北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 411-417. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.03.006
维吾尔族、哈萨克族和汉族大学生体重指数与体能指数的关系
- 1. 华东师范大学体育与健康学院,上海 200062
2. 新疆师范大学体育学院,乌鲁木齐 830054
Comparative research on the relationship between body mass index and physical fitness index among the Uygur, Kazakh and Han ethnic college students
Weimin LI1,2,Zufeiya TUERDI2,*( )
)
- 1. College of Physical Education and Health, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2. Institute of Physical Education, Xinjiang Normal University, Urumqi 830054, China
摘要:
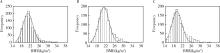
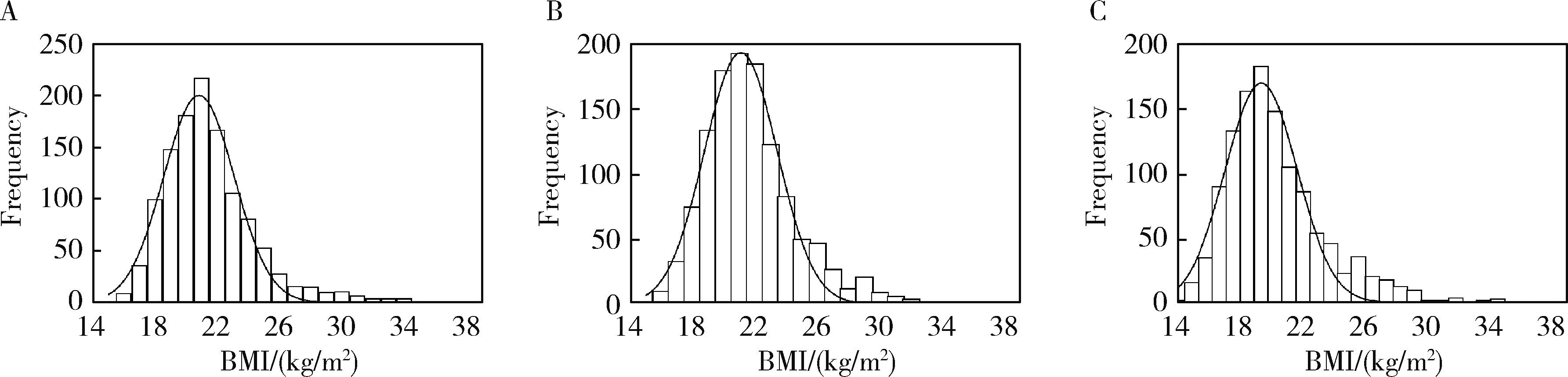
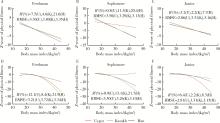
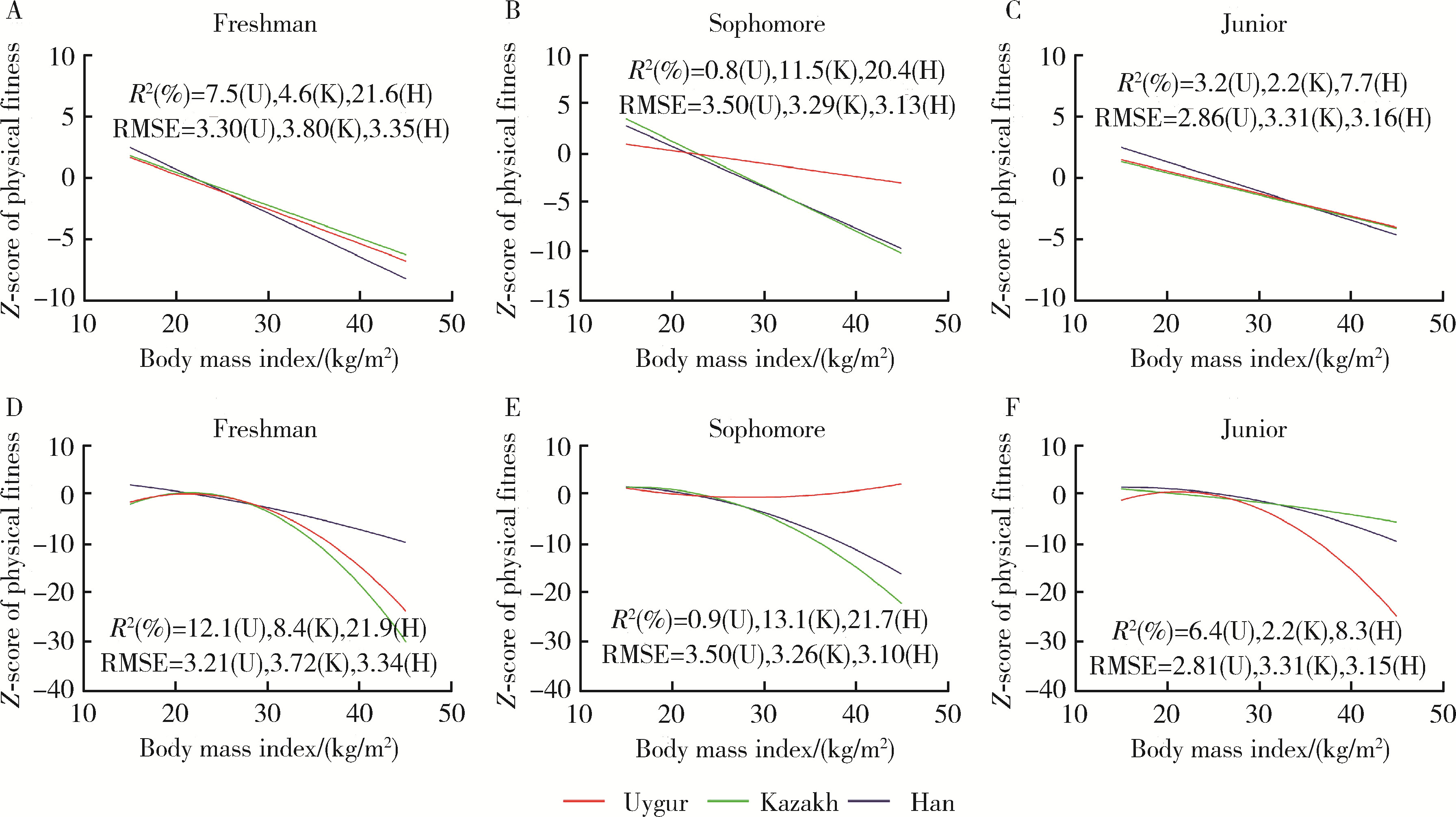
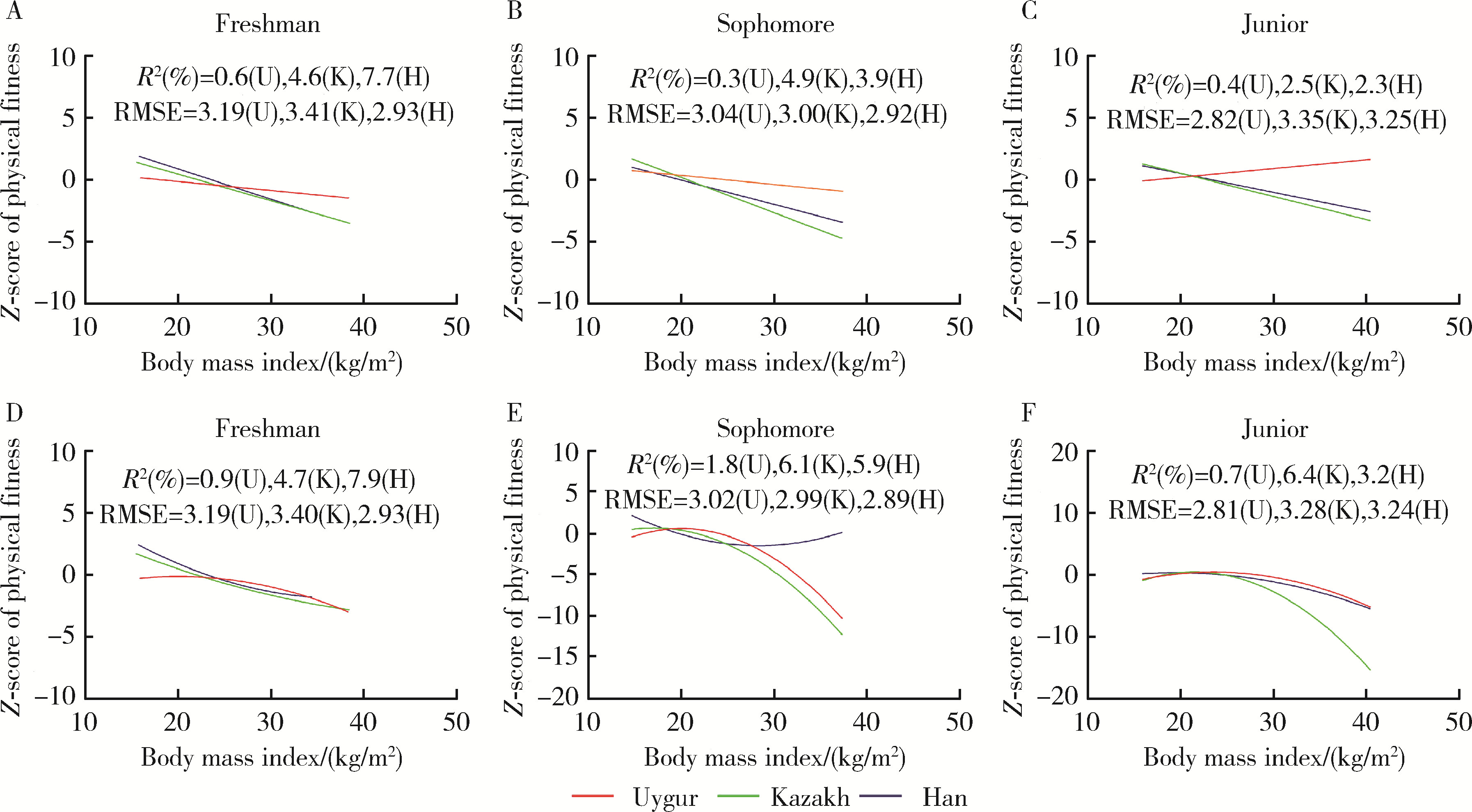
目的: 了解维吾尔族、哈萨克族和汉族大学生的营养和体能状况,调查不同民族体重指数(body mass index,BMI)和体能指数(physical fitness index,PFI)之间的非线性联系。方法: 采用分层随机整群抽样方法,抽取2021年新疆维吾尔自治区某高校非体育专业的维吾尔族、哈萨克族和汉族共3 600名大学生作为研究对象,测量身高、体质量、肺活量、50米跑、立定跳远、坐位体前屈、仰卧起坐/引体向上和耐力跑,计算体重指数和各测试成绩的标准化Z分数以及PFI等指标,对数据进行卡方检验、单因素方差分析和非线性二次回归分析。结果: 汉族大学生的超重(16.00%)和肥胖(8.08%)检出率明显高于维吾尔族(11.83%和4.08%)和哈萨克族(13.58%和4.58%)大学生,低体重检出率维吾尔族(11.92%)最高,哈萨克族最低(9.75%)。三个民族总体和男女之间BMI分级检出率差异均有统计学意义(P均<0.05)。维吾尔族、哈萨克族和汉族不同BMI分级大学生之间PFI差异均有统计学意义(P均<0.05),总体表现出正常体重组高于其他体重组,且超重组高于肥胖组,但是低体重组的PFI最高。非线性二次回归显示,维吾尔族男女和哈萨克族男生的曲线呈倒“J”形,PFI随着BMI的增大先升高后下降,其余曲线呈弧形,PFI随着BMI的增大而下降。结论: 维吾尔族、哈萨克族和汉族大学生超重肥胖会带来体能的下降,但是哈萨克族低体重组男女大学生和汉族低体重组女大学生的体能好于正常体重组。着重提高维吾尔族低体重和超重男生、汉族超重女生的体能可以有效缩小民族内各体重等级和民族间的大学生体能差异。
中图分类号:
- G804.49
| 1 | 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2014年全国学生体质与健康调研结果报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2016: 11. |
| 2 | 费夕, 李红娟. 不同BMI筛查标准判别大学生肥胖准确性评价[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2019, 40 (3): 423- 425. |
| 3 |
Li H , Li D , Wang X , et al. The role of dietary patterns and dietary quality on body composition of adolescents in Chinese college[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14 (21): 4544.
doi: 10.3390/nu14214544 |
| 4 |
Vila-Martí A , Elío I , Sumalla-Cano S . Eating behavior during first-year college students, including eating disorders-ruvic-runeat-tac project. protocol of an observational multicentric study[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 18 (18): 9457.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph18189457 |
| 5 |
Miller KG , Hartman JM . Influence of physical activity on weight status during the first year of college[J]. J Am Coll Health, 2020, 68 (3): 258- 262.
doi: 10.1080/07448481.2018.1539398 |
| 6 |
Global BMI Mortality Collaboration , Di Angelantonio E , Bhupathiraju S , et al. Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: Individual-participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents[J]. Lancet, 2016, 388 (10046): 776- 786.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30175-1 |
| 7 |
Ackerman SE , Blackburn OA , Marchildon F , et al. Insights into the link between obesity and cancer[J]. Curr Obes Rep, 2017, 6 (2): 195- 203.
doi: 10.1007/s13679-017-0263-x |
| 8 |
唐慧, 张雪婷, 王翠喆, 等. 中国新疆地区肥胖、糖尿病前期和2型糖尿病检出率及民族分布特征[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2020, 36 (10): 1381- 1389.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2020.10.022 |
| 9 |
Ramírez-Vélez R , Garcia-Hermoso A , Prieto-Benavides DH , et al. Muscle mass to visceral fat ratio is an important predictor of the metabolic syndrome in college students[J]. Br J Nutr, 2019, 121 (3): 330- 339.
doi: 10.1017/S0007114518003392 |
| 10 |
Sugimoto D , Tamura Y , Takeno K , et al. Clinical features of nonobese, apparently healthy, Japanese men with reduced adipose tissue insulin sensitivity[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2019, 104 (6): 2325- 2333.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-02190 |
| 11 | Tang X , Liu S , Chen D , et al. The role of the fat mass and obesity-associated protein in the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 17 (2): 2473- 2478. |
| 12 |
Chen X , Cui J , Zhang Y , et al. The association between BMI and health-related physical fitness among Chinese college students: A cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Public Health, 2020, 20 (1): 444.
doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-08517-8 |
| 13 |
Hallal PC , Andersen LB , Bull FC , et al. Global physical activity levels: Surveillance progress, pitfalls, and prospects[J]. Lancet, 2012, 380 (9838): 247- 257.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60646-1 |
| 14 | Wang GL , Zhang R , Zhou YT , et al. Combined effects of a body shape index and serum C-reactive protein on ischemic stroke incidence among Mongolians in China[J]. Biomed Environ Sci, 2019, 32 (3): 169- 176. |
| 15 | Vandoni M , Calcaterra V , Carnevale Pellino V , et al. "Fitness and fatness" in children and adolescents: An Italian cross-sectional study[J]. Children (Basel), 2021, 8 (9): 762. |
| 16 |
Ortega FB , Ruiz JR , Labayen I , et al. The fat but fit paradox: What we know and don't know about it[J]. Br J Sports Med, 2018, 52 (3): 151- 153.
doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2016-097400 |
| 17 | 李占宇, 郑亚莉, 张晓丹. 天津市大学生体重指数与身体素质的关联性[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2016, 37 (8): 1190- 1192. |
| 18 | Hingorjo MR , Zehra S , Hasan Z , et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness and its association with adiposity indices in young adults[J]. Pak J Med Sci, 2017, 33 (3): 659- 664. |
| 19 |
Huang YC , Malina RM . BMI and health-related physical fitness in Taiwanese youth 9-18 years[J]. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 2007, 39 (4): 701- 708.
doi: 10.1249/mss.0b013e31802f0512 |
| 20 | 张茜, 时凯旋, 王钟音. 大学生体能测试的时间变化趋势及与身体质量指数的关系研究[J]. 中国健康教育, 2022, 38 (1): 56- 61. |
| 21 |
Sun F , He Q , Sun X , et al. The association between body mass index and muscular fitness in Chinese college freshmen[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19 (21): 14060.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph192114060 |
| 22 |
McEligot AJ , Mitra S , Beam W . The association between fitness and obesity in diverse multi-ethnic college students[J]. J Am Coll Health, 2021, 69 (3): 290- 297.
doi: 10.1080/07448481.2019.1665054 |
| 23 |
李淑娟, 李刚, 德力格尔, 等. 内蒙古大学生BMI指数与身体素质的相关性研究[J]. 内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学汉文版), 2015, 44 (4): 547- 550.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8735.2015.04.028 |
| 24 | 康玲, 陈玲娟, 姜涛. 新疆某高校维吾尔族汉族大学生体成分及其与身体素质的相关性[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2017, 38 (8): 1254- 1256. |
| 25 | 教育部. 国家学生体质健康标准(2014年修订)[EB/OL]. [2014-07-28]. httpp://www.csh.edu.cn/. |
| 26 | 杨梦利, 彭玉林, 娄晓民, 等. 河南大学生体重指数与身体素质的关系[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2018, 39 (7): 1101- 1103. |
| 27 | 国际生命科学学会中国办事处中国肥胖问题工作组联合数据汇总分析协作组. 中国成人体质指数分类的推荐意见简介[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2001, 35 (5): 62- 63. |
| 28 | 吕若然, 段佳丽, 孙颖, 等. 北京市青少年1955—2010年生长发育长期趋势分析[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2016, 37 (9): 1281- 1285. |
| 29 | 龚睿, 李爽. 维吾尔族和汉族大学生身体形态与机能对比分析[J]. 当代体育科技, 2020, 10 (22): 156- 158. |
| 30 | 侯现振. 新疆哈、维大学生体质特征的比较研究[J]. 体育科技文献通报, 2018, 26 (5): 103- 105. |
| 31 |
Jiang S , Peng S , Yang T , et al. Overweight and obesity among Chinese college students: An exploration of gender as related to external environmental influences[J]. Am J Mens Health, 2018, 12 (4): 926- 934.
doi: 10.1177/1557988317750990 |
| 32 |
李海霞, 李晓梅, 陶静, 等. 新疆维吾尔自治区不同民族中小学生超重和肥胖现状分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2014, 35 (1): 9- 12.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2014.01.003 |
| 33 | 张艺玲, 赖圳宾, 邱爱明, 等. 厦门市中小学生营养状况与身体素质指标的相关性[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2021, 42 (8): 1212- 1215. |
| 34 | 王纯, 邵平. 西藏自治区世居藏族青年BMI与身体机能指标和素质指标的相关性分析[J]. 中国体育科技, 2016, 52 (2): 62-70, 79. |
| 35 | 邵君, 孙毅, 尹小俭, 等. 中国日本儿童青少年体质量指数与体能指数的关系[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2019, 40 (11): 1616- 1619. |
| [1] | 李成跃, 王浩, 阿力木江·依米提·塔尔肯. 1985——2019年新疆维吾尔族中小学生生长发育的长期趋势[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 802-808. |
| [2] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 体重指数与类风湿关节炎临床特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [3] | 史欣然,安美静,陈天娇,马军. 饮奶行为在家庭社会经济状况与儿童青少年体重指数间的中介作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 308-313. |
| [4] | 张欣,娜荷芽,叶墨,王梦楠,魏少明,孙亚慧,张复兵,孙昕霙,常春,史宇晖. 北京大学生艾滋病相关知识、态度、行为的变化特点及影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 462-468. |
| [5] | 武丽君, 宋小芸, 库尔班江, 石亚妹, 黄慈波, 黄嘉, 刘爱华, 米克拉依, 滕玉芬, 古丽娜, 孟新艳, 单新洁, 木亚赛, 苑爱萍, 张莉. 新疆吐鲁番地区维吾尔族人群高尿酸血症和痛风的流行病学调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(2): 250-253. |
| [6] | 王义, 贺利军, 周哲, 赵文峰, 那彦群. 30~50岁男性前列腺体积与体重指数、血压、血脂及血糖的相关性分析 [J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(3): 460-462. |
| [7] | 张静, 丁士刚, 杨雪玲, 王晔, 张贺军. 胃黏膜病理学改变、体重指数与血清ghrelin和瘦素关系的研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(5): 543-546. |
| [8] | 季成叶, 孙军玲. 中国学生超重、肥胖流行现状与15年流行趋势[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2004, 36(2): 194-197. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 172
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 232
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||