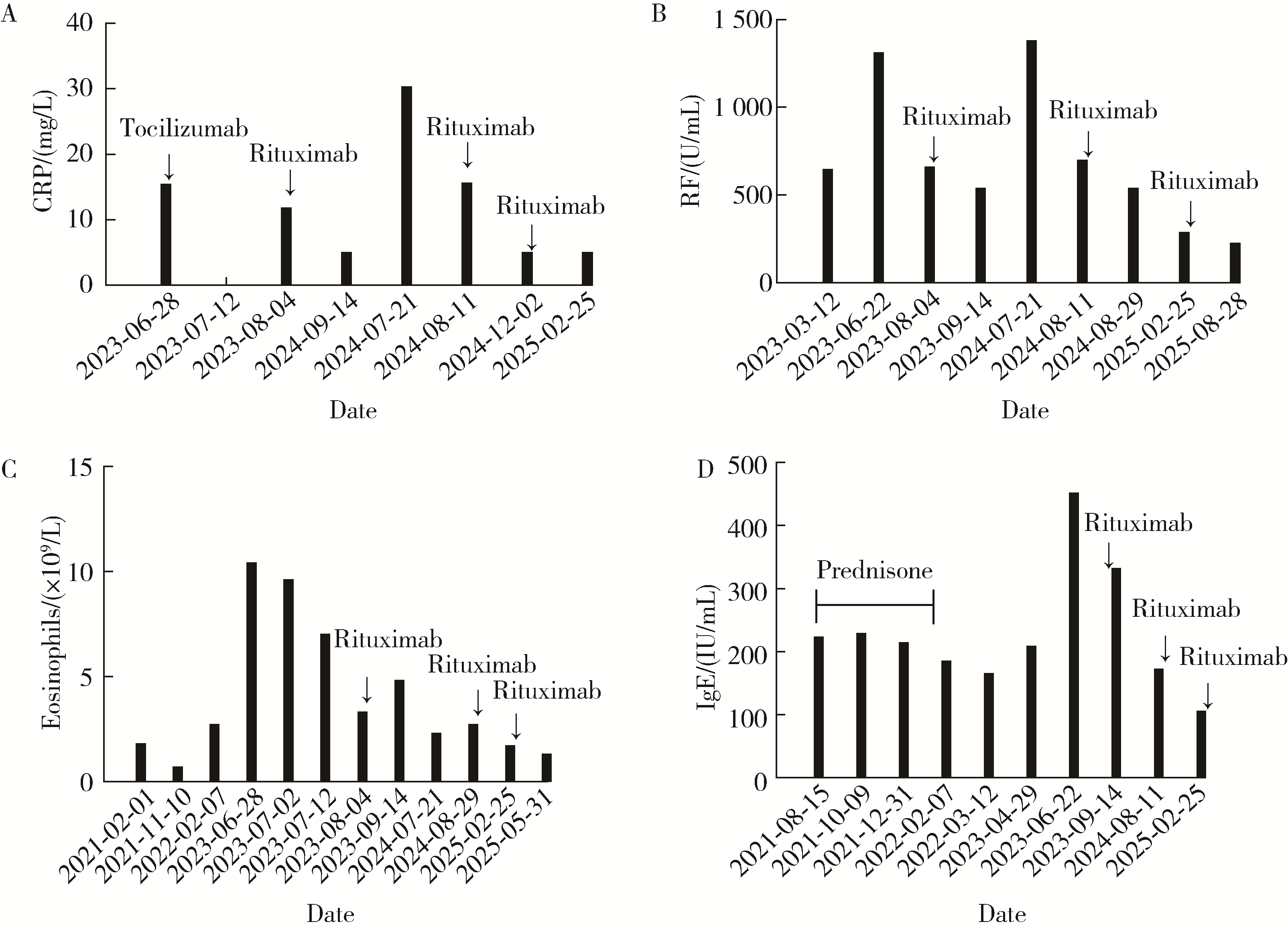
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (6): 1203-1207. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.06.029
Previous Articles Next Articles
Rheumatoid arthritis combined with IgG4-related disease successfully treated with rituximab: A case report
Yan DING, Lifang WANG, Chaoran LI, Zhemin LU, Lianjie SHI*( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University Shougang Hospital, Beijing 100144, China
CLC Number:
- R593.2
| 1 |
doi: 10.1002/art.41120 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1007/s00296-018-4191-1 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2015-000070 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1038/s41584-018-0109-2 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2016.07.003 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52847-6 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken336 |
| 8 |
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.5996 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1016/S0952-7915(96)80058-6 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1007/s00428-002-0702-1 |
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310336 |
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04699-8 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14920 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1782218 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206605 |
| 20 |
张文, 董凌莉, 朱剑, 等. IgG 4相关性疾病诊治中国专家共识[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2021, 60 (3): 192- 206.
|
| 21 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2019.12.029 |
| [1] | Tao WU, Jianzi LIN, Yafeng ZHU, Jianda MA, Peiwen JIA, Lijuan YANG, jie PAN, Yaowei ZOU, Ying YANG, Ye LU, Lie DAI. Serum inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H3 is identified as a potential biomarker for myopenia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using proteomic profiling [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(6): 1024-1031. |
| [2] | Yayun ZHAO, Mengfan NI, Xue LI, Bei WANG, Gong CHENG, Jing HE, Yuebo JIN. Clinical efficacy and safety of rituximab in treating renal injury in primary Sjögren syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(6): 1051-1060. |
| [3] | Ju YANG, Jing XU, Juhua DAI, Lianjie SHI. Expression of lumican protein in serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and its correlation with disease and immune activities [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(5): 911-918. |
| [4] | Lianghua FENG, Lirong HONG, Yujia CHEN, Xueming CAI. Role and mechanism of ubiquitin-specific protease 35 in ferroptosis of rheumatoid arthritis-fibroblast like synoviocytes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(5): 919-925. |
| [5] | Peiwen JIA, Ying YANG, Yaowei ZOU, Zhiming OUYANG, Jianzi LIN, Jianda MA, Kuimin YANG, Lie DAI. Clinical characteristics of overlapping syndromes of low muscle mass in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and their impact on physical function [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1009-1016. |
| [6] | Doudou MA, Zhemin LU, Qian GUO, Sha ZHU, Jin GU, Yan DING, Lianjie SHI. Successful treatment of rheumatoid arthritis complicated with myasthenia gravis with low-dose rituximab: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1110-1114. |
| [7] | Rui YAN, Dan KE, Yan ZHANG, Li LI, Huanran SU, Wei CHEN, Mingxia SUN, Xiaomin LIU, Liang LUO. Diagnostic significance of serum chemokine CXCL-10 and Krebs von den lungen-6 level in patients with rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 956-962. |
| [8] | Liang ZHAO, Chenglong SHI, Ke MA, Jing ZHAO, Xiao WANG, Xiaoyan XING, Wanxing MO, Yirui LIAN, Chao GAO, Yuhui LI. Immunological characteristics of patients with anti-synthetase syndrome overlap with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 972-979. |
| [9] | Yijun HAN, Xiaoli CHEN, Changhong LI, Jinxia ZHAO. Application status of methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 994-1000. |
| [10] | Dongwu LIU, Jie CHEN, Mingli GAO, Jing YU. Rheumatoid arthritis with Castleman-like histopathology in lymph nodes: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [11] | Huina HUANG,Jing ZHAO,Xiangge ZHAO,Ziran BAI,Xia LI,Guan WANG. Regulatory effect of lactate on peripheral blood CD4+ T cell subsets in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [12] | Xiaofei TANG,Yonghong LI,Qiuling DING,Zhuo SUN,Yang ZHANG,Yumei WANG,Meiyi TIAN,Jian LIU. Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [13] | Xue ZOU,Xiao-juan BAI,Li-qing ZHANG. Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [14] | Lu FENG,Jia-yu ZHAI,Jin-xia ZHAO. Medical visit status and clinical features in patients with IgG4 related disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1028-1032. |
| [15] | Jie WU,Wen ZHANG,Shu LIANG,Yi-lu QIN,Wen-qiang FAN. Pregnancy-associated neuromyelitis optical spectrum disorder combined with primary Sjögren's syndrome: A critical illness case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1118-1124. |
|
||