北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 376-380. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.02.028
原发性醛固酮增多症术后持续性重度高钾血症1例
- 1.北京大学第一医院 内分泌科, 北京 100034
2.北京大学第一医院 泌尿外科,北京 100034
Persistent and serious hyperkalemia after surgery of primary aldosteronism: A case report
WANG Wei1,CAI Lin2,GAO Ying1,GUO Xiao-hui1,ZHANG Jun-qing1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Endocrinology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
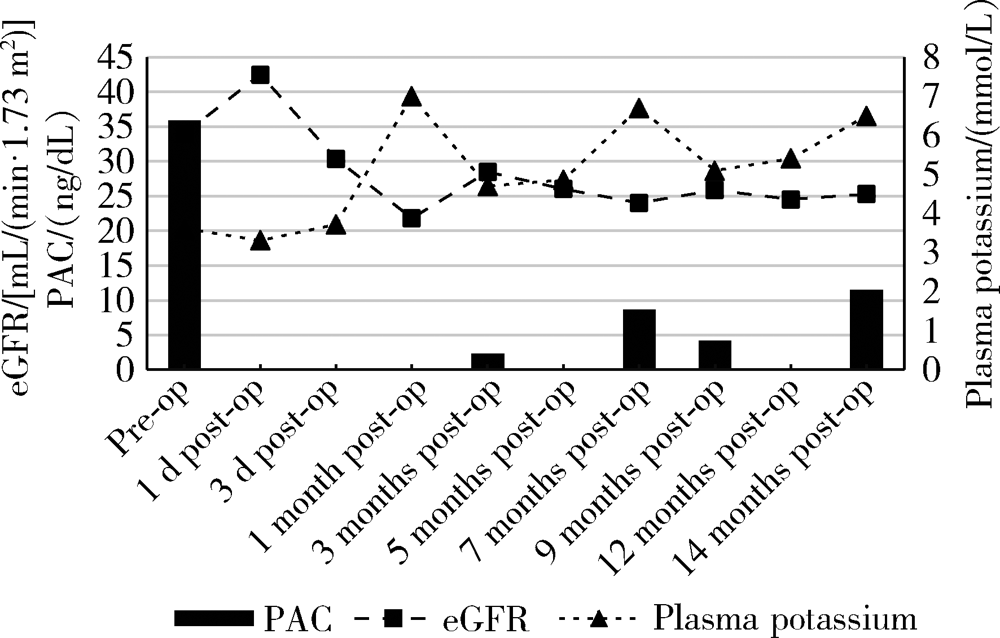
高钾血症是原发性醛固酮增多症术后可能发生的并发症之一,但原发性醛固酮增多症术后的高钾血症在临床实践中并不常见,而持续性重度高钾血症更加罕见,临床工作中该并发症也未得到足够的重视。本研究报告1例原发性醛固酮增多症患者肾上腺腺瘤术后出现持续性严重高钾血症的病例,并进行长期随访。患者因原发性醛固酮增多症行经腹腔镜左肾上腺肿物切除术,术后病理学诊断示肾上腺皮质腺瘤。术后1个月随访发现高钾血症,血钾最高7.0 mmol/L,患者自觉皮肤瘙痒、恶心、心悸。复查血浆醛固酮水平由术前35.69 ng/dL降至术后 2.12 ng/dL,24 h尿钾排出明显减少。醛固酮激素的明显下降导致尿钾排出减少可能是引起患者术后高钾血症的原因。予聚磺苯乙烯钠散、呋塞米、复方甘草酸苷降钾治疗,至术后随访14个月患者仍需服用降钾药物来维持血钾水平。用“原发性醛固酮增多症”“高钾血症”“手术治疗”检索2009至2019年发表在PubMed及万方数据库的相关文献,发现原发性醛固酮增多症术后高钾血症的发生率约为6%~29%,大多数以轻中度、一过性高血钾为主,19%~33%的高血钾患者为持续性,影响原发性醛固酮增多症术后高钾的危险因素主要包括肾功能减退、年龄大和高血压病程长等。本研究通过该病例结合文献复习,总结原发性醛固酮增多症手术治疗后出现高钾血症患者的临床特点,以提高临床医生对该严重并发症的认识,尤其对有高危因素的患者,术后更需密切监测血钾。
中图分类号:
- R589.4
| [1] |
Huang WT, Chau T, Wu ST, et al. Prolonged hyperkalemia following unilateral adrenalectomy for primary hyperaldosteronism[J]. Clin Nephrol, 2010, 73(5):392-397.
pmid: 20420801 |
| [2] |
Fischer E, Hanslik G, Pallauf A, et al. Prolonged zona glomerulosa insufficiency causing hyperkalemia in primary aldosteronism after adrenalectomy[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2012, 97(11):3965-3973.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-2234 pmid: 22893716 |
| [3] |
Chiang WF, Cheng CJ, Wu ST, et al. Incidence and factors of post-adrenalectomy hyperkalemia in patients with aldosterone producing adenoma[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2013, 424(9):114-118.
doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.017 |
| [4] |
Hibi Y, Hayakawa N, Hasegawa M, et al. Unmasked renal impairment and prolonged hyperkalemia after unilateral adrenalectomy for primary aldosteronism coexisting with primary hyper-parathyroidism: Report of a case[J]. Surg Today, 2015, 45(2):241-246.
doi: 10.1007/s00595-013-0813-0 |
| [5] |
Tahir A, McLaughlin K, Kline G. Severe hyperkalemia following adrenalectomy for aldosteronoma: Prediction, pathogenesis and approach to clinical management: A case series[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2016, 16(1):43.
doi: 10.1186/s12902-016-0121-y pmid: 27460219 |
| [6] |
Park KS, Kim JH, Yang YS, et al. Outcomes analysis of surgical and medical treatments for patients with primary aldosteronism[J]. Endocr J, 2017, 64(6):623-632.
doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ16-0530 |
| [7] |
Wada N, Shibayama Y, Umakoshi H, et al. Hyperkalemia in both surgically and medically treated patients with primary aldosteronism[J]. J Hum Hypertens, 2017, 31(10):627-632.
doi: 10.1038/jhh.2017.38 pmid: 28540931 |
| [8] |
Takeda M, Yamamoto K, Akasaka H, et al. Clinical characteristics and postoperative outcomes of primary aldosteronism in the elderly[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 103(10):3620-3629.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-00059 pmid: 30099522 |
| [9] | 丁韶丽, 阎文军, 赫曼, 等. 原发性醛固酮增多症患者肾上腺切除术中并发严重高钾血症1例[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2018, 38(4):509-510. |
| [10] |
Shariq OA, Bancos I, Cronin PA, et al. Contralateral suppression of aldosterone at adrenal venous sampling predicts hyperkalemia following adrenalectomy for primary aldosteronism[J]. Surgery, 2018, 163(1):183-190.
doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2017.07.034 |
| [11] |
Taniguchi R, Koshiyama H, Yamauchi M, et al. A case of aldosterone-producing adenoma with severe postoperative hyperkalemia[J]. Tohoku J Exp Med, 1998, 186(3):215-223.
pmid: 10348217 |
| [1] | 陈斌,吴超,刘彬,于涛,王振宇. 脊髓髓内海绵状血管瘤患者不同治疗方式的预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 652-657. |
| [2] | 皇甫宇超,杜依青,于路平,徐涛. 原发性醛固酮增多症术后高血压未治愈的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 686-691. |
| [3] | 洪鹏,田晓军,赵小钰,杨飞龙,刘茁,陆敏,赵磊,马潞林. 肾移植术后双侧乳头状肾癌1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 811-813. |
| [4] | 杨洁,张然,刘宇楠,王佃灿. 表现为耳后区巨大肿物的口外型舌下腺囊肿1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 193-195. |
| [5] | 唐琦,林榕城,姚林,张争,郝瀚,张崔建,蔡林,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 肾癌术后局部复发患者的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 628-631. |
| [6] | 汪宇鹏, 陈宝霞, 苏凯杰, 孙丽杰, 张媛, 郭丽君, 高炜. 高钾血症导致起搏器起搏和感知功能异常1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(6): 980-982. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 216
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 820
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||