北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 586-590. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.03.029
131I相关唾液腺炎的炎症分级及内镜治疗
李潇1,苏家增1,张严妍1,张丽琪2,张亚琼2,柳登高2,△( ),俞光岩1,△(
),俞光岩1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院?口腔医院,口腔颌面外科,北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院?口腔医院,放射科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Inflammation grading and sialoendoscopic treatment of131I radioiodine-induced sialadenitis
Xiao LI1,Jia-zeng SU1,Yan-yan ZHANG1,Li-qi ZHANG2,Ya-qiong ZHANG2,Deng-gao LIU2,△( ),Guang-yan YU1,△(
),Guang-yan YU1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
2. Department of Oral Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
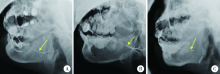
目的 结合唾液腺造影及内镜表现对131I相关唾液腺炎进行炎症分级,评估分析内镜治疗的疗效。 方法 收集2012年11月至2018年10月间在北京大学口腔医院进行唾液腺内镜检查与治疗的131I相关唾液腺炎患者的临床及影像学资料,分析唾液腺造影与内镜表现的特点并进行炎症分级。根据病变程度,采取内镜下生理盐水与地塞米松混合液灌洗、机械扩张等治疗,术后进行随访。 结果 42例131I相关唾液腺炎患者中,男性5例、女性37例,男女比例为1 ∶7.4,症状为唾液腺区反复肿胀、疼痛或口干等。腮腺造影主要表现为一处或多处导管狭窄,部分病例分支导管未显影。唾液腺内镜主要表现为导管不同程度狭窄,可见分支导管闭锁。根据腮腺造影及内镜所见分为3级:(1)轻度炎症:主导管存在狭窄和扩张,但0.9 mm内镜可通过;(2)中度炎症:主导管存在一处重度狭窄,内镜不能直接通过;(3)重度炎症:主导管存在2处以上重度狭窄、弥漫性狭窄或导管闭锁。33例(65侧)131I相关唾液腺炎患者的腮腺同时接受唾液腺造影与内镜检查,其中轻度炎症8侧,中度炎症23侧,重度炎症34侧。内镜治疗后经3~72个月随访,效果评价为显效22侧,缓解22侧,无效19侧,失访2侧,总有效率为69.8%。 结论131I相关唾液腺炎的临床、腮腺造影以及唾液腺内镜表现具有明确的特点,据此我们提出131I相关唾液腺炎炎症严重程度的分级标准。唾液腺内镜技术可以明显缓解131I相关唾液腺炎患者的主观临床症状,对于早期病变效果更佳。
中图分类号:
- R781.7
| [1] | van Nostrand D. The benefits and risks of I-131 therapy in patients with well-differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid, 2009,19(12):1381-1391. |
| [2] | Lu L, Shan F, Li W, et al. Short-term side effects after radioiodine treatment in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2016,2016(9):1-5. |
| [3] | De Luca R, Vicidomini A, Trodella M, et al. Sialoendoscopy: A viable treatment for I131 induced sialoadenitis [J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014,52(7):641-646. |
| [4] | 柳登高, 郭玉娇, 姜岚, 等. 43例慢性阻塞性腮腺炎内镜治疗疗效观察[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2012,47(9):81-84. |
| [5] | Ish-Shalom S, Durleshter L, Segal E, et al. Sialochemical and oxidative analyses in radioactive131I-treated patients with thyroid carcinoma [J]. Eur J Endocrinol, 2008,158(5):677-681. |
| [6] | Badam RK, Suram J, Babu DB, et al. Assessment of salivary gland function using salivary scintigraphy in pre and post radioactive iodine therapy in diagnosed thyroid carcinoma patients[J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2016,10(1):60-62. |
| [7] | Ali MJ. Iodine-131 therapy and nasolacrimal duct obstructions: What we know and what we need to know[J]. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg, 2016,32(4):243-248. |
| [8] | Maruoka Y, Baba S, Isoda T, et al. A functional scoring system based on salivary gland scintigraphy for evaluating salivary gland dysfunction secondary to 131I therapy in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma [J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2017, 11(8): TC23-TC28. |
| [9] |
Jarzab B, Handkiewicz-Junak D, Wloch J. Juvenile differentiated thyroid carcinoma and the role of radioiodine in its treatment: a qualitative review[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2005,12(4):773-803.
pmid: 16322322 |
| [10] | Wu CB, Xi H, Zhou Q, et al. Sialendoscopy-assisted treatment for radioiodine-induced sialadenitis[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2015,73(3):475-481. |
| [11] |
Allweiss P, Braunstein GD, Katz A, et al. Sialadenitis following131I therapy for thyroid carcinoma: Concise communication [J]. J Nucl Med, 1984,25(7):755-758.
pmid: 6737074 |
| [12] |
Silberstein EB. Reducing the incidence of131I-induced sialadenitis: the role of pilocarpine [J]. J Nucl Med, 2008,49(4):546-549.
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.107.049411 pmid: 18344428 |
| [13] | Ko KY, Kao CH, Lin CL, et al. 131I treatment for thyroid cancer and the risk of developing salivary and lacrimal gland dysfunction and a second primary malignancy: A nationwide population-based cohort study [J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imag, 2015,42(8):1172-1178. |
| [14] | Chow S. Side effects of high-dose radioactive iodine for ablation or treatment of differentiated thyroid carcinoma[J]. J HK Coll Radiol, 2005(8):127-135. |
| [15] |
Malpani BL, Samuel AM, Ray S. Quantification of salivary gland function in thyroid cancer patients treated with radioiodine[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 1996,35(3):535-540.
pmid: 8655377 |
| [16] |
Geres AE, Mereshian PS, Fernández S, et al. Sialadenitis after radioiodine therapy: Analysis of factors that influence the response to medical treatment[J]. Endocrinol Nutr, 2015,62(10):493-498.
pmid: 26459118 |
| [17] |
Wu JQ, Feng HJ, Ouyang W, et al. Systematic evaluation of salivary gland damage following I-131 therapy in differentiated thyroid cancer patients by quantitative scintigraphy and clinical follow-up[J]. Nucl Med Commun, 2015,36(8):819.
doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000325 pmid: 25932534 |
| [18] | Nahlieli O, Nazarian Y. Sialadenitis following radioiodine therapy a new diagnostic and treatment modality[J]. Oral Disease, 2006,12(5):476-479. |
| [19] |
Gonzalez ME, Muttikkal TJ, Rehm PK. Sialadenitis following low dose I-131 diagnostic thyroid scan with Thyrogen® (recombinant human thyroid stimulating hormone-thyrotropin alfa) [J]. J Radiol Case Rep, 2015,9(6):44-49.
pmid: 26622936 |
| [20] | Prendes BL, Orloff LA, Eisele DW. Therapeutic sialendoscopy for the management of radioiodine sialadenitis[J]. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2012,138(1):15-19. |
| [1] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | 李正芳,罗采南,武丽君,吴雪,孟新艳,陈晓梅,石亚妹,钟岩. 抗氨基甲酰化蛋白抗体在诊断类风湿关节炎中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [4] | 李文菁,张保宙,李恒,赖良鹏,杜辉,孙宁,龚晓峰,李莹,王岩,武勇. 胫距跟融合治疗终末期踝和后足病变的中短期临床结果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [5] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [6] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [7] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [8] | 薛蔚,董樑,钱宏阳,费笑晨. 前列腺癌新辅助治疗与辅助治疗的现状及进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 775-780. |
| [9] | 邱敏,宗有龙,王滨帅,杨斌,徐楚潇,孙争辉,陆敏,赵磊,卢剑,刘承,田晓军,马潞林. 腹腔镜肾部分切除术治疗中高复杂程度肾肿瘤的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [10] | 王磊,韩天栋,江卫星,李钧,张道新,田野. 主动迁移技术与原位碎石技术在输尿管软镜治疗1~2 cm输尿管上段结石中的安全性和有效性比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 553-557. |
| [11] | 熊焰,李鑫,梁丽,李东,鄢丽敏,李雪迎,邸吉廷,李挺. 甲状腺粗针穿刺活检病理诊断的准确性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [12] | 哈雪梅,姚永正,孙莉华,辛春杨,熊焰. 实性肺胎盘样变形1例及文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [13] | 宁博涵,张青霞,杨慧,董颖. 伴间质细胞增生、玻璃样变性及索状结构的子宫内膜样腺癌1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [14] | 陈适,刘田. 重视系统性血管炎的早期识别和个体化治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1065-1067. |
| [15] | 曹瑞洁,姚中强,焦朋清,崔立刚. 不同分类标准对中国大动脉炎的诊断效能比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1128-1133. |
|
||