促结缔组织增生型成釉细胞瘤(desmoplastic ameloblastoma,DA)是一种特殊类型的成釉细胞瘤,其主要病理特征是肿瘤间质中结缔组织大量增生,肿瘤性上皮岛或条索边缘细胞呈扁平状紧密排列,可见化生性骨形成[1]。最早由Eversole于1984年报道[2],1992年和2005年WHO牙源性肿瘤分类中将其归类为成釉细胞瘤的一种亚型[3,4]。DA的发病率较低(8.65%)[5],多位于前牙区[6],与常见实性多囊型成釉细胞瘤(solid/multicystic ameloblastoma,SA)和单囊型成釉细胞瘤(unicystic ameloblastoma,UA)相比,存在一些临床、影像和病理学的独特性[7]。既往文献中针对性大样本的研究报道较少[6,8],本研究拟通过回顾性分析DA与其他类型成釉细胞瘤的临床和影像区别,进一步探讨DA的CT影像学特点。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例资料
收集2000年7月至2017年8月期间就诊于北京大学口腔医院、经手术治疗和病理检查确诊、病例资料完整的成釉细胞瘤病例,回顾性分析临床特点、各类型成釉细胞瘤的构成比和发病部位。选取螺旋CT资料完整的DA病例作为研究对象,以SA和UA病例各50例作为对照组,进行CT影像学特征比较分析。
1.2 影像学检查与分析
由两名影像科医生共同阅片并结合手术治疗记录确定成釉细胞瘤的发病部位,以前牙区、前磨牙区、磨牙区、下颌升支区、下颌角区、上颌窦区进行分区研究。螺旋CT检查于8层螺旋CT(Brightspeed,GE,USA)或16层螺旋CT(Optima,GE,USA)中完成,扫描和重建参数如下:电压120~140 kV;管电流200~380 mA;螺矩1.65 :1;扫描时间1 s;层厚1.25 mm;间隔1.25 mm。
调阅相关病例DICOM格式CT资料,由两名影像科医生于监视器中使用多平面重组软件共同读片,分别于软组织窗及骨窗观察。提取影像学关键特征进行分析:边界、周围骨质变化、外形、内部结构、囊实性、牙移位、牙根吸收、牙周膜情况、密质骨连续性或骨膜反应。测量长轴径、颊舌径、高度评价肿物的颊舌向膨隆程度,沿病变区牙列或颌骨走形方向测量长轴径,沿肿物的颊舌向测量颊舌径,肿物冠状位方向的最大径定义为高度。在病变内部测量圆形感兴趣区(region of interest,ROI),测量平均CT值。
1.3 统计学方法
应用SPSS 11.0软件进行统计学分析。年龄、高度、颊舌径、近远中径及CT值为计量资料,应用方差分析检验;性别、部位、颊舌膨隆、受累牙的特点、边界特点和内部结构为计数资料,应用卡方检验。P<0.05为差异存在统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 一般临床资料
共获得1 269例成釉细胞瘤病例,其中DA 50例(3.9%)、SA 776例(61.2%)、UA 374例(29.5%)、外周型成釉细胞瘤18例(1.4%)、其他类型成釉细胞瘤(成釉细胞纤维瘤、成釉细胞纤维牙本质瘤、角化型成釉细胞瘤等)51例(4.0%)。20例(1.6%)成釉细胞瘤发生恶变,DA合并其他类型成釉细胞瘤6例。776例SA中选734例资料完整者进行统计,374例UA中选350例资料完整者进行统计。三种类型成釉细胞瘤患者性别、年龄及患病部位详见表1。
表1 三种类型成釉细胞瘤的一般情况
Table 1
| Items | DA | SA | UA | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, Femal/Male | 13/37 | 319/415 | 159/191 | <0.001 |
| Age/years, | 43.9±12.4 | 35.3±15.5 | 30.3±14.7 | <0.001 |
| Site | <0.001 | |||
| Between canine, Maxilla/Mandible | 13/18 | 8/89 | 8/36 | <0.001 |
| Premolar, Maxilla/Mandible | 10/5 | 16/98 | 6/45 | <0.001 |
| Molar, Maxilla/Mandible | 0/2 | 20/166 | 3/119 | 0.037 |
| Ramus, n | 2 | 307 | 129 | 0.001 |
| Other sites, n | 0 | 10 | 1 | <0.001 |
DA, desmoplastic ameloblastoma; SA, solid/multicystic ameloblastoma; UA, unicystic ameloblastoma. Other sites including infratemporal fossa, region infraorbitalis, zygoma.
2.2 CT影像学表现
表2 促结缔组织增生型成釉细胞瘤影像学表现
Table 2
| Items | DA (n=28) | SA (n=50) | UA (n=50) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expansion, lingual/buccal | 27/11 | 50/50 | 50/48 | <0.001 | |
| Size/mm, | |||||
| Height | 29.2±9.6 | 39.5±13.9 | 32.6±8.8 | <0.001 | |
| Mesio-distal | 41.0±18.9 | 69.1±24.4 | 59.1±17.3 | <0.001 | |
| Buccal-lingual | 23.7±10.0 | 32.4±12.8 | 29.3±8.8 | 0.004 | |
| Tooth, n | |||||
| Displacement | 23 | 30 | 27 | 0.043 | |
| Root resorption | 23 | 40 | 33 | 0.166 | |
| Periodontal destruction | 25 | 44 | 41 | 0.584 | |
| Boundary, n | |||||
| Scallop border | 21 | 2 | 0 | <0.001 | |
| Curved border | 7 | 48 | 50 | <0.001 | |
| Clear/ill defined | 8/20 | 50/0 | 50/0 | <0.001 | |
| Cortex thinning | 17 | 50 | 50 | <0.001 | |
| Cortex destruction | 4 | 0 | 0 | <0.001 | |
| Internal, n | |||||
| Septa | 24 | 46 | 17 | <0.001 | |
| Ossification | 21 | 0 | 0 | <0.001 | |
| CT value/HU, | 488.8±164.0 (Ⅰ) | 33.1±36.4 | 21.5±7.2 | <0.001* | |
| 171.7±102.8 (Ⅱ) | |||||
| 42.1±8.8 (Ⅲ) | |||||
DA, desmoplastic ameloblastoma; SA, solid/multicystic ameloblastoma; UA, unicystic ameloblastoma. *CT values of DA(type Ⅰ,Ⅱ,Ⅲ) are higher than those of SA and UA.
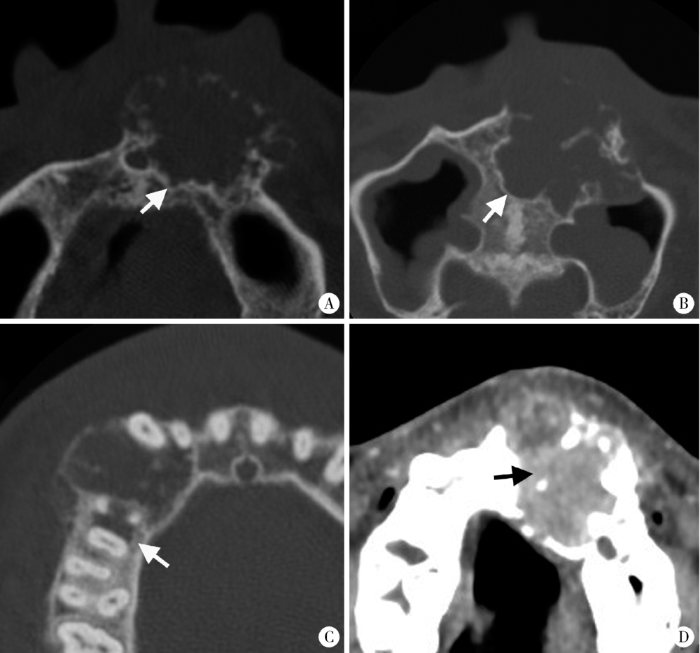
图1
图1
促结缔组织增生型成釉细胞瘤的边界形态特征
Figure 1
The boundary features of DA
A-B, DA shows scalloped shape with short sclerosed border on axial CT images (white arrows); C, Ill-defined border, infiltration into surrounding bone (white arrow) and locally destroyed cortex can be observed in DA; D, DA shows as solid mass on CT (black arrow).
图2
图2
促结缔组织增生型成釉细胞瘤成骨致密型(Ⅰ型)
Figure 2
The densely ossifying DA (type Ⅰ)
CT images shows the internal ossifications appear like bone trabecular (white arrow, A) or densely ossification (white arrow, B).
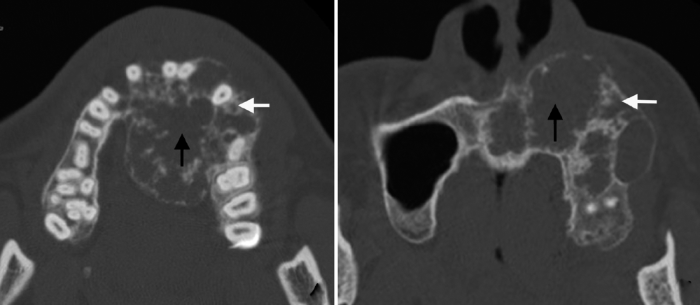
图3
图3
促结缔组织增生型成釉细胞瘤蜂窝/皂泡型(Ⅱ型)
Figure 3
The honeycomb/soap bubble type of DA (type Ⅱ)
Axial CT images shows the scattered inhomogeneous ossifications appearing as honeycomb (white arrows) or soap bubbles (black arrows).
图4
图4
促结缔组织增生型成釉细胞瘤成骨稀疏型(Ⅲ型)
Figure 4
The sparsely ossifying type of DA (type Ⅲ)
Sparse internal ossification is observed on axial CT images (white arrow).
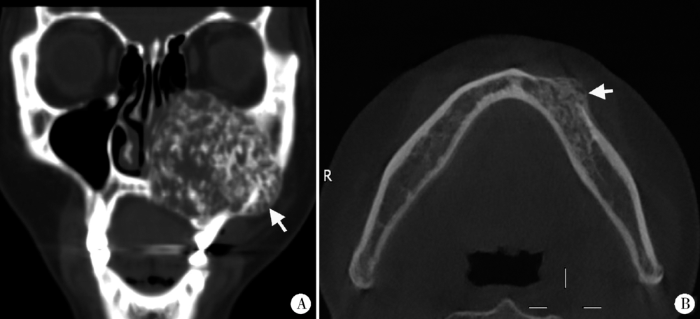
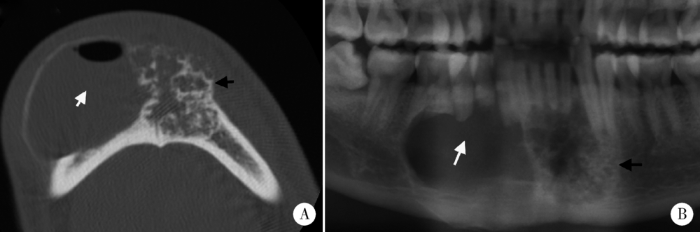
DA也可见伴发于SA或UA病例中(6例,图5)。
图5
图5
促结缔组织增生型成釉细胞瘤混合型
Figure 5
The hybrid type of DA
Axial CT image (A) and cropped panoramic tomography (B) shows the lesion is composed of the unicystic part (white arrows) and ossification part of DA (black arrows).
3 讨论
1984年Eversole等[2]初次报道了3例特殊类型的成釉细胞瘤,其病理特点为伴有结缔组织的大量增生。1992年WHO牙源性肿瘤分类将成釉细胞瘤分为经典的成釉细胞瘤(滤泡型和丛状型)、UA和其他多种类型的成釉细胞瘤(促结缔组织增生型、棘皮瘤型、基底细胞型等)[3]。2005年WHO牙源性肿瘤分类将成釉细胞瘤分为4类:SA、UA、外周型成釉细胞瘤及促结缔组织增生型成釉细胞瘤,将棘皮瘤型、基底细胞型、颗粒细胞型等成釉细胞瘤列入实性/多囊型成釉细胞瘤[4]。2017年 WHO牙源性肿瘤分类更新,将DA定义为实性型成釉细胞瘤的一种亚型[7]。尽管分类方法有所演变,但对于DA的组织病理学表现的观点基本一致。
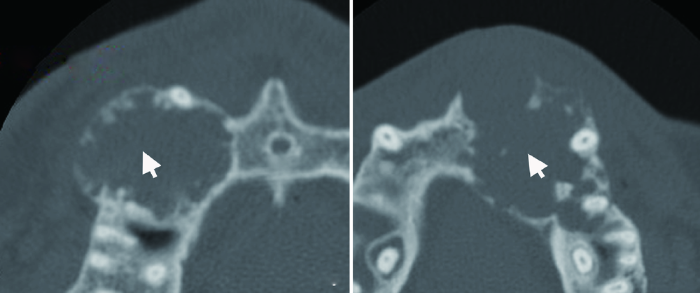
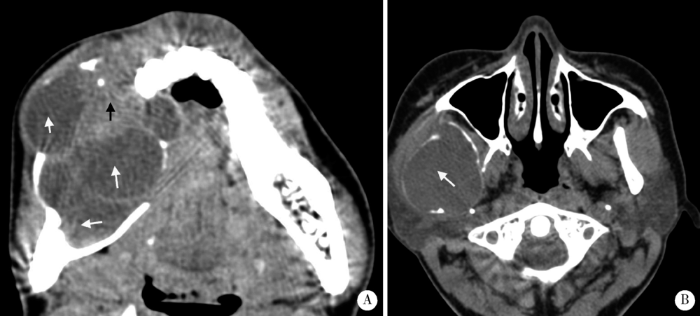
图6
图6
典型实性多囊型(A)和单囊型(B)成釉细胞瘤
Figure 6
Classic solid/multicystic (A) and unicystic (B) ameloblastomas
The solid/multicystic type is composed of multilocullar cyst (white arrow, A) and solid content (black arrow, A). The unicystic type shows homogenous cyst (white arrow, B).
从肿物的三维形态上来看,DA的形态更接近于球形,高度与长轴径比值(0.76)和颊舌径与长轴径比值(0.63)更接近于1,表明DA在发生和发展过程中受到颌骨形态限制较少,而SA和UA表现有明显的沿颌骨长轴发展、长轴径较长的特点。
组织病理学方面,DA中常可见有化生性类骨质小梁结构(metaplastic bone)形成(图7), 应与CT影像中观察到的不同程度的骨化现象相关。化生性类骨质小梁的形成机制并不清楚。影像检查可观察到的病变内部成骨结构向硬化性边界逐渐过渡而呈现边界欠清的表现,需要与恶性病变相鉴别。CT可以分别于软组织窗和骨窗中观察病变内部结构。综合分析DA特殊的边界形态、发病部位和内部结构特征,可以有助于DA的术前诊断。常见的内部存在骨化结构特征的颌骨肿瘤或瘤样病变还包括骨化纤维瘤、根尖周骨结构不良、成骨细胞瘤等,在影像学诊断中需注意鉴别诊断。
图7
图7
促结缔组织增生型成釉细胞瘤组织学中化生性成骨(箭头,HE ×200)
Figure 7
Histology of metaplastic bone in desmoplastic ameloblastoma (arrow, HE ×200)
综上所述,CT有助于DA的影像学诊断。DA多发生于前牙区及前磨牙区,CT特征具有一定的特异性,表现为内部含有不同程度的骨化现象、边界清楚或欠清楚的实性病灶。
参考文献
Ameloblastomas with pronounced desmoplasia
[J].
The WHO histological typing of odontogenic tumours. A commentary on the Second Edition
[J].
World Health Organization classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours
[J].
890例颌骨成釉细胞瘤发病构成比分析
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-4979.2015.03.011
Magsci
[本文引用: 2]

目的:了解颌骨成釉细胞瘤的构成现状, 为临床诊疗提供帮助。方法:回顾性分析2003-01—2014-6间于我科住院治疗的890例颌骨成釉细胞瘤的临床资料,对其性别、年龄、发病部位、病理分类进行分析。结果:890例成釉细胞瘤中平均年龄40.15岁,男女比例1.62∶1。下颌骨受累724例(81.35%),上颌骨受累166例(18.65%),左右颌骨发病率基本相同,颌骨任一部位均可见成釉细胞瘤的发生,但下颌磨牙及下颌升支区为最易受累部位。病理亚型中实体型378例,单囊型427例,为成釉细胞瘤最为常见的病理亚型。结论:成釉细胞瘤好发于青年,多见于下颌骨,男性发病率较女性高,实体型及单囊型为成釉细胞瘤最为常见的病理亚型,临床诊治中应注意其相应特点。
Some current concepts on the pathology of ameloblastomas
[J].