108.
doi: 10.4047/jap.2014.6.2.103 pmid: 4024553 |
| [3] |
Guaita M, Hogl B . Current treatments of bruxism[J]. Curr Treat Options Neurol, 2016,18(2):10.
doi: 10.1007/s11940-016-0396-3 |
| [4] | Bumann A, Lotzmann U . TMJ disorders and orofacial pain: The role of dentistry in a multidisciplinary diagnostic approach[M]. Stuttgart, New York: Thieme, 2002. |
| [5] | Ye H, Li X, Wang G , et al. A novel computer-aided design/computer-assisted manufacture method for one-piece removable partial denture and evaluation of fit[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2018, doi: 10.11607/ijp.5508. |
| [6] | 李欣欣, 柳玉树, 孙玉春 , 等. 计算机辅助设计与制作一体化聚醚醚酮可摘局部义齿不同形态组件的适合性评价 [J/OL]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, [ 2018- 12- 07]. . |
| [7] | 金智文, 韩建民, 刘云松 , 等. 聚醚醚酮制作可摘义齿人工牙耐磨性及硬度的研究[J]. 口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2018,19(4):236-240. |
| [8] |
Lavigne GJ, Khoury S, Abe S , et al. Bruxism physiology and pathology: An overview for clinicians[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2008,35(7):476-494.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.2008.01881.x pmid: 18557915 |
| [9] |
Manfredini D, Winocur E, Guarda-Nardini L , et al. Epidemiology of bruxism in adults: A systematic review of the literature[J]. J Orofac Pain, 2013,27(2):99-110.
doi: 10.11607/jop.921 pmid: 23630682 |
| [10] |
Dubé C, Rompré PH, Manzini C , et al. Quantitative polygraphic controlled study on efficacy and safety of oral splint devices in tooth-grinding subjects[J]. J Dent Res, 2004,83(5):398-403.
doi: 10.1177/154405910408300509 pmid: 15111632 |
| [11] |
王志瑜, 黄虹, 马明 , 等. 青年夜磨牙症患者经弹性牙合垫治疗前后咬合变化特征的研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2016,32(6):857-860.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2016.06.024 |
| [12] |
刘党利 . 硬牙合垫和软牙合垫治疗夜磨牙的效果比较[J]. 临床医学, 2005,25(10):64-65.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3548.2005.10.044 |
| [13] |
Berntsen C, Kleven M, Heian M , et al. Clinical comparison of conventional and additive manufactured stabilization splints[J]. Acta Biomater Odontol Scand, 2018,4(1):81-89.
doi: 10.1080/23337931.2018.1497491 |
| [14] |
Salmi M, Paloheimo KS, Tuomi J , et al. A digital process for additive manufacturing of occlusal splints: A clinical pilot study[J]. J R Soc Interface, 2013,10(84):20130203.
doi: 10.1098/rsif.2013.0203 pmid: 3673156 |
| [15] |
吴忠文 . 聚醚醚酮类树脂的国际、国内发展历程及新进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2010,38(12):1-4.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3536.2010.12.001 |
| [16] |
邓纯博, 刘冬妍, 刘吉泉 , 等. 聚醚醚酮及其复合材料作为骨科植入物的研究进展[J]. 生物医学工程与临床, 2009,13(5):473-477.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7090.2009.09.026 |
| [17] |
Zoidis P, Papathanasiou I, Polyzois G . The use of a modified poly-ether-ether-ketone (PEEK) as an alternative framework material for removable dental prostheses: A clinical report[J]. J Pros-thodont, 2016,25(7):580-584.
doi: 10.1111/jopr.12325 pmid: 26216668 |
| [18] |
贾洪诚, 王璇 . 应用T-scan Ⅲ型系统分析牙周基础治疗前后咬合变化的临床研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2015,31(4):484-487.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2015.05.07 |
| [1] | Xinyu XU,Ling WU,Fengqi SONG,Zili LI,Yi ZHANG,Xiaojing LIU. Mandibular condyle localization in orthognathic surgery based on mandibular movement trajectory and its preliminary accuracy verification [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [2] | Sui LI,Wenjie MA,Shimin WANG,Qian DING,Yao SUN,Lei ZHANG. Trueness of different digital design methods for incisal guidance of maxillary anterior implant-supported single crowns [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [3] | FENG Sha-wei,GUO Hui,WANG Yong,ZHAO Yi-jiao,LIU He. Initial establishment of digital reference standardized crown models of the primary teeth [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 327-334. |
| [4] | LI Yi,WONG Lai U,LIU Xiao-qiang,ZHOU Ti,LYU Ji-zhe,TAN Jian-guo. Marginal features of CAD/CAM laminate veneers with different materials and thicknesses [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 140-145. |
| [5] | QIU Shu-ting,ZHU Yu-jia,WANG Shi-min,WANG Fei-long,YE Hong-qiang,ZHAO Yi-jiao,LIU Yun-song,WANG Yong,ZHOU Yong-sheng. Preliminary clinical application verification of complete digital workflow of design lips symmetry reference plane based on posed smile [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 193-199. |
| [6] | XU Xiao-xiang,CAO Ye,ZHAO Yi-jiao,JIA Lu,XIE Qiu-fei. In vitro evaluation of the application of digital individual tooth tray in the impression making of mandibular full-arch crown abutments [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 54-61. |
| [7] | YUE Zhao-guo,ZHANG Hai-dong,YANG Jing-wen,HOU Jian-xia. Comparison of residual cement between CAD/CAM customized abutments and stock abutments via digital measurement in vitro [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 69-75. |
| [8] | LI Zheng,LIU Yu-shu,WANG Shi-min,ZHANG Rui,JIA Lu,YE Hong-qiang,HU Wen-jie,ZHAO Wen-yan,LIU Yun-song,ZHOU Yong-sheng. Application of biocopy function of temporary crown occlusal morphology in patients with severe attrition [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 62-68. |
| [9] | FANG Shuo-bo,YANG Guang-ju,KANG Yan-feng,SUN Yu-chun,XIE Qiu-fei. Method and accuracy of determining the jaw position of repositioning splint with the aid of digital technique [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 76-82. |
| [10] | Lang YOU,Ke-hui DENG,Wei-wei LI,Yi-jiao ZHAO,Yu-chun SUN,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Visual sensitivity threshold of lateral view of nasolabial Angle changes in edentulous jaw patients [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2020, 52(1): 107-112. |
| [11] | Shuo CHEN,Yang HE,Jin-gang AN,Yi ZHANG. Application of computer-aided virtual mandibular position in the simultaneous treatment of children with temporomandibular joint ankylosis and jaw deformity [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(5): 954-958. |
| [12] | Kuan-paul WANG,Hong-qiang YE,Hu CHEN,Yong WANG,Yu-chun SUN,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Establishment and preliminary clinical evaluation of edentulous custom trays designed and fabricated by chair-side CAD and 3D printing systems [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 349-355. |
| [13] | Xin-xin LI,Yu-shu LIU,Yu-chun SUN,Hu CHEN,Hong-qiang YE,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Evaluation of one-piece polyetheretherketone removable partial denture fabricated by computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 335-339. |
| [14] | PENG Li, WANG Zu-hua, SUN Yu-chun, QU Wei,HAN Yang, LIANG Yu-hong. Computer aided design and three-dimensional printing forapicoectomy guide template [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 905-910. |
| [15] | CHAI Jin-you, LIU Jian-zhang, WANG Bing, QU Jian, SUN Zhen, GAO Wen-hui, GUO Tian-hao, FENG Hai-lan, PAN Shao-xia. Evaluation of the fabrication deviation of a kind of milling digital implant surgical guides#br# [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 892-898. |
|
||