北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 632-636. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.006
等离子针状电极在经尿道近输尿管口膀胱肿瘤切除术中的临床应用(附16例报道)
- 北京大学国际医院泌尿外科,北京 102206
Clinical application of the needle electrode in transurethral plasmakinetic resection of bladder tumor around ureteral orifice: A report of 16 cases
Tian WANG,Xin HONG,Xiao-feng WANG( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
摘要:
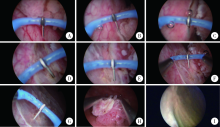
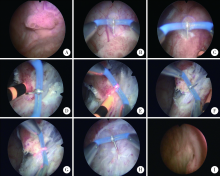
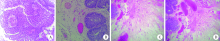
目的: 探讨等离子针状电极在经尿道近输尿管口膀胱肿瘤切除术中的应用价值。方法: 回顾性分析北京大学国际医院泌尿外科2015年6月至2019年12月期间收治的16例接受经尿道等离子针状电极切除的近输尿管口膀胱肿瘤患者的临床资料。肿瘤基底部距离输尿管口1 cm以内者7例,其中侵犯输尿管口者2例,距输尿管口1~2 cm者9例。全部研究对象术前均明确诊断并除外手术禁忌,采用等离子针状电极对肿瘤进行整块切除,将全部切除组织送病理检查,术后行规律灌注治疗并随访。对手术时间、闭孔神经反射发生率、出血量、输尿管导管或双猪尾管留置情况、术后肾积水发生率、肿瘤临床分期、复发率等进行统计分析。结果: 16例患者均顺利完成手术,手术时间16~57 min,平均(32.6±11.8) min,所有患者均未发生明显闭孔神经反射及围手术期出血。术中肿瘤切除前需要预置输尿管导管7例,术后继续留置输尿管导管4例,更换留置双猪尾管3例。术后病理提示所有肿瘤均为尿路上皮癌,其中低级别9例、高级别7例;病理分期:Ta期10例、T1期5例、T2a期1例,所有肿瘤基底部及侧切缘均为阴性。所有患者接受3~56个月的随访,平均(26.0±18.1)个月,无1例出现上尿路积水和肿瘤复发。结论: 经尿道等离子针状电极可以整块切除膀胱肿瘤,减少闭孔神经反射并有效保护输尿管口结构,是一种治疗近输尿管口膀胱肿瘤安全、有效的手术方式。
中图分类号:
- R737.14
| [1] | van den Bosch S, Alfred Witjes J. Long-term cancer-specific survival in patients with high-risk, non-muscle-invasive bladder can-cer and tumour progression: A systematic review[J]. Ero Urol, 2011,60(3):493-500. |
| [2] | 那彦群, 叶章群, 孙颖浩, 等. 2014版中国泌尿外科疾病诊断治疗指南[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014: 36-39. |
| [3] |
Sharma D, Singh VP, Agarwal N, et al. Obturator nerve block in transurethral resection of bladder tumor: A comparative study by two techniques[J]. Anesth Essays Res, 2017,11(1):101-104.
pmid: 28298765 |
| [4] |
Engilbertsson H, Aaltonen KE, Björnsson S, et al. Transurethral bladder tumor resection can cause seeding of cancer cells into the bloodstream[J]. J Urol, 2015,193(1):53-57.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.06.083 |
| [5] |
Brauers A, Buettner R, Jakse G. Second resection and prognosis of primary high risk superficial bladder cancer: Is cystectomy often too early?[J]. J Urol, 2001,165(3):808-810.
pmid: 11176474 |
| [6] |
He D, Fan J, Wu K, et al. Novel green-light KTP laser en bloc encleation for nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer: Technique and initial clinical experience[J]. J Endourol, 2014,28(8):975-979.
doi: 10.1089/end.2013.0740 pmid: 24735433 |
| [7] | 张翼飞, 梁朝朝, 施浩强, 等. 整块剜除术治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤[J]. 中华腔镜泌尿外科杂志: 电子版, 2016,10(6):11-14. |
| [8] | Yang H, Shi L, Chen G, et a1. Transurethral needle electrode resection of bladder tumor: a technique obtaining en bloc resection and obviating obturator nerve stimulation[J]. World J Nephrol Urol, 2015,4(3):232-236. |
| [9] | 梅骅, 陈凌武, 高新, 等. 泌尿外科手术学[M]. 第3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008: 201-205. |
| [10] |
Chou E, Lin A, Chen K, et al. Superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the ureteral orifice: Higher risk of developing subsequent upper urinary tract tumors[J]. Int J Urol, 2006,13(6):682-685.
doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2006.01385.x pmid: 16834642 |
| [1] | 王明瑞, 王起, 胡浩, 赖金惠, 唐鑫伟, 万春艳, 许克新, 徐涛. 覆膜金属输尿管支架治疗盆腔脂肪增多症所致肾积水的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [2] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [3] | 王明瑞,刘军,熊六林,于路平,胡浩,许克新,徐涛. 经皮微通道-微电子肾镜-微超声探针碎石术治疗1.5~2.5 cm肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [4] | 应沂岑,杜毅聪,李志华,张一鸣,李新飞,王冰,张鹏,朱宏建,周利群,杨昆霖,李学松. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下颊黏膜补片输尿管成形术治疗复杂输尿管狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [5] | 杨文博,余磊,张维宇,徐涛,王强. 带线输尿管支架自排技术在肾移植受者中的效果及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [6] | 徐心雨,吴灵,宋凤岐,李自力,张益,刘筱菁. 基于下颌运动轨迹的正颌外科术中下颌骨髁突定位方法及初步精度验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [7] | 蔡安东,王晓霞,周文娟,柳忠豪. 下颌前突畸形患者上颌骨及髁突虚拟位置与术后现实位置的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 74-80. |
| [8] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [9] | 张心灵,林志禹,陈玉杰,董文芳,杨欣. 脊柱后路内固定术后切口愈合不良的整形外科治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 910-914. |
| [10] | 秦彩朋,王飞,杜依青,张晓威,李清,刘士军,徐涛. 无症状无积水输尿管结石4例患者的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 939-942. |
| [11] | 马建勋,夏有辰,李比,赵红梅,雷玉涛,布希. 乳腺癌改良根治术后即刻乳房重建的方式选择[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 612-618. |
| [12] | 林国中,谢京城,陈晓东,杨军. 成人原发性脊髓拴系综合征的分型及显微外科手术治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 641-645. |
| [13] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [14] | 崔云鹏,施学东,刘佳,米川,王冰,潘元星,林云飞. 经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定联合可扩张管状牵开器下肿瘤切除治疗脊柱转移瘤的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 530-536. |
| [15] | 王磊,韩天栋,江卫星,李钧,张道新,田野. 主动迁移技术与原位碎石技术在输尿管软镜治疗1~2 cm输尿管上段结石中的安全性和有效性比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 553-557. |
|
||