北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 975-979. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.024
口腔黏膜补片与脱细胞真皮基质补片治疗长段尿道狭窄的疗效和安全性对比
冷汶远, 高端, 李晓宇, 左炜, 胡伟民, 朱振鹏, 徐纯如, 林健*( ), 李学松*(
), 李学松*( )
)
- 北京大学第一医院泌尿外科, 北京大学泌尿外科研究所, 国家泌尿男生殖系肿瘤研究中心, 北京 100034
Comparison of efficacy and safety of oral mucosa grafts and acellular dermal matrix grafts in the treatment of long-segment urethral stricture
Wenyuan LENG, Duan GAO, Xiaoyu LI, Wei ZUO, Weimin HU, Zhenpeng ZHU, Chunru XU, Jian LIN*( ), Xuesong LI*(
), Xuesong LI*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital; Institute of Urology, Peking University; National Urological Cancer Center, Beijing 100034, China
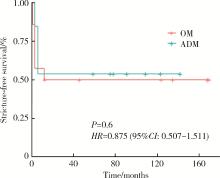
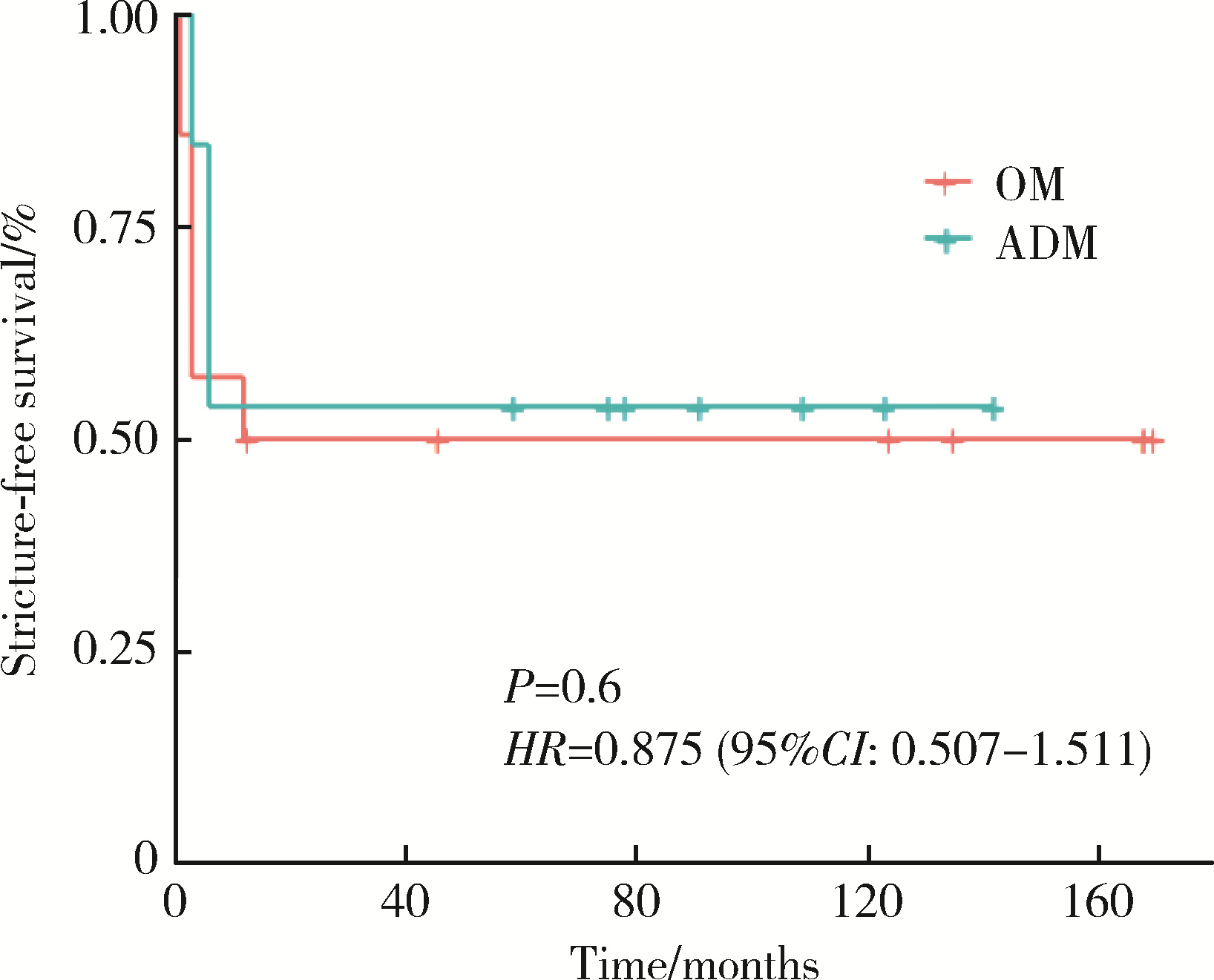
摘要: 目的: 对比口腔黏膜(oral mucosa, OM)补片和脱细胞真皮基质(acellular dermal matrix, ADM)补片治疗长段尿道狭窄的疗效和安全性的差异。方法: 回顾性收集2010年5月至2023年9月就诊于北京大学第一医院的27例因长段尿道狭窄需接受补片尿道重建术的患者资料, 其中14例患者接受OM补片修补, 13例接受ADM补片修补。按照术中使用补片材料不同, 将患者分为OM组和ADM组, 两组患者平均年龄分别为(43.3±14.0)岁、(54.2±15.9)岁, 平均体重指数分别为(24.7±4.3) kg/m2、(25.4±4.8) kg/m2。OM组主要病因为特发性尿道狭窄, ADM组主要病因为硬化性苔藓样病。结果: 所有患者的手术均顺利完成, 两组的中位狭窄长度分别为4.5 (2.5, 9.0) cm、5.0 (2.0, 14.0) cm(P=0.555), 中位手术时间分别为160 (71, 221) min、134 (112, 274) min(P=0.065), 尿管留置时间分别为1.5 (1.0, 6.0) 个月、3.0 (1.0, 3.0) 个月, 术后中位随访时间分别为12.5 (1.0, 170.0)个月、59.0 (3.0, 142.0) 个月, 手术成功率分别为50.00%、53.85%。两组患者的术后末次随访生活质量(quality of life, QoL)和国际前列腺症状评分(international prostate symptom score, IPSS)差异无统计学意义, 两组术后无狭窄生存率的差异亦无统计学意义(HR=0.875, 95%CI: 0.507~1.511, P=0.6)。安全性方面, OM组有3例患者出现性功能障碍, 2例患者出现口腔并发症; ADM组有1例患者出现术后感染。结论: ADM补片在治疗长段尿道狭窄(包括由硬化性苔藓样病引起的复杂病例)中的疗效和安全性与OM补片相当, 但受限于研究样本量较小, 上述结论可能存在一定局限性, 未来需要更大样本量的队列研究以进一步验证。
中图分类号:
- R699.6
| 1 |
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.05.022 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.07.087 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.05.023 |
| 4 |
徐月敏. 尿道狭窄的病因与治疗现状[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2011, 32 (11): 725- 727.
|
| 5 |
doi: 10.1007/s11934-018-0769-0 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121917 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.02.3102 |
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.08.014 |
| 9 |
陈彩芳, 曾铭强, 薛睿智, 等. 男性尿道狭窄病因与治疗方式[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2018, 43 (5): 520- 527.
|
| 10 |
doi: 10.21037/tau-21-1149 |
| 11 |
林健, 郝金瑞, 金杰, 等. 人同种异体真皮脱细胞基质在尿道重建中的临床应用[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2005, 85 (15): 1057- 1059.
|
| 12 |
徐月敏, 张炯, 傅强, 等. 小肠黏膜下脱细胞基质修复前尿道狭窄的疗效分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2011, 32 (6): 419- 422.
|
| 13 |
doi: 10.1007/s00345-024-04795-8 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1111/iju.14786 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.1177/2192568217701105 |
| [1] | 朱慧, 闵赛南, 苏家增, 陈艳, 彭歆, 于尧, 俞光岩. 口腔黏膜嗜酸性溃疡的临床病理分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(3): 620-625. |
| [2] | 王鹃, 邱立新, 尉华杰. 下颌磨牙穿龈形态设计对种植体周围软组织影响的随机对照临床研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 65-72. |
| [3] | 王杰, 王建伟, 夏海缀, 徐啸, 翟建坡, 何峰, 黄广林, 李贵忠. 阴茎远端尿道狭窄疾病的手术治疗方式[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1075-1082. |
| [4] | 刘振华,王建伟,黄广林,李贵忠,满立波. 尿道狭窄患者术前菌尿的病原菌分布及危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 943-947. |
| [5] | 王建伟,徐啸,鲍正清,刘振华,何峰,黄广林,满立波. 耻骨下缘部分切除辅助后尿道吻合术在男性骨盆骨折后尿道离断修复中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 798-802. |
| [6] | 周培茹, 蒋析, 华红. 口腔黏膜病患者口腔种植的时机及注意事项[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 5-8. |
| [7] | 王建伟,满立波,黄广林,何峰,王海,王海东,徐啸,李伟,翟建坡,刘振华. 口腔黏膜背侧移植结合阴茎带蒂皮瓣腹侧覆盖治疗阴茎部尿道狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 641-645. |
| [8] | 王建伟,满立波,黄广林,王海,徐啸,朱晓斐,李玮,刘振华. 经会阴三步法手术策略治疗单纯性男性骨盆骨折后尿道离断[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 617-620. |
| [9] | 王莺, Obada Barry, Gerhard Wahl, 陈波,林野. 应用激光多普勒血流仪监测口腔黏膜血流[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 697-701. |
| [10] | 谢天朋, 黄晓波, 许清泉, 叶海云, 杨庆亚, 王晓峰. B超监测下球囊扩张治疗尿道狭窄5例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(4): 657-658. |
| [11] | 黄广林, 满立波, 王海, 王建伟, 翟建坡, 朱晓斐, 周宁, 徐啸. 使用尿道旋切刀治疗女性尿道闭锁[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(4): 574-577. |
| [12] | 丁宁, 闫志敏, 华红. 实时荧光定量PCR法检测原发性Sjögren综合征口腔真菌菌群[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(1): 17-21. |
| [13] | 曹婕*, 刘宏伟, 刘晓松, 金建秋, 张平. 口腔黏膜微核细胞数与上皮异常增生病损癌变的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(4): 600-602. |
| [14] | 林野, 邱立新, 胡秀莲, 王莺, 李健慧. 硬腭游离黏膜移植在种植体周软组织结构重建中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2007, 39(1): 21-25. |
| [15] | 杨天智, 陈大兵, 张强. 不同吸收促进剂及酶抑制剂对胰岛素体内及体外口腔黏膜渗透性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2001, 33(3): 238-242. |
|
||