北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 967-974. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.023
穿颧种植体上颌窦段成骨的影像学研究
于子杨1, 郭厚佐1, 蒋析1, 韩玮华2, 林野1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院种植科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. 中国医学科学院北京协和医学院, 北京协和医院口腔科, 北京 100730
Imaging study of osteogenesis in maxillary sinus segment of zygomatic implants
Ziyang YU1, Houzuo GUO1, Xi JIANG1, Weihua HAN2, Ye LIN1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Implantology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digi-tal Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Stomatology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College & Chinese Academy of Medical Science, Beijing 100730, China
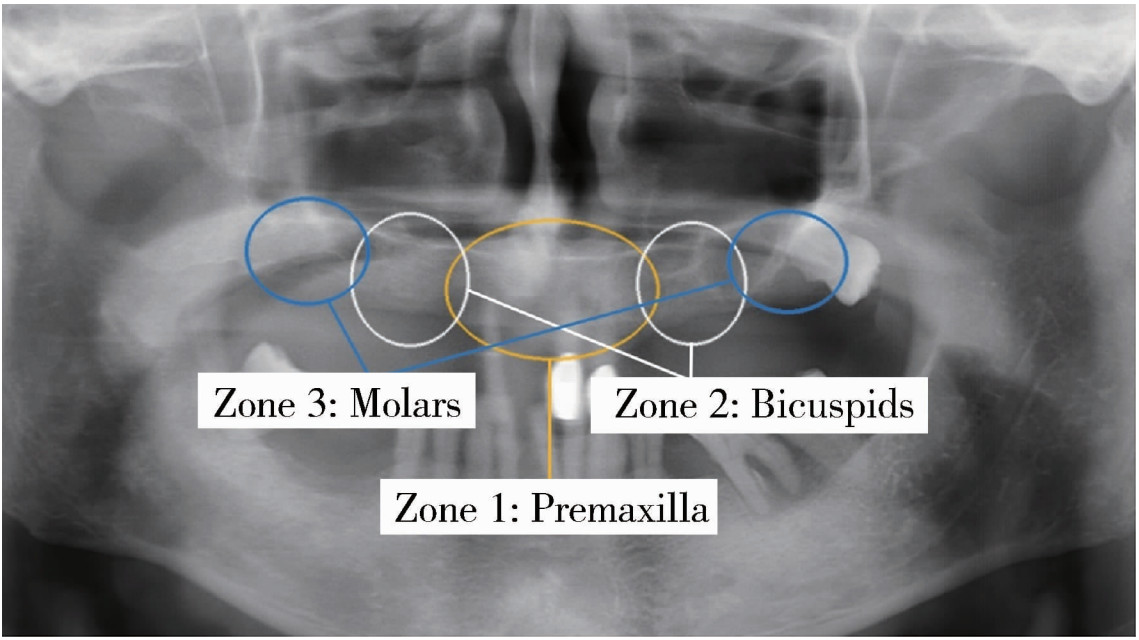
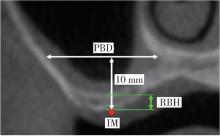
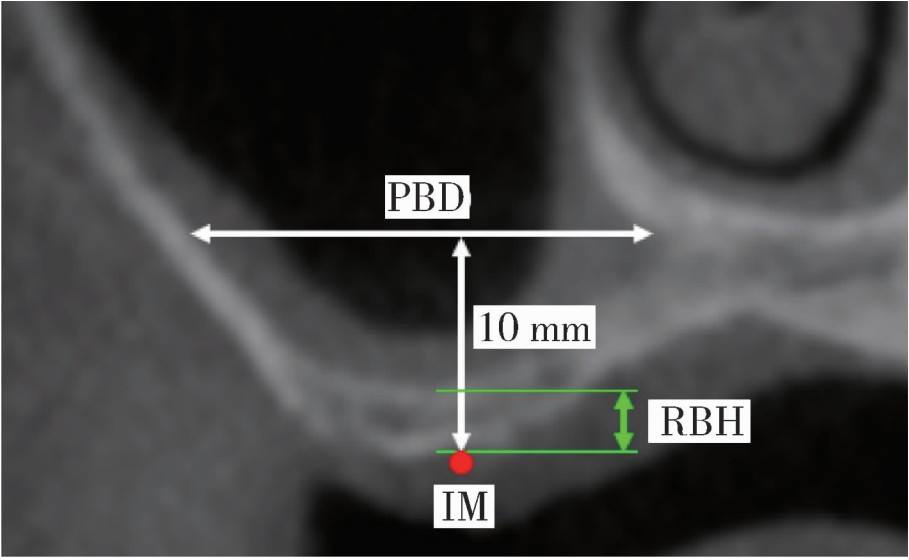
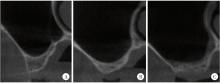
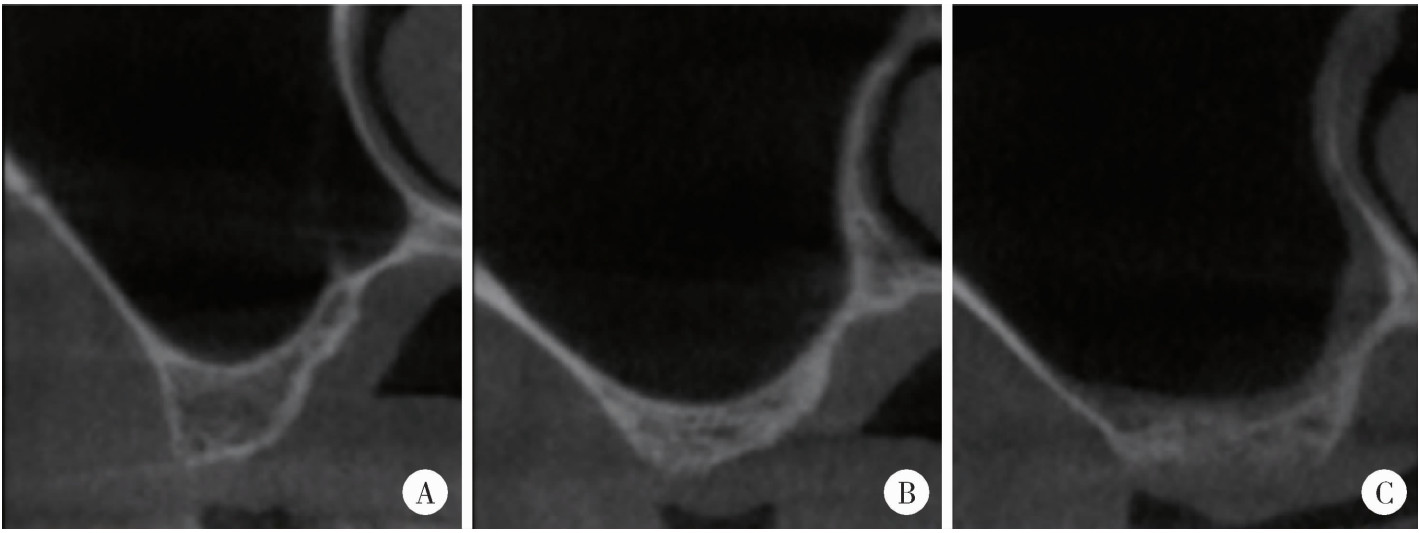
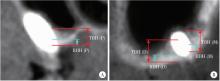
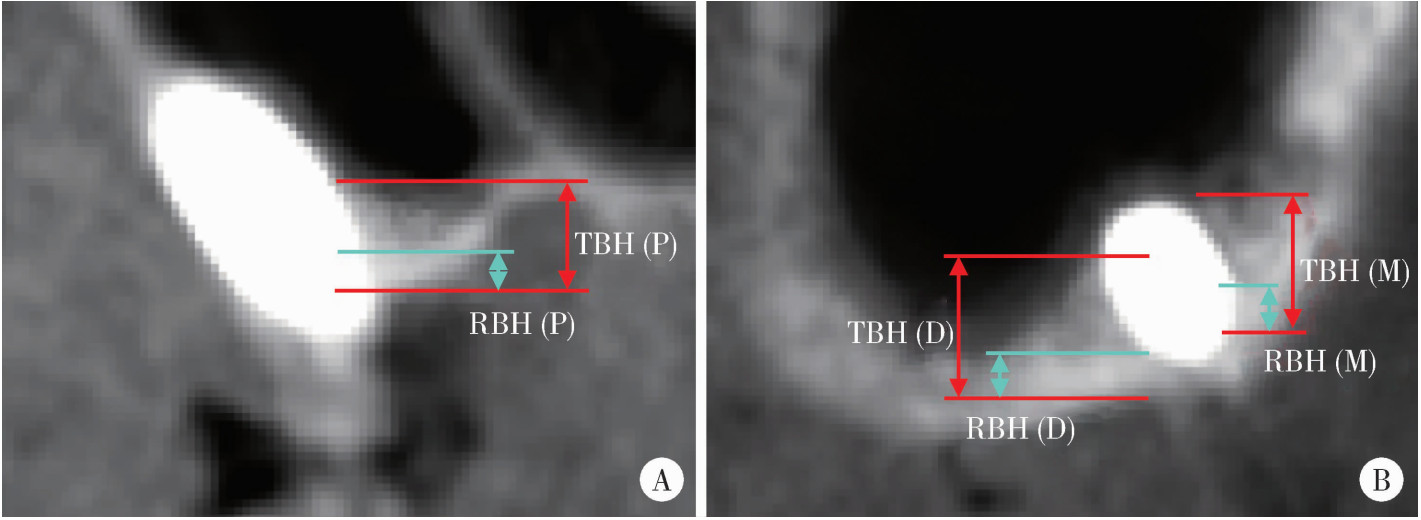
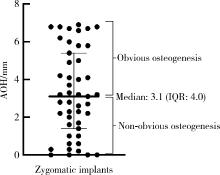
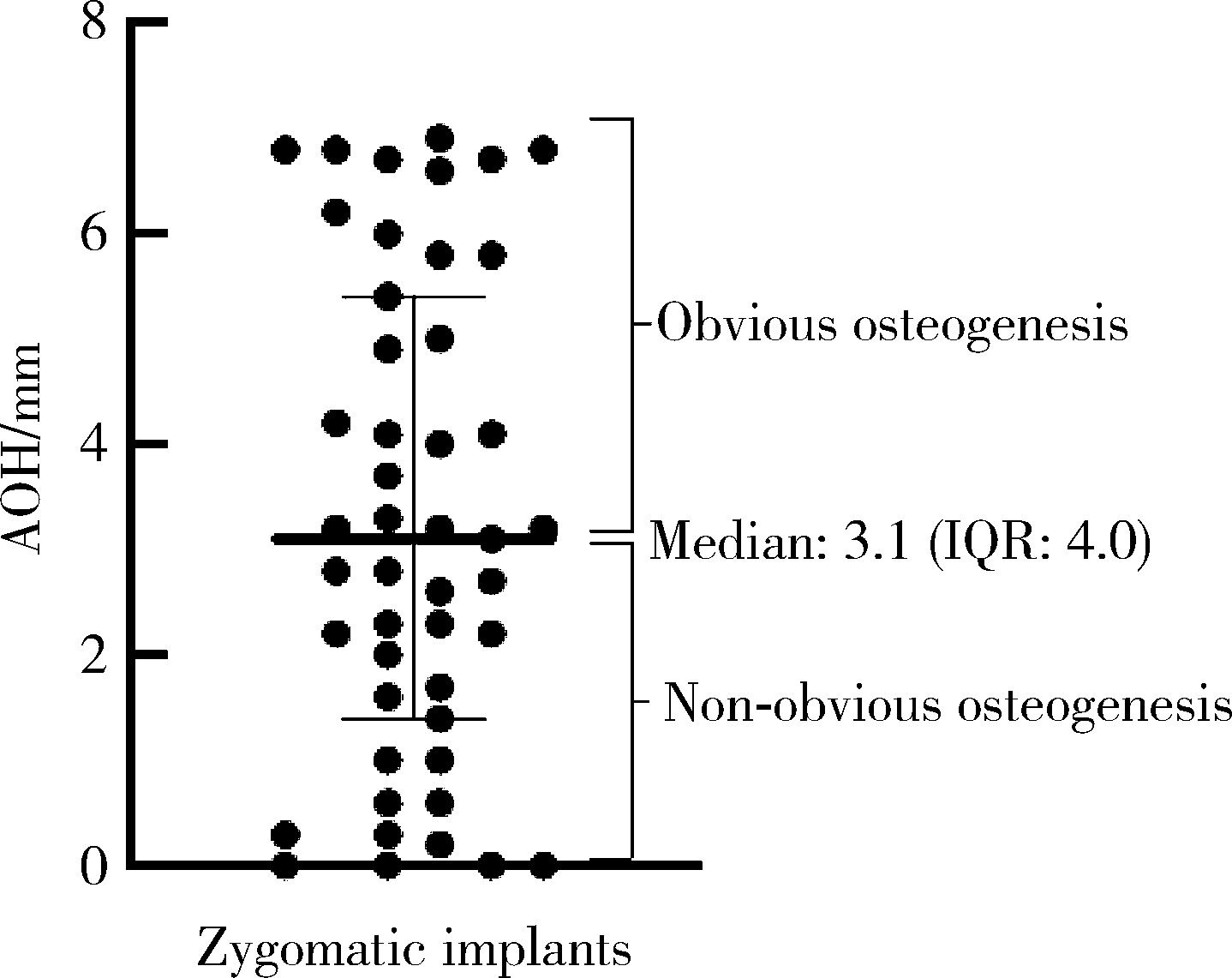
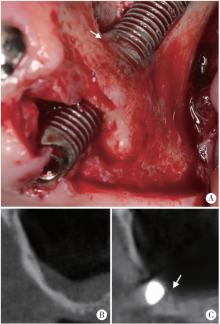
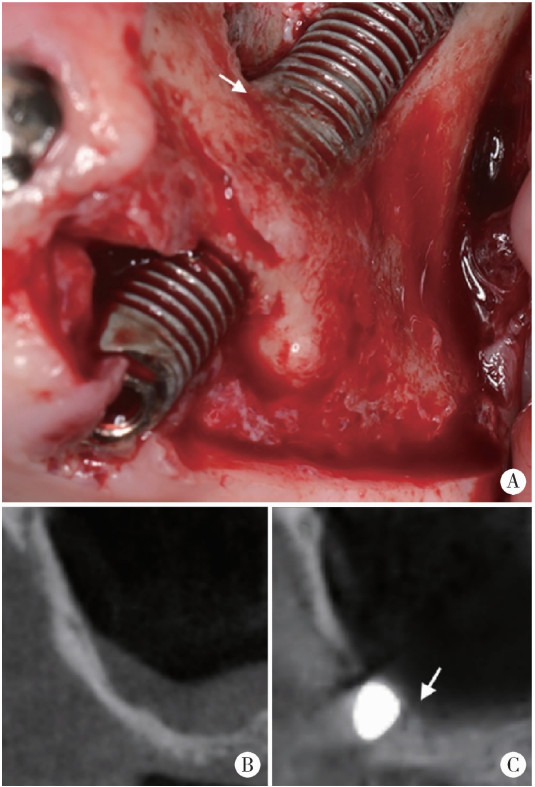
摘要: 目的: 使用影像学手段评估穿颧种植体植入1年后上颌窦段的成骨情况, 并探讨患者因素、上颌窦解剖因素和手术因素对成骨效果的影响。方法: 本研究为回顾性研究, 纳入2017年7月至2022年1月于北京大学口腔医院种植科行穿颧种植且种植体穿行上颌窦的患者, 于术前、术后即刻和术后1年拍摄锥形束CT(cone beam CT, CBCT), 测量并计算种植体在上颌窦段的平均成骨高度(average osteogenesis height, AOH), 同时记录剩余牙槽骨高度(residual bone height, RBH)、上颌窦底颊腭向宽度和形态、术中上颌窦黏膜完整性以及患者和种植体基本情况。通过对比解剖条件和手术特征, 分析不同情况下AOH的差异, 并以中位数为阈值将AOH分为两组(明显成骨、不明显成骨), 使用广义线性混合模型评估成骨情况的影响因素。结果: 纳入患者24例, 共植入47枚穿颧种植体。在平均12.1个月的随访期内未见种植体失败, 种植体存留率100%。术后CBCT显示43枚种植体的上颌窦段出现成骨影像, 新骨起自上颌窦底, AOH中位数为3.1 mm(四分位距: 4.0 mm)。上颌窦宽度方面, 纳入患者包含宽型上颌窦31例(66.0%)和窄型上颌窦16例(34.0%); 解剖形态方面, 包含锥形17例(36.2%)、卵圆形20例(42.6%)、方形10例(21.3%)。术前RBH中位数为2.8 mm(四分位距: 2.2 mm)。广义线性混合模型单因素分析显示, 明显成骨率与RBH(OR=2.09, P=0.006)有关, 多因素分析显示RBH(OR=2.55, P=0.022)和锥形上颌窦形态(OR=11.44, P=0.040)与术后明显成骨率有统计学相关性。结论: 穿颧种植体植入1年后上颌窦底有成骨影像, 较大的RBH和锥形上颌窦形态可能是成骨的有利因素。
中图分类号:
- R782.12
| 1 |
Tavelli C, Tedesco A. Survival and complication rate of zygomatic implants: A systematic review[J/OL]. J Oral Implantol (2022-12-06) [2023-01-24]. doi: 10.1563/aaid-joi-D-22-00008.
|
| 2 |
doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.1995.060405.x |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.14027 |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
周国辉. 穿颧骨植体在无牙上颌的应用[J]. 中国口腔种植学杂志, 2009, 14 (2): 28- 29.
|
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2012.12.006 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2015.01.009 |
| 10 |
林柏均, 吕鸣樾, 袁泉. 影响经牙槽嵴顶上颌窦底提升术成骨效果的解剖因素分析[J]. 口腔医学, 2022, 42 (3): 193- 199.
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2007.06.687 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.11607/jomi.7488 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.090686 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.02034.x |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.12477 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.1111/cid.12606 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.13891 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2021.03.016 |
| 20 |
doi: 10.1007/s00784-020-03432-z |
| 21 |
doi: 10.1111/jre.12402 |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
doi: 10.1111/cid.12218 |
| 25 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2007.01372.x |
| 26 |
林野. 上颌窦植骨与种植[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2020: 205.
|
| 27 |
doi: 10.1097/ID.0000000000000554 |
| 28 |
doi: 10.1111/cid.12298 |
| 29 |
郑小菲, 莫安春, 朱娟芳, 等. 上颌窦解剖因素对经牙槽嵴顶上颌窦底提升术成骨效果的影响[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38 (6): 652- 656.
|
| [1] | 王宇蓝, 曾浩, 张玉峰. 口腔种植中血浆基质的临床转化现状与前沿探索[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(5): 836-840. |
| [2] | 王鹃, 邱立新, 尉华杰. 下颌磨牙穿龈形态设计对种植体周围软组织影响的随机对照临床研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 65-72. |
| [3] | 王聪伟,高敏,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损术后义齿修复的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [4] | 丁茜,李文锦,孙丰博,谷景华,林元华,张磊. 表面处理对氧化钇和氧化镁稳定的氧化锆种植体晶相及断裂强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 721-728. |
| [5] | 孙菲,刘建,李思琪,危伊萍,胡文杰,王翠. 种植体黏膜下微生物在健康种植体和种植体周炎中的构成与差异:一项横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 30-37. |
| [6] | 蓝璘,贺洋,安金刚,张益. 颧骨缺损不同修复重建方法和预后的回顾性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 356-362. |
| [7] | 杜文瑜,杨静文,姜婷. 甲磺酸去铁胺促进大鼠颅骨临界骨缺损血管化骨再生的早期连续观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1171-1177. |
| [8] | 梁峰,吴敏节,邹立东. 后牙区单牙种植修复5年后的临床修复疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 970-976. |
| [9] | 张胜男,安娜,欧阳翔英,刘颖君,王雪奎. 生长停滞特异性蛋白6在人牙周膜细胞迁移及成骨分化中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 9-15. |
| [10] | 释栋,曹婕,戴世爱,孟焕新. 植体周炎再生治疗短期疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 58-63. |
| [11] | 林春平,卢松鹤,朱浚鑫,胡洪成,岳兆国,唐志辉. 个性化根形种植体的螺纹形态对周围牙槽骨应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1130-1137. |
| [12] | 王倩,李丹,唐志辉. 上颌窦底内提升术同期种植窦内成骨的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 925-930. |
| [13] | 刘潇倩,陈秋雯,冯海兰,王兵,屈健,孙振,衡墨迪,潘韶霞. 无牙颌患者locator附着体种植覆盖义齿修复后口腔卫生维护的纵向研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 136-144. |
| [14] | 隋华欣,吕培军,王勇,冯驭驰. 低能量激光照射对人脂肪来源干细胞/海藻酸钠/明胶三维生物打印体成骨能力的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 868-875. |
| [15] | 吴敏节,邹立东,梁峰. 上前牙即刻种植即刻修复负载3年后软、硬组织变化的临床观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 694-699. |
|
||