北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 334-339. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.018
部分下颌下腺切除术治疗下颌下腺良性肿瘤的临床效果
杨源源1,2, 张珊珊2, 俞光岩3, 杨辉俊2,*( ), 杨宏宇2,*(
), 杨宏宇2,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院综合二科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2. 北京大学深圳医院口腔医学中心口腔颌面外科,广东省高水平临床重点专科,广东省口腔疾病诊疗技术工程技术研究中心,广东深圳 518036
3. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔颌面外科,北京 100081
Clinical outcomes of partial sialoadenectomy for the treatment of benign tumors in the submandibular gland
Yuanyuan YANG1,2, Shanshan ZHANG2, Guangyan YU3, Huijun YANG2,*( ), Hongyu YANG2,*(
), Hongyu YANG2,*( )
)
- 1. Department of General Dentistry Ⅱ, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Stomatological Center, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital & Guangdong Province High-level Clinical Key Specialty & Guangdong Province Engineering Research Center of Oral Disease Diagnosis and Treatment, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong, China
3. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
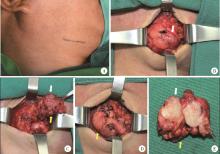
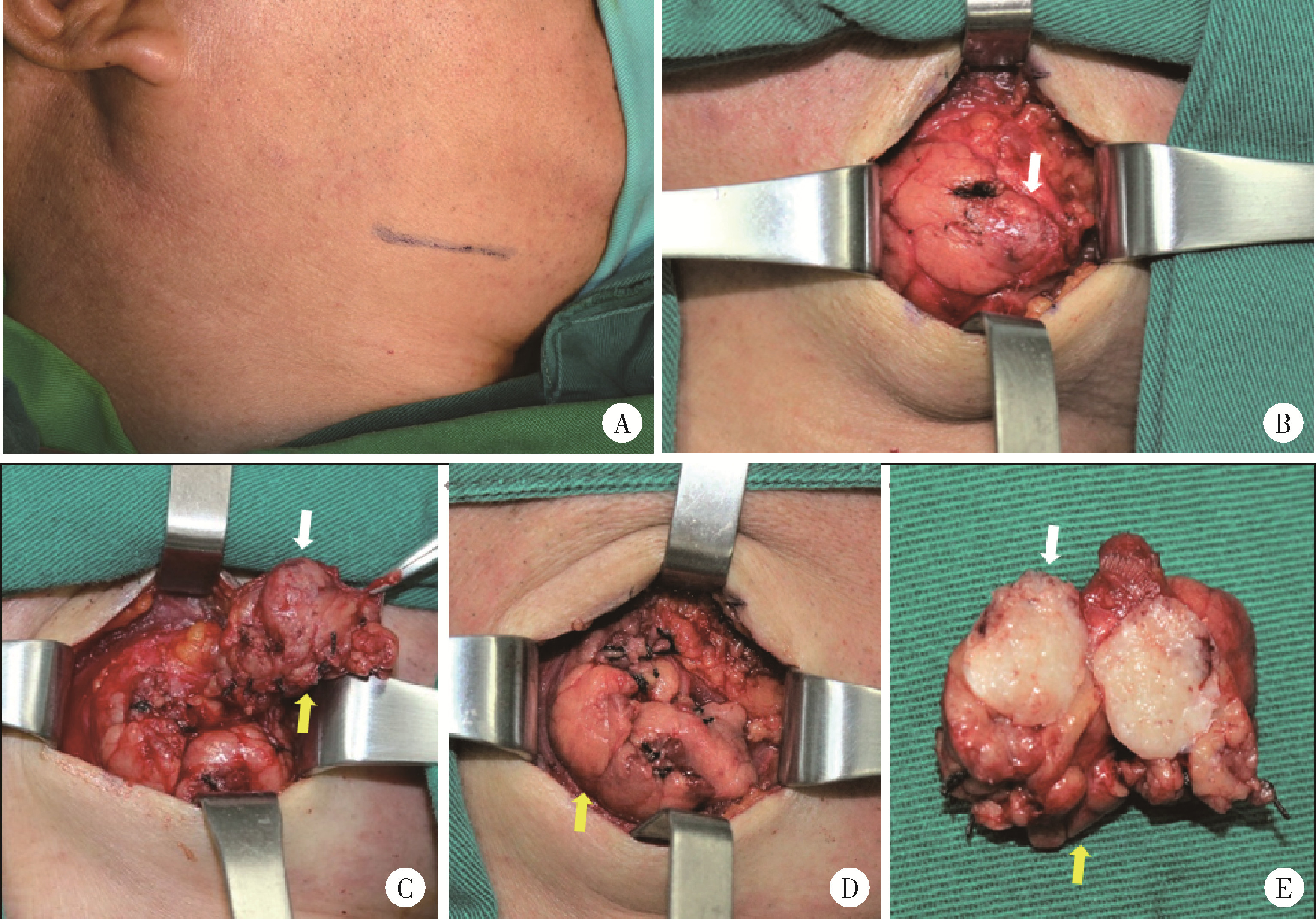
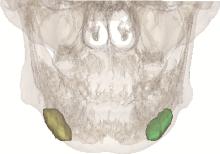
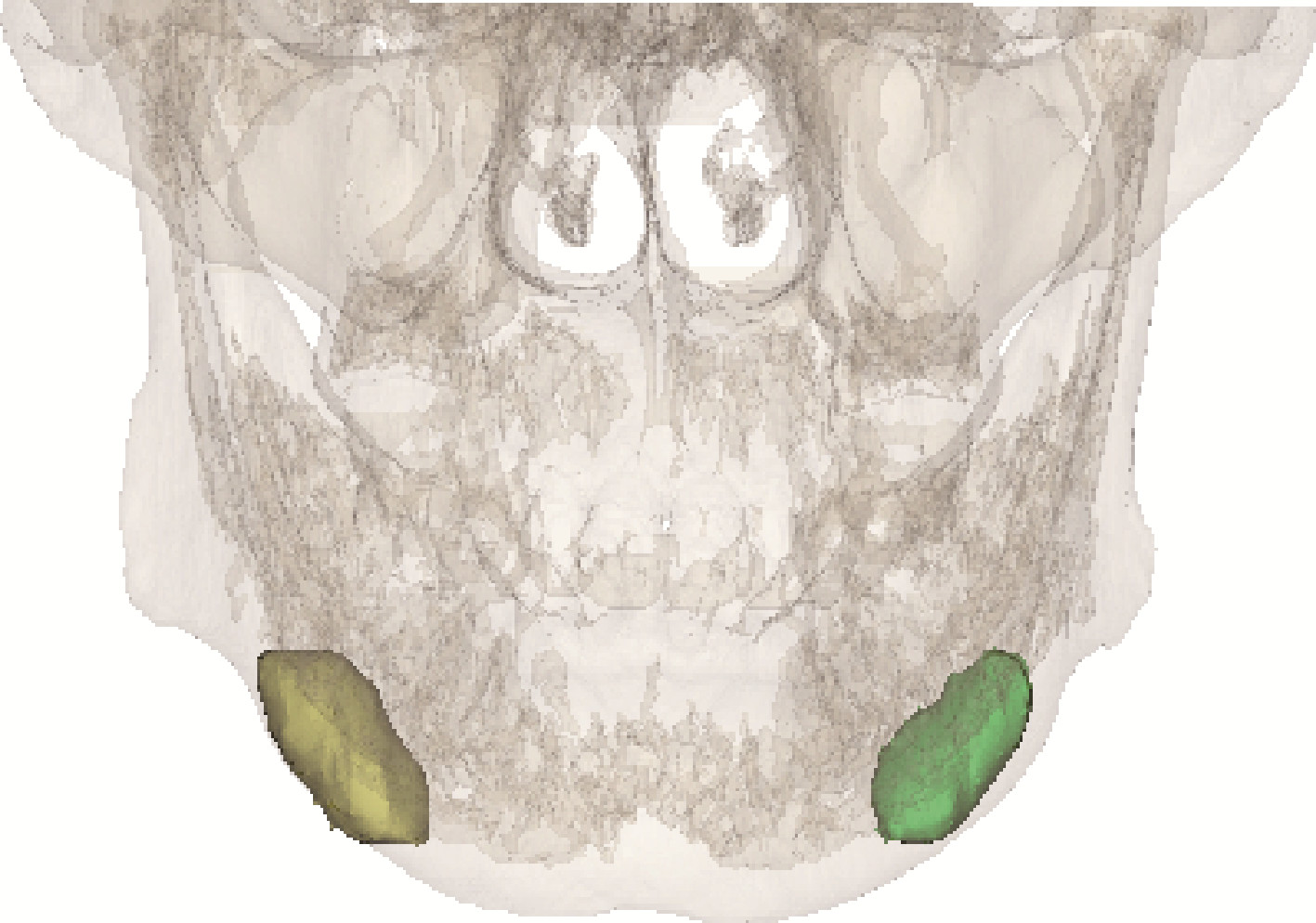
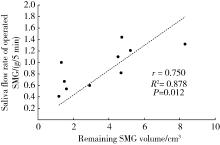
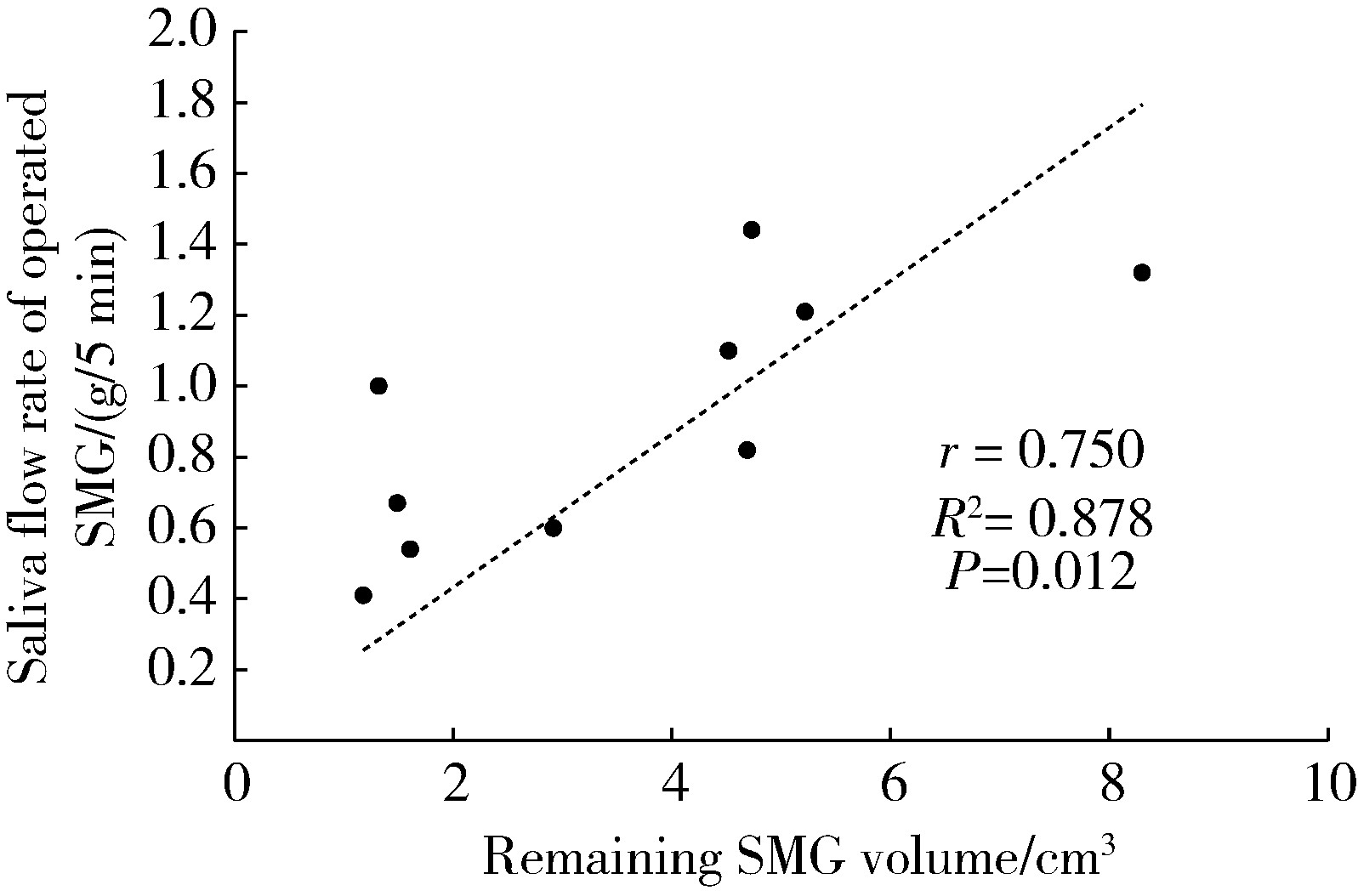
目的: 分析部分下颌下腺切除术对于下颌下腺良性肿瘤治疗的临床效果,探讨部分下颌下腺切除术的应用价值。方法: 纳入2017年10月至2021年2月于北京大学深圳医院口腔颌面外科行手术治疗的下颌下腺多形性腺瘤患者并对其进行随访评估,其中15例行部分下颌下腺切除术(部分切除组),18例行常规下颌下腺切除术(全切除组),比较两组术后唾液分泌、口干程度、面颈部容貌、神经损伤、肿瘤复发情况,并分析部分切除组健侧和患侧腺体体积、唾液流率及两者之间的相关性。结果: 两组患者在随访期内均未见肿瘤复发。部分切除组及全切除组术后静息全唾液流率分别为(2.15±1.10) g/5 min及(1.35±0.97) g/5 min,差异有统计学意义(t=2.208,P=0.035),口干症状部分切除组较全切除组轻(Z=-2.244,P=0.025);在部分切除组中,同一患者健侧和患侧下颌下腺静息唾液流率分别为(1.18±0.40) g/5 min及(0.92±0.40) g/5 min,差异有统计学意义(t=-2.821,P=0.014),而当患侧腺体剩余80%以上时,健侧和患侧静息唾液流率差异无统计学意义(t=-0.027,P=0.980),单位体积腺体唾液流率健侧和患侧差异无统计学意义(t=-0.015,P=0.989),剩余腺体的体积与唾液流率呈正相关(r=0.750,P=0.012)。部分切除组术后容貌满意度略高于全切除组,但差异无统计学意义;两组术后均未出现神经损伤症状。结论: 部分下颌下腺切除术在根治良性肿瘤的同时保留腺体分泌功能,并发症更少,可以提高患者生活质量。
中图分类号:
- R782.7
| 1 |
Roblegg E , Coughran A , Sirjani D . Saliva: An all-rounder of our body[J]. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 2019, 142, 133- 141.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.06.016 |
| 2 |
Carpenter GH . The secretion, components, and properties of saliva[J]. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol, 2013, 4, 267- 276.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-030212-182700 |
| 3 |
de Brito Neves CP , Lira RB , Chulam TC , et al. Retroauricular endoscope-assisted versus conventional submandibular gland excision for benign and malignant tumors[J]. Surg Endosc, 2020, 34 (1): 39- 46.
doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-07173-3 |
| 4 |
Cammaroto G , Vicini C , Montevecchi F , et al. Submandibular gland excision: From external surgery to robotic intraoral and extraoral approaches[J]. Oral Dis, 2020, 26 (5): 853- 857.
doi: 10.1111/odi.13340 |
| 5 |
Dhiwakar M , Ronen O , Malone J , et al. Feasibility of submandi-bular gland preservation in neck dissection: A prospective anatomic-pathologic study[J]. Head Neck, 2011, 33 (5): 603- 609.
doi: 10.1002/hed.21499 |
| 6 |
Proctor GB , Shaalan AM . Disease-induced changes in salivary gland function and the composition of saliva[J]. J Dent Res, 2021, 100 (11): 1201- 1209.
doi: 10.1177/00220345211004842 |
| 7 |
Yu GY , Ma DQ , Liu XB , et al. Local excision of the parotid gland in the treatment of Warthin' s tumour[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1998, 36 (3): 186- 189.
doi: 10.1016/S0266-4356(98)90495-8 |
| 8 |
Roh JL , Park CI . Gland-preserving surgery for pleomorphic adenoma in the submandibular gland[J]. Br J Surg, 2008, 95 (10): 1252- 1256.
doi: 10.1002/bjs.6306 |
| 9 |
Xu H , Mao C , Liu JM , et al. Microanatomic study of the vascular and duct system of the submandibular gland[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2011, 69 (4): 1103- 1107.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2010.03.006 |
| 10 |
Min R , Zun Z , Siyi L , et al. Gland-preserving surgery can effectively preserve gland function without increased recurrence in treatment of benign submandibular gland tumour[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2013, 51 (7): 615- 619.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2013.01.009 |
| 11 |
Yang TL , Ko JY , Lou PJ , et al. Gland-preserving robotic surgery for benign submandibular gland tumours: A comparison between robotic and open techniques[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014, 52 (5): 420- 424.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2014.02.015 |
| 12 |
Ge N , Peng X , Zhang L , et al. Partial sialoadenectomy for the treatment of benign tumours in the submandibular gland[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2016, 45 (6): 750- 755.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2015.12.013 |
| 13 |
李巍, 孙志鹏, 刘筱菁, 等. 腮腺和颌下腺体积的测量[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46 (2): 288- 293.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2014.02.022 |
| 14 |
Huang L , Wang Z , Shan Z , et al. Nasal asymmetry changes during growth and development in 6- to 12-year-old children with repaired unilateral cleft lip and palate: A 3D computed tomography analysis[J]. J Anat, 2022, 240 (1): 155- 165.
doi: 10.1111/joa.13538 |
| 15 |
俞光岩. 要重视下颌下腺功能器官的保护[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2017, 52 (4): 204- 205.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2017.04.002 |
| 16 |
Ethunandan M , Davies B , Pratt CA , et al. Primary epithelial submandibular salivary gland tumours: Review of management in a district general hospital setting[J]. Oral Oncol, 2009, 45 (2): 173- 176.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2008.04.011 |
| 17 |
Li LJ , Li Y , Wen YM , et al. Clinical analysis of salivary gland tumor cases in West China in past 50 years[J]. Oral Oncol, 2008, 44 (2): 187- 192.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2007.01.016 |
| 18 |
Tian Z , Li L , Wang L , et al. Salivary gland neoplasms in oral and maxillofacial regions: A 23-year retrospective study of 6 982 cases in an eastern Chinese population[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2010, 39 (3): 235- 242.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2009.10.016 |
| 19 |
Gao M , Hao Y , Huang MX , et al. Salivary gland tumours in a northern Chinese population: A 50-year retrospective study of 7 190 cases[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 46 (3): 343- 349.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2016.09.021 |
| 20 |
Hu Y , Zheng C , Cao R , et al. Resection of benign tumours of the submandibular gland with harmonic scalpel-assisted minimally extracapsular dissection[J]. J Int Med Res, 2020, 48 (1): 300060519892783.
doi: 10.1177/0300060519892783 |
| 21 |
Li L , Gao XL , Song YZ , et al. Anatomy of arteries and veins of submandibular glands[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2007, 120 (13): 1179- 1182.
doi: 10.1097/00029330-200707010-00013 |
| 22 |
Garcia-Serrano G , Moñux A , Maranillo E , et al. Vascular clinical anatomy of the submandibular gland[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2020, 48 (6): 582- 589.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2020.04.004 |
| 23 | 王张嵩, 谢舒乐, 张汉卿, 等. 2 456例唾液腺肿瘤临床病理分析[J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2020, 28 (5): 298- 302. |
| 24 | Andreasen S , Therkildsen MH , Bjørndal K , et al. Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland 1985-2010: A Danish nationwide study of incidence, recurrence rate, and malignant transformation[J]. Head Neck, 2016, 38 (Suppl 1): E1364- E1369. |
| 25 | Dai L , Lou W , Fang Q , et al. Recurrent pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland: Experience of 128 patients with first recurrence[J]. J Oncol, 2020, 2020, 6645340. |
| 26 |
Valstar MH , de Ridder M , van den Broek EC , et al. Salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma in the Netherlands: A nationwide observational study of primary tumor incidence, malignant transformation, recurrence, and risk factors for recurrence[J]. Oral Oncol, 2017, 66, 93- 99.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.01.004 |
| 27 |
Roldan-Valadez E , Garcia-Ulloa AC , Gonzalez-Gutierrez O , et al. 3D volumetry comparison using 3T magnetic resonance imaging between normal and adenoma-containing pituitary glands[J]. Neurol India, 2011, 59 (5): 696- 699.
doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.86543 |
| 28 |
王怡平, 蔡志刚, 彭歆, 等. 下颌下腺质量和体积的实体体外检测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53 (1): 126- 132.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.019 |
| 29 |
Hong X , Zhang YY , Li W , et al. Treatment of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis: Outcomes of glucocorticoid therapy combined with steroid-sparing agents[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2018, 20 (1): 12.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1507-6 |
| [1] | 任军,杨朵. 提高过继性T细胞免疫治疗临床疗效的新思考----肠道菌群与肿瘤免疫[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 204-206. |
| [2] | 弓煦,赵颖,李巍然,高雪梅. 不同疗程戴用口腔矫治器治疗阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的疗效对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 115-119. |
| [3] | 梁宇红, 陈智滨, 王嘉德. 超声波与声波根管冲洗的清理效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(6): 970-972. |
|
||