北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1027-1032. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.015
可溶性内皮糖蛋白在抗磷脂综合征患者的血清水平及临床意义
李记1,2,郑莉1,石连杰2,徐婧2,舒建龙3,张学武3,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科, 北京 100044
2. 北京大学国际医院风湿免疫科, 北京 102206
3. 广西国际壮医医院风湿病科, 南宁 530011
Increased serum soluble-endoglin level and its clinical significance in antiphospholipid syndrome
Ji LI1,2,Li ZHENG1,Lian-jie SHI2,Jing XU2,Jian-long SHU3,Xue-wu ZHANG3,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’ s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
3. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Guangxi International Zhuang Medical Hospital, Nanning 530011, China
摘要:
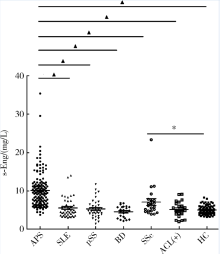
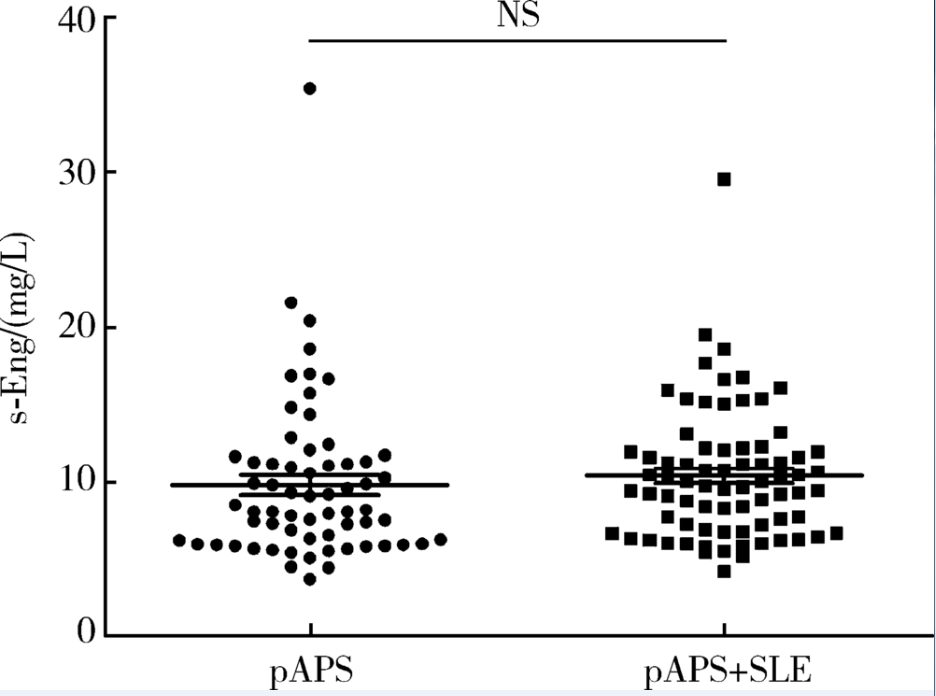
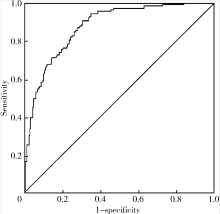
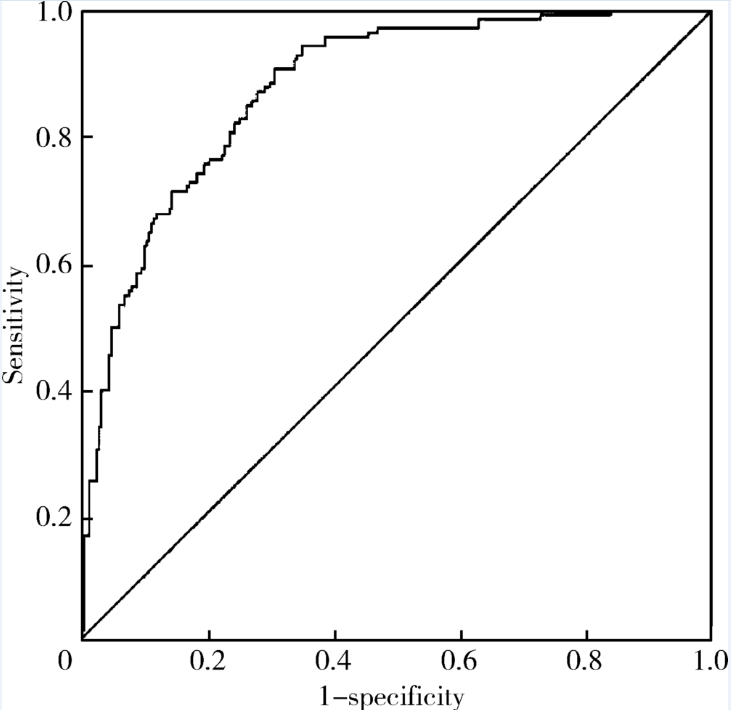
目的: 检测可溶性内皮糖蛋白(soluble endoglin,s-Eng)在抗磷脂综合征(antiphospholipid syndrome,APS)患者的血清水平并分析其潜在临床意义。方法: 采用酶联免疫吸附试验方法检测139例APS患者[原发性APS患者64例,继发于系统性红斑狼疮(systemic lupus erythematosus,SLE)的APS患者75例]、44例不符合APS诊断的单纯SLE患者、37例原发性干燥综合征(primary sjogren syndrome,pSS)患者、23例白塞病(Behcet’s disease,BD)患者、22例系统性硬化病(systemic sclerosis,SSc)患者、22例持续抗心磷脂抗体(anticardiolipin antibody,aCL)阳性但无法诊断SLE或APS者(单纯aCL阳性组)及87例健康对照(health control,HC)的s-Eng血清水平,分析APS患者外周血s-Eng水平与其临床及实验室表现的关系。数据分析采用 t检验、方差分析、Mann-Whitney U 检验、Pearson’s χ 2检验。 结果: (1)APS患者血清s-Eng水平[(10.15±4.64) mg/L]显著高于其他风湿病患者[单纯SLE(5.55±2.51) mg/L,pSS(5.32±2.34) mg/L,BD(4.58±1.53) mg/L, SSc(7.11±4.18) mg/L]、单纯aCL阳性组[(5.17±2.00) mg/L]及HC组[(5.04±1.11) mg/L],P均小于0.001。原发性APS患者与继发于SLE的APS患者血清s-Eng水平差异无统计学意义[(9.83±5.15) mg/L vs. (10.42±4.18) mg/L,P =0.12]。单纯aCL阳性组血清s-Eng水平与HC组差异无统计学意义[(5.17±2.00) mg/L vs.(5.04±1.11) mg/L, P>0.05]。(2)以正常对照者血清s-Eng的
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| [1] |
Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T , et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2006,4(2):295-306.
doi: 10.1111/jth.2006.4.issue-2 |
| [2] |
Pierangeli SS, Colden-Stanfield M, Liu X , et al. Antiphospholi-pid antibodies from antiphospholipid syndrome patients activate endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo[J]. Circulation, 1999,99(15):1997-2002.
doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.99.15.1997 |
| [3] |
Dunoyer-Geindre S, de Moerloose P, Galve-de Rochemonteix B , et al. NFκB is an essential intermediate in the activation of endothelial cells by anti-β2-glycoprotein 1 antibodies[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2002,88(5):851-857.
doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1613313 |
| [4] |
Charakida M, Besler C, Batuca JR , et al. Vascular abnormalities, paraoxonase activity, and dysfunctional HDL in primary antiphospholipid syndrome[J]. JAMA, 2009,302(11):1210-1217.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1346 |
| [5] |
Ames PR, Batuca JR, Ciampa A , et al. Clinical relevance of nitric oxide metabolites and nitrative stress in thrombotic primary antiphospholipid syndrome[J]. J Rheumatol, 2010,37(12):2523-2530.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.100494 pmid: 20889602 |
| [6] |
Ramesh S, Morrell CN, Tarango C , et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies promote leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion and thrombosis in mice by antagonizing eNOS via β2GPI and apoER2[J]. J Clin Invest, 2011,121(1):120-131.
doi: 10.1172/JCI39828 pmid: 3007129 |
| [7] |
Toporsian M, Gros R, Kabir MG , et al. A role for endoglin in coupling eNOS activity and regulating vascular tone revealed in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia[J]. Circ Res, 2005,96(6):684-692.
doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000159936.38601.22 pmid: 15718503 |
| [8] |
Alt A, Miguel-Romero L, Donderis J , et al. Structural and functional insights into endoglin ligand recognition and binding[J]. PLoS One, 2012,7(2):e29948.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029948 pmid: 22347366 |
| [9] |
Bernabeu C, Conley BA, Vary CP . Novel biochemical pathways of endoglin in vascular cell physiology[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2007,102(6):1375-1388.
doi: 10.1002/jcb.21594 pmid: 17975795 |
| [10] |
Blazquez-Medela AM, Garcia-Ortiz L, Gomez-Marcos MA , et al. Increased plasma soluble endoglin levels as an indicator of cardiovascular alterations in hypertensive and diabetic patients[J]. BMC Med, 2010,8:86.
doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-86 pmid: 21171985 |
| [11] |
Strasky Z, Vecerova L, Rathouska J , et al. Cholesterol effects on endoglin and its downstream pathways in ApoE/LDLR double knockout mice[J]. Circ J, 2011,75(7):1747-1755.
doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-10-1285 pmid: 21576826 |
| [12] |
Vitverova B, Blazickova K, Najmanova I , et al. Soluble endoglin and hypercholesterolemia aggravate endothelial and vessel wall dysfunction in mouse aorta[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2018,271:15-25.
doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.02.008 pmid: 29459262 |
| [13] |
Emeksiz HC, Bideci A, Damar Ç , et al. Soluble endoglin level increase occurs prior to development of subclinical structural vascular alterations in diabetic adolescents[J]. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol, 2016,8(3):313-320.
doi: 10.4274/jcrpe |
| [14] |
Rathouska J, Jezkova K, Nemeckova I , et al. Soluble endoglin, hypercholesterolemia and endothelial dysfunction[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2015,243(2):383-388.
doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.10.003 pmid: 26520890 |
| [15] |
Bassyouni IH, El-Shazly R, Azkalany GS , et al. Clinical significance of soluble-endoglin levels in systemic lupus erythematosus: possible association with anti-phospholipid syndrome[J]. Lupus, 2012,21(14):1565-1570.
doi: 10.1177/0961203312460115 pmid: 22941564 |
| [16] |
Barbara NP, Wrana JL, Letarte M . Endoglin is an accessory protein that interacts with the signaling receptor complex of multiple members of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily[J]. J Biol Chem, 1999,274(2):584-594.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.2.584 |
| [17] |
Kapur NK, Wilson S, Yunis AA , et al. Reduced endoglin activity limits cardiac fibrosis and improves survival in heart failure[J]. Circulation, 2012,125(22):2728-2738.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.080002 |
| [18] |
Venkatesha S, Toporsian M, Lam C , et al. Soluble endoglin contributes to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia[J]. Nat Med, 2006,12(6):642-649.
doi: 10.1038/nm1429 pmid: 16751767 |
| [19] |
Chatterjee A, Black SM, Catravas JD . Endothelial nitric oxide (NO) and its pathophysiologic regulation[J]. Vascul Pharmacol, 2008,49(4/5/6):134-140.
doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2008.06.008 pmid: 2592563 |
| [20] |
Palmer RM, Ferrige AG, Moncada S . Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor[J]. Nature, 1987,327(6122):524-526.
doi: 10.1038/327524a0 |
| [21] |
de Caterina R, Libby P, Peng HB , et al. Nitric oxide decreases cytokine-induced endothelial activation: nitric oxide selectively reduces endothelial expression of adhesion molecules and proinflammatory cytokines[J]. J Clin Invest, 1995,96(1):60-68.
doi: 10.1172/JCI118074 |
| [22] |
Radomski MW, Palmer RM, Moncada S . Endogenous nitric oxide inhibits human platelet adhesion to vascular endothelium[J]. Lancet, 1987,2(8567):1057-1058.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(87)91481-4 pmid: 2889967 |
| [23] |
Lauer T, Preik M, Rassaf T , et al. Plasma nitrite rather than nitrate reflects regional endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity but lacks intrinsic vasodilator action[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2001,98(22):12814-12819.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.221381098 pmid: 11606734 |
| [24] |
Robak E, Kierstan M, Cebula B , et al. Circulating endothelial cells and angiogenic proteins in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2009,18(4):332-341.
doi: 10.1177/0961203308097572 pmid: 19276301 |
| [25] |
Cervera R, Serrano R, Pons-Estel GJ , et al. Morbidity and mortality in the antiphospholipid syndrome during a 10-year period: a multicentre prospective study of 1000 patients[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2015,74(6):1011-1018.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204838 pmid: 24464962 |
| [26] |
Derksen RH, de Groot PG . The obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome[J]. J Reprod Immunol, 2008,77(1):41-50.
doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2006.12.003 |
| [27] |
Holers VM, Girardi G, Mo L , et al. Complement C3 activation is required for antiphospholipid antibody-induced fetal loss[J]. J Exp Med, 2002,195(2):211-220.
doi: 10.1084/jem.200116116 pmid: 11805148 |
| [28] |
Soh MC, Pasupathy D, Gray G , et al. Persistent antiphospholipid antibodies do not contribute to adverse pregnancy outcomes[J]. Rheumatology(Oxford), 2013,52(9):1642-1647.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ket173 pmid: 3741478 |
| [29] |
Levine RJ, Lam C, Qian C , et al. Soluble endoglin and other circulating antiangiogenic factors in preeclampsia[J]. N Eng J Med, 2006,355(10):992-1005.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa055352 pmid: 15805796 |
| [1] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [2] | 卢情怡,艾尼扎提·哈斯木,李宇菲,李春. 抗神经酰胺抗体在抗磷脂综合征中的分布及临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1139-1143. |
| [3] | 洪丽荣,陈雨佳,江庆来,贾汝琳,李春,冯亮华. 新型血栓四项联合常规凝血指标预测抗磷脂综合征患者血栓形成的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1033-1038. |
| [4] | 庄金满,李天润,李选,栾景源,王昌明,冯琦琛,韩金涛. Rotarex旋切导管在股腘动脉狭窄合并血栓形成中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 328-332. |
| [5] | 侯玉珂,蔡青猛,刘香君,贠泽霖,李春,张学武. 氧化型低密度脂蛋白抗体在抗磷脂综合征中的临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1117-1122. |
| [6] | 王玉华,张国华,张令令,罗俊丽,高兰. 系统性红斑狼疮合并自发性肾上腺出血1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1178-1181. |
| [7] | 顾婕昱,陆翠,石慧,杨程德. 14例恶性抗磷脂综合征病例报道及临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1033-1038. |
| [8] | 郑晓娟, 邓晓莉, 刘湘源. 54例抗磷脂综合征患者的妊娠结局[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(2): 323-328. |
| [9] | 褚亚明, 窦勇, 李玉军, 周一新△. 人工膝关节置换术后小腿深静脉血栓的转归[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(5): 708-710. |
| [10] | 唐琦,宋毅,李学松,张崔建,蔡林,宋刚,张骞,王进,何志嵩,周利群. 肾癌伴静脉瘤栓患者的外科治疗策略及长期疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(4): 549-. |
| [11] | 李茹*, 周云杉*, 贾园, 栗占国. 抗磷脂综合征患者血栓事件的危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(5): 788-791. |
| [12] | 于峥嵘, 李淳德, 邑晓东, 林景荣, 刘宪义, 刘洪, 卢海霖. 脊柱手术后静脉血栓栓塞的预防[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(5): 661-665. |
| [13] | 高鹏骥, 朱继业, 栗光明, 冷希圣. 合并门静脉血栓的肝病患者的肝移植方法及疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(5): 558-560. |
| [14] | 宋琳琳, 吴新民, 袁训芝, 袁家颖, 赵国立. 易栓症相关分子与髋膝关节大手术后下肢深静脉血栓[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(2): 237-238. |
|
||