Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1032-1036. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.06.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
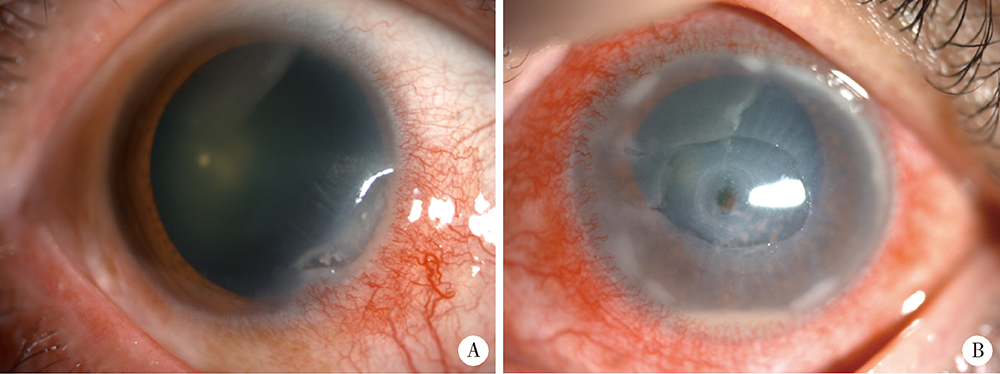
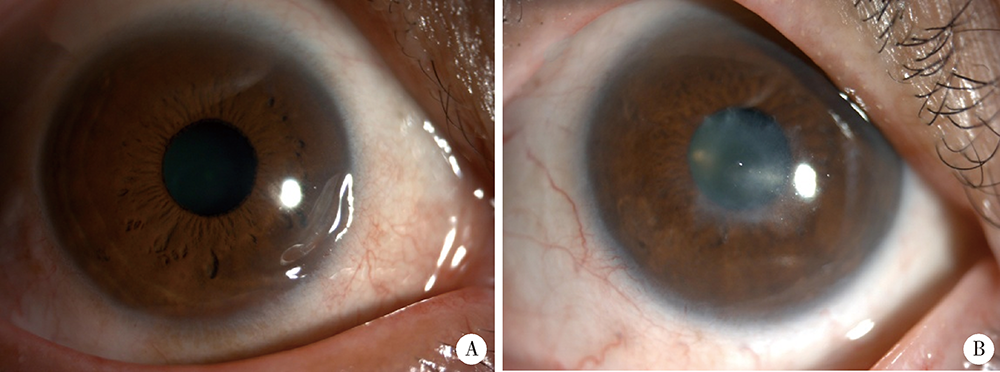
Clinical characteristics and risk factors of rheumatoid arthritis with ulcerative keratitis
LUO Liang1,2,HUO Wen-gang3,ZHANG Qin4,△( ),LI Chun1,△(
),LI Chun1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Rehabilitation, Chongqing Rehabilitation Hospital of Integrated Traditional and Western, Chongqing 400013, China
3. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Hebei Yiling Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050091, China
4. Department of Ophthalmology, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R593.22
| [1] | Jayaraj K, Alvin G, Charles S, et al. Correlation of ocular manifestations with the duration and activity of disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2017, 6(1):34-37. |
| [2] | Hamideh F, Prete P. Ophthalmologic manifestations of rheumatic diseases[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2001, 30(4):217-241. |
| [3] |
Foster CS, Forstot SL, Wilson LA. Mortality rate in rheumatoid arthritis patients developing necrotizing scleritis or peripheral ulcerative keratitis: effects of systemic immune suppression[J]. Ophthalmology, 1984, 91(10):1253-1263.
pmid: 6514289 |
| [4] |
Zandavalli F, Castro G, Mazzucco M, et. al. Infliximab is effective in difficult-to-control peripheral ulcerative keratitis. A report of three cases[J]. Rev Bras Reumatol, 2015, 55(3):310-312.
doi: 10.1016/j.rbr.2014.05.006 pmid: 25440698 |
| [5] |
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman J, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology / European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010, 62(9):2569-2581.
doi: 10.1002/art.27584 |
| [6] | Yoshida M, Hariya T, Yokokura S, et al. Concomitant herpes simplex keratitis and autoimmune-associated ulcerative keratitis in rheumatoid arthritis patients[J]. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep, 2020, 18:100648. |
| [7] |
Artifoni M, Rothschild R, Brézin A, et al. Ocular inflammatory diseases associated with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2014, 10(2):108-116.
doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2013.185 pmid: 24323074 |
| [8] |
Watanabe R, Ishii T, Yoshida M, et al. Ulcerative keratitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the modern biologic era: a series of eight cases and literature review[J]. Int J Rheum Dis, 2017, 20(2):225-230.
doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12688 pmid: 26179634 |
| [9] |
Harrold R, Shan Y, Rebello S, et al. Prevalence of Sjögren’s syndrome associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the USA: an observational study from the Corrona registry[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2020, 39(6):1899-1905.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05004-8 pmid: 32130579 |
| [10] |
Singh S, Das V, Basu S. Ocular involvement in Sjögren syndrome: risk factors for severe visual impairment and vision-threatening corneal complications[J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2021, 225:11-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2020.12.019 |
| [11] |
Maseda D, Bonami R, Crofford L. Regulation of B lymphocytes and plasma cells by innate immune mechanisms and stromal cells in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Expert Rev Clin Immunol, 2014, 10(6):747-762.
doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2014.907744 |
| [12] |
Galor A, Thorne J. Scleritis and peripheral ulcerative keratitis[J]. Rheum Dis Clin North Am, 2007, 33(4):835-854.
doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2007.08.002 |
| [13] | Wang F, Misra L, Patel V. In vivo confocal microscopy of the human cornea in the assessment of peripheral neuropathy and systemic diseases[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2015, 2015:951081. |
| [14] |
Sainz M, Foster S, Jabbur S, et al. Ocular characteristics and disease associations in scleritis-associated peripheral keratopathy[J]. Arch Ophthalmol, 2002, 120(1):15-19.
doi: 10.1001/archopht.120.1.15 |
| [15] |
Knox NE, Tole DM, Georgoudis P, et al. Peripheral ulcerative keratitis and corneal melt: a 10-year single center review with historical comparison[J]. Cornea, 2014, 33(1):27-31.
doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000008 |
| [16] | 祝磊, 王丽娅, 张俊杰, 等. 0.05%他克莫司滴眼液治疗难治性免疫相关角膜溃疡的疗效及安全性研究[J]. 中华实验眼科杂志, 2015, 33(9):823-827. |
| [17] | 杨纪忠, 李冰. 类风湿关节炎相关性边缘角膜溃疡临床分析[J]. 山西医药杂志, 2009, 38(8):748-749. |
| [18] |
Bonnet I, Rousseau A, Duraffour P, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in peripheral ulcerative keratitis associated with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. RMD Open, 2021, 7(1):e001472.
doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001472 |
| [19] |
Lucia D, Lara S, Vanesa R, et al. Biologic therapy in severe and refractory peripheral ulcerative keratitis (PUK). Multicenter study of 34 patients[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2020, 50(4):608-615.
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.03.023 |
| [20] |
Puéchal X, Gottenberg E, Berthelot M, et al. Rituximab therapy for systemic vasculitis associated with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the autoimmunity and rituximab registry[J]. Arthritis Care Res, 2012, 64(3):331-339.
doi: 10.1002/acr.20689 |
| [21] |
Peter K, Dirk B, Susann A, et al. Rapid healing of peripheral ulcerative keratitis in rheumatoid arthritis with prednisone, methotrexate and adalimumab combination therapy[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2017, 56(7):1094.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex007 |
| [22] |
Messmer M, Foster S. Vasculitic peripheral ulcerative keratitis[J]. Surv Ophthalmol, 1999, 43(5):379-396.
pmid: 10340557 |
| [23] |
Messmer M, Foster S. Destructive corneal and scleral disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis: medical and surgical management[J]. Cornea, 1995, 14(4):408-417.
pmid: 7671613 |
| [1] | Dongwu LIU, Jie CHEN, Mingli GAO, Jing YU. Rheumatoid arthritis with Castleman-like histopathology in lymph nodes: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [2] | Huina HUANG,Jing ZHAO,Xiangge ZHAO,Ziran BAI,Xia LI,Guan WANG. Regulatory effect of lactate on peripheral blood CD4+ T cell subsets in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [3] | Xiaofei TANG,Yonghong LI,Qiuling DING,Zhuo SUN,Yang ZHANG,Yumei WANG,Meiyi TIAN,Jian LIU. Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [4] | Xue ZOU,Xiao-juan BAI,Li-qing ZHANG. Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [5] | Qi WU,Yue-ming CAI,Juan HE,Wen-di HUANG,Qing-wen WANG. Correlation between dyslipidemia and rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [6] | Jing-feng ZHANG,Yin-ji JIN,Hui WEI,Zhong-qiang YAO,Jin-xia ZHAO. Correlation analysis between body mass index and clinical characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [7] | Yin-ji JIN,Lin SUN,Jin-xia ZHAO,Xiang-yuan LIU. Significance of IgA isotype of anti-v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homologue B1 antibody in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [8] | Wen-xin CAI,Shi-cheng LI,Yi-ming LIU,Ru-yu LIANG,Jing LI,Jian-ping GUO,Fan-lei HU,Xiao-lin SUN,Chun LI,Xu LIU,Hua YE,Li-zong DENG,Ru LI,Zhan-guo LI. A cross-sectional study on the clinical phenotypes of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [9] | Fang CHENG,Shao-ying YANG,Xing-xing FANG,Xuan WANG,Fu-tao ZHAO. Role of the CCL28-CCR10 pathway in monocyte migration in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [10] | Rui LIU,Jin-xia ZHAO,Liang YAN. Clinical characteristics of patients with rheumatoid arthritis complicated with venous thrombosis of lower extremities [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
| [11] | Jing-feng ZHANG,Yin-ji JIN,Hui WEI,Zhong-qiang YAO,Jin-xia ZHAO. Cross-sectional study on quality of life and disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1086-1093. |
| [12] | GAO Chao,CHEN Li-hong,WANG Li,YAO Hong,HUANG Xiao-wei,JIA Yu-bo,LIU Tian. Validation of the Pollard’s classification criteria (2010) for rheumatoid arthritis patients with fibromyalgia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 278-282. |
| [13] | ZHONG Hua,XU Li-ling,BAI Ming-xin,SU Yin. Effect of chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 on bone erosion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1026-1031. |
| [14] | LOU Xue,LIAO Li,LI Xing-jun,WANG Nan,LIU Shuang,CUI Ruo-mei,XU Jian. Methylation status and expression of TWEAK gene promoter region in peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
| [15] | ZHANG Lu,HU Xiao-hong,CHEN Cheng,CAI Yue-ming,WANG Qing-wen,ZHAO Jin-xia. Analysis of cervical instability and clinical characteristics in treatment-naive rheumatoid arthritis patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1049-1054. |
|
||