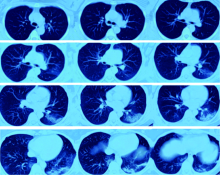
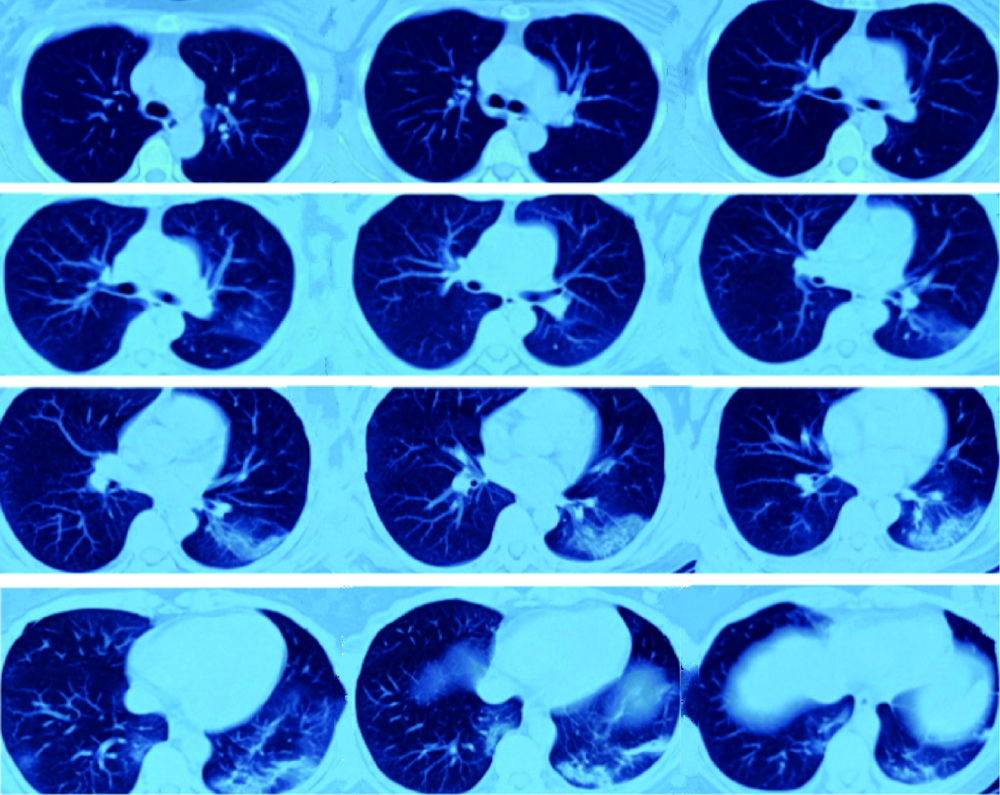
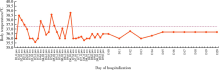
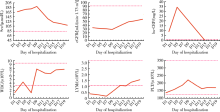
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 780-784. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.033
肾移植术后感染新型冠状病毒1例
李秋钰1,程秦1,赵志伶2,代妮妮1,曾琳3,朱兰4,郭炜5,李超2,王军红6,李姝6,葛庆岗2,沈宁1,△( )
)
- 1.北京大学第三医院呼吸与危重医学科,北京 100191
2.北京大学第三医院危重医学科,北京 100191
3.北京大学第三医院临床流行病学研究中心,北京 100191
4.华中科技大学同济医院器官移植科,武汉 430030
5.北京大学第三医院放射科,北京 100191
6.北京大学第三医院急诊科,北京 100191
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in renal transplant recipients: A case report
Qiu-yu LI1,Qin CHENG1,Zhi-ling ZHAO2,Ni-ni DAI1,Lin ZENG3,Lan ZHU4,Wei GUO5,Chao LI2,Jun-hong WANG6,Shu LI6,Qing-gang GE2,Ning SHEN1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Critical Care Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
3. Research Center of Clinical Epidemiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
4. Institute of Organ Transplantation, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, China
5. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
6. Department of Emergency, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
中图分类号:
- R563.1
| [1] |
Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study[J]. Lancet, 2020,395(10223):507-513.
pmid: 32007143 |
| [2] | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Transplant Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients[J]. Am J Transplant, 2009,9(Suppl 3):S1-155. |
| [3] |
Kumar D, Michaels MG, Morris MI, et al. Outcomes from pandemic influenza A H1N1 infection in recipients of solid-organ transplants: a multicentre cohort study[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2010,10(8):521-526.
pmid: 20620116 |
| [4] | Zhang H, Chen Y, Yuan Q, et al. Identification of kidney transplant recipients with coronavirus disease 2019[J]. Eur Urol, 2020,77(6):742-747. |
| [5] | Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China[J]. JAMA, 2020,323(11):1061-1069. |
| [6] | Lansbury L, Rodrigo C, Leonardi-Bee J, et al. Corticosteroids as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of influenza [J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2019, 2(2): CD010406. |
| [7] |
Russell CD, Millar JE, Baillie JK. Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury[J]. Lancet, 2020,395(10223):473-475.
pmid: 32043983 |
| [1] | 丁汉东, 王琴, 廖贵益, 郝宗耀. 肾移植术后并发消化道出血的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 902-907. |
| [2] | 杨文博,余磊,张维宇,徐涛,王强. 带线输尿管支架自排技术在肾移植受者中的效果及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [3] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [4] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [5] | 康志宇,王磊磊,韩永正,郭向阳. 北京冬季奥林匹克运动会运动员手术的麻醉管理[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 770-773. |
| [6] | 陈明隆,刘笑晗,郭静. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情下儿童父母社会支持与养育倦怠的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 520-525. |
| [7] | 洪鹏,田晓军,赵小钰,杨飞龙,刘茁,陆敏,赵磊,马潞林. 肾移植术后双侧乳头状肾癌1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 811-813. |
| [8] | 陈美恋,高燕,郭维,左力,王天兵. 新型冠状病毒肺炎患者床旁血液净化治疗的感染防控[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 414-419. |
| [9] | 杨航,杨林承,张瑞涛,凌云鹏,葛庆岗. 合并高血压、冠心病、糖尿病的新型冠状病毒肺炎患者发生病死的危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 420-424. |
| [10] | 赵磊,张洪宪,侯小飞,刘磊,陆敏,韩永,马潞林. 来氟米特联合羟苯磺酸钙治疗肾移植术后BK病毒相关性肾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 385-389. |
| [11] | 马凯,曲星珂,许清泉,熊六林,叶雄俊,安立哲,陈伟男,黄晓波. 肾移植术后移植肾输尿管膀胱吻合口狭窄的腔内治疗:13例报道[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1155-1158. |
| [12] | 杨帆,周云杉,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮合并获得性血友病A 1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1108-1111. |
| [13] | 邱敏,邓绍晖,侯小飞,卢剑,陆敏,刘可,张树栋,马潞林. 腹腔镜膀胱全切及回肠膀胱术治疗女性肾移植术后膀胱癌的可行性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 945-封三. |
| [14] | 郝一昌,侯小飞,赵磊,肖春雷,刘茁,张帆,马潞林. 全腹腔镜移植输尿管膀胱再植术处理肾移植术后输尿管狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 705-710. |
| [15] | 赵磊, 马潞林, 张洪宪, 侯小飞, 刘磊, 付燕, 寇允更, 宋一萌. 后腹腔镜活体供肾切取193例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 867-871. |
|
||