北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 911-918. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.015
Lumican蛋白在类风湿关节炎患者血清中的表达及其与疾病和免疫活动的相关性
- 1. 遂宁市中心医院老年医学科,四川遂宁 629000
2. 川北医学院临床医学系,四川南充 637000
3. 北京大学国际医院风湿免疫科,北京 102206
4. 北京大学国际医院检验科,北京 102206
5. 北京大学首钢医院风湿免疫科,北京 100144
Expression of lumican protein in serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and its correlation with disease and immune activities
Ju YANG1,2, Jing XU3, Juhua DAI4, Lianjie SHI5,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Geriatrics, Suining Central Hospital, Suining 629000, Sichuan, China
2. Department of Clinical Medicine, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan, China
3. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
4. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
5. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University Shougang Hospital, Beijing 100144, China
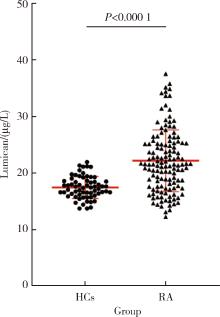
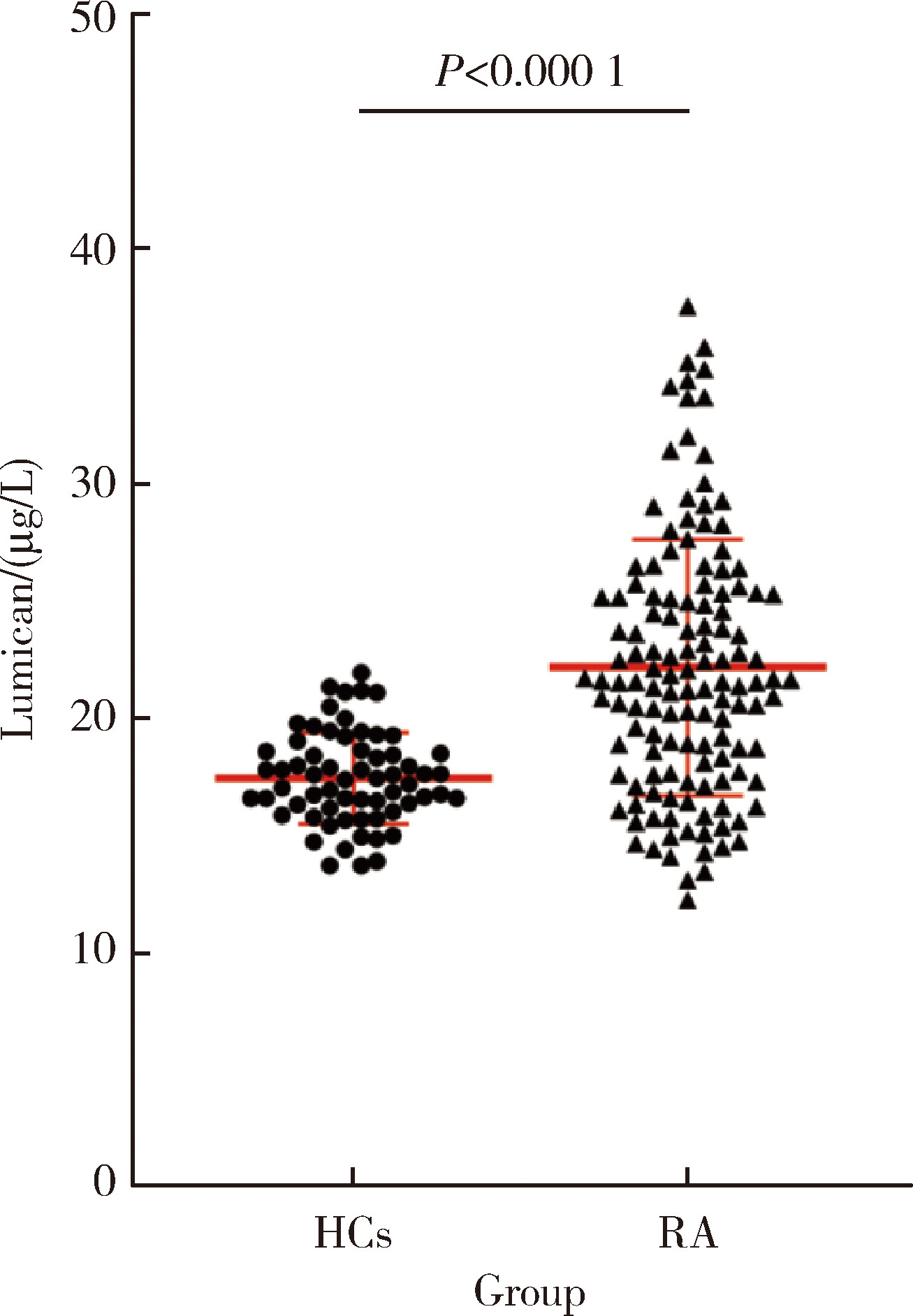
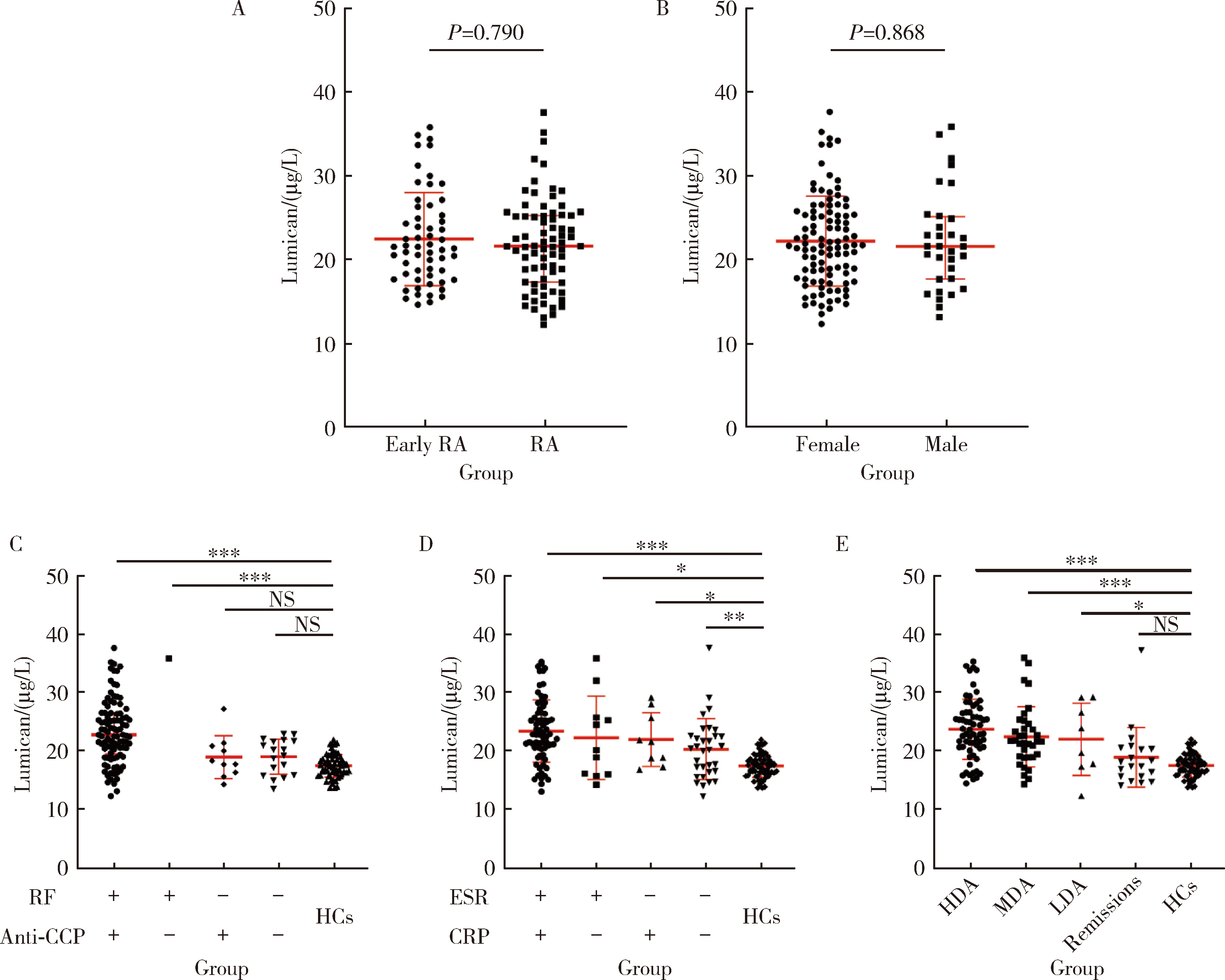
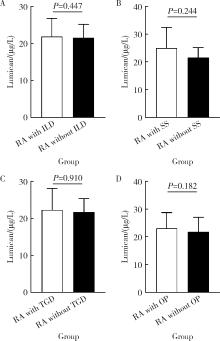
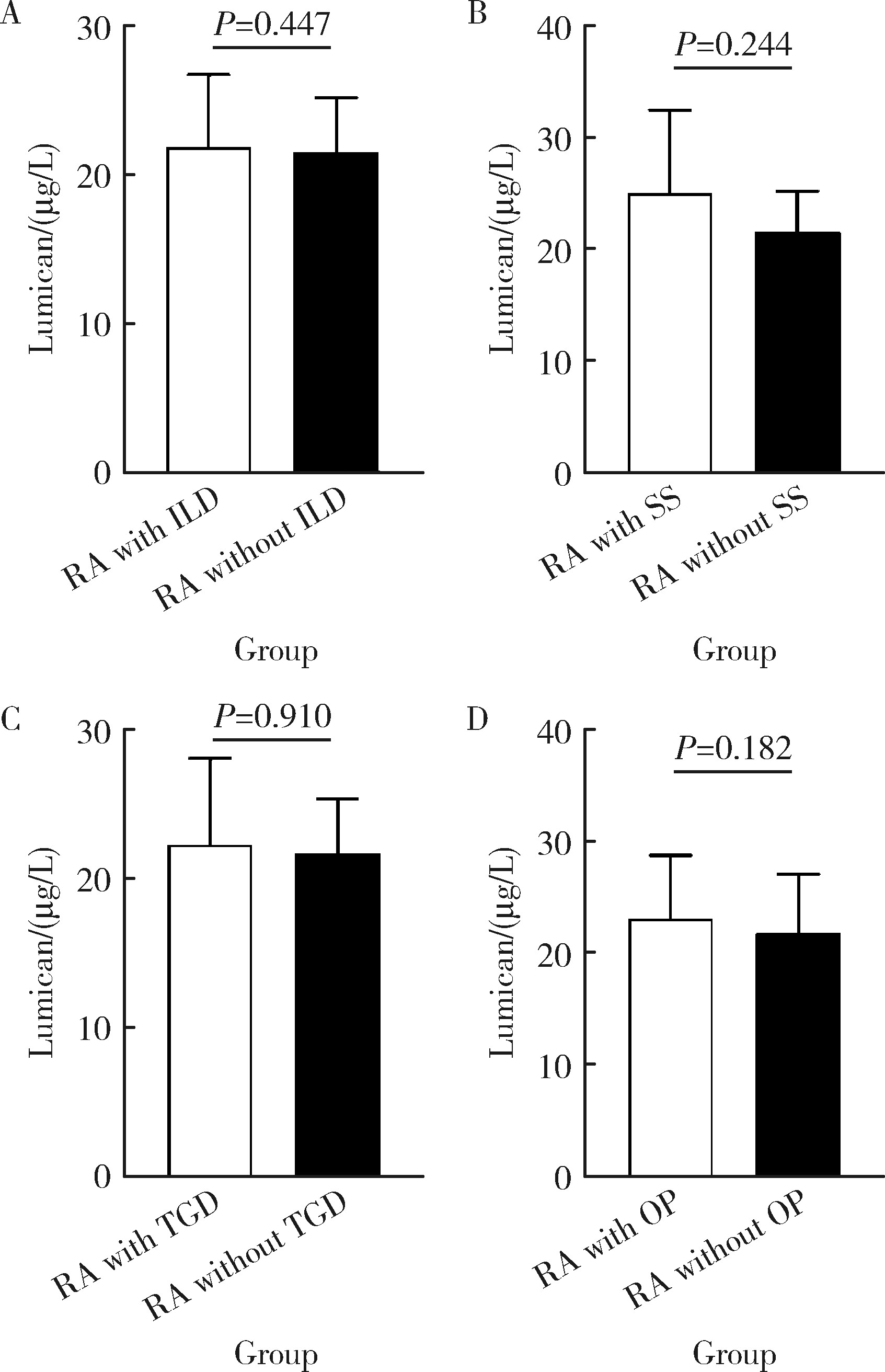
摘要: 目的: 探讨基膜聚糖(lumican, LUM)蛋白在类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis, RA)患者血清中的表达水平及其与RA疾病及免疫活动的相关性。方法: 采用酶联免疫吸附法检测RA患者和健康对照者血清LUM水平,收集患者临床及实验室资料,对比不同特征RA患者血清LUM的表达差异,分析血清LUM水平与临床及实验室指标间的相关性。数据分析分别采用独立样本t检验、Spearman相关分析、方差分析及LSD-t检验、K-W检验及Bonferroni检验、卡方检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。结果: RA患者血清LUM水平显著高于健康对照者(P<0.000 1)。LUM与红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ESR)、C反应蛋白(C-reactive protein, CRP)、类风湿因子(rheumatoid factor, RF)、免疫球蛋白A(immunoglobulin A, IgA)、血小板计数和28个关节的疾病活动度评分(28-joint disease activity score,DAS28)相关(P<0.05)。不同病程及性别的RA患者血清LUM差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),RF阳性的RA患者血清LUM显著高于RF阴性的RA患者和健康对照者(P<0.05),不同ESR、CRP水平的RA患者血清LUM水平均显著高于健康对照者(P<0.05),疾病处于缓解期的RA患者血清LUM水平显著低于疾病处于中、高度活动度的RA患者(P<0.05),RF阳性的RA患者血清LUM阳性率显著高于RF阴性的患者(P<0.05)。结论: LUM蛋白有可能成为一个反映RA疾病活动度及免疫活动度的生物标记物。
中图分类号:
- R593.22
| 1 |
doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2018.1 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.06.010 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2016.12.003 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00086.2022 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00088.2022 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1007/s12079-021-00616-4 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.1369/0022155417738752 |
| 8 |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21942 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2009.00850.x |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1002/ibd.21713 |
| 11 |
徐迈宇, 陈钢, 陈雷, 等. 肝细胞癌中Lumican的表达及意义[J]. 肝胆胰外科杂志, 2011, 23(5): 398- 399.
|
| 12 |
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00605 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.120751 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.138461 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.10.011 |
| 16 |
田新平, 李梦涛, 曾小峰. 我国类风湿关节炎诊治现状与挑战: 来自中国类风湿关节炎2019年年度报告[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2021, 60(7): 593- 598.
|
| 17 |
曾小峰, 朱松林, 谭爱春, 等. 我国类风湿关节炎疾病负担和生存质量研究的系统评价[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2013, 13(3): 300- 307.
|
| 18 |
doi: 10.1084/jem.20160792 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.10.1329 |
| 20 |
doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00239.x |
| 21 |
doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200101)44:1<41::AID-ANR6>3.0.CO;2-0 |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
doi: 10.1136/adc.2009.174367 |
| 24 |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1507387112 |
| 25 |
doi: 10.3390/ijms22094717 |
| 26 |
doi: 10.3904/kjim.2022.015 |
| [1] | 冯亮华, 洪丽荣, 陈雨佳, 蔡学明. 泛素特异性蛋白酶35对类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞铁死亡的作用及机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(5): 919-925. |
| [2] | 贾霈雯, 杨迎, 邹耀威, 欧阳志明, 林建子, 马剑达, 杨葵敏, 戴冽. 类风湿关节炎患者低肌肉量综合征的临床特征及其对躯体功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1009-1016. |
| [3] | 马豆豆, 卢哲敏, 郭倩, 朱莎, 古今, 丁艳, 石连杰. 小剂量利妥昔单抗成功治疗类风湿关节炎合并重症肌无力1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1110-1114. |
| [4] | 闫蕊, 柯丹, 张妍, 李丽, 苏焕然, 陈伟, 孙明霞, 刘晓敏, 罗靓. 血清趋化因子CXCL-10和涎液化糖链抗原6水平在类风湿关节炎合并肺间质病变患者中的诊断和病情评估价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 956-962. |
| [5] | 赵亮, 史成龙, 马柯, 赵静, 王潇, 邢晓燕, 莫万星, 练益瑞, 高超, 李玉慧. 抗合成酶综合征重叠类风湿关节炎患者的免疫学特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 972-979. |
| [6] | 韩艺钧, 陈小莉, 李常虹, 赵金霞. 甲氨蝶呤在类风湿关节炎患者中的应用现状[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 994-1000. |
| [7] | 刘东武, 陈杰, 高明利, 于静. 类风湿关节炎伴发淋巴结Castleman样病理改变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [8] | 黄会娜,赵静,赵祥格,白自然,李霞,王冠. 乳酸对类风湿关节炎患者外周血CD4+T细胞亚群的调控作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [9] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [10] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [11] | 吴琦,蔡月明,何娟,黄文蒂,王庆文. 血脂异常与类风湿关节炎肺间质病变的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [12] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 体重指数与类风湿关节炎临床特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [13] | 金银姬,孙琳,赵金霞,刘湘源. 血清IgA型抗鼠科肉瘤病毒癌基因同源物B1抗体在类风湿关节炎中的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [14] | 蔡文心,李仕成,刘一鸣,梁如玉,李静,郭建萍,胡凡磊,孙晓麟,李春,刘栩,叶华,邓立宗,李茹,栗占国. 类风湿关节炎临床分层及其特征的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [15] | 程昉,杨邵英,房星星,王璇,赵福涛. CCL28-CCR10通路在类风湿关节炎单核细胞迁移中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
|
||