北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 925-930. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.05.022
上颌窦底内提升术同期种植窦内成骨的临床效果
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,牙周科 国家口腔疾病临床研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程试验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,第二门诊部 国家口腔疾病临床研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程试验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Sinus floor elevation and simultaneous dental implantation: A long term retrospective study of sinus bone gain
Qian WANG1,Dan LI2,Zhi-hui TANG2,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Periodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Second Clinical Division, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
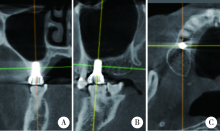
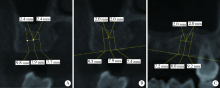
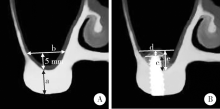
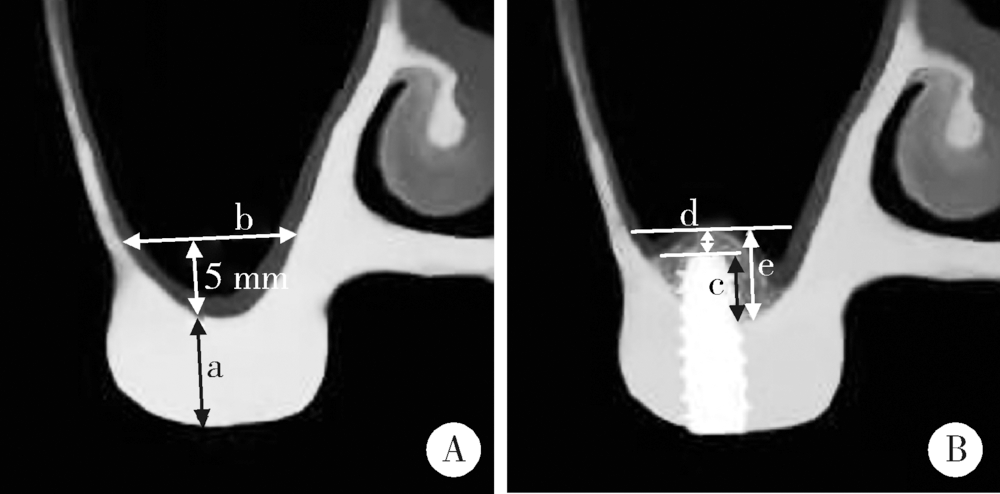
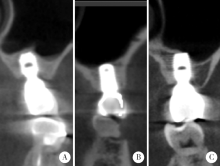
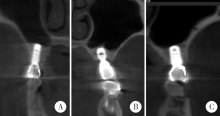
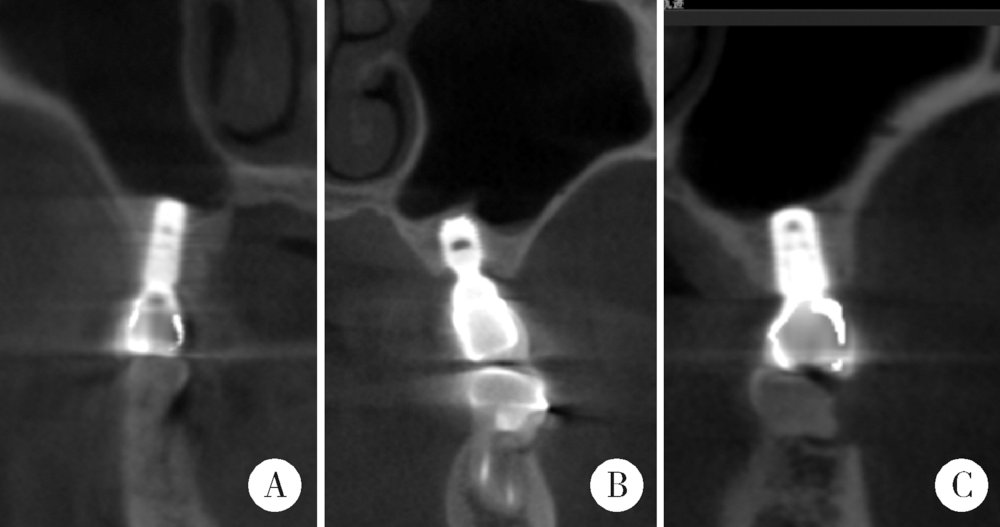
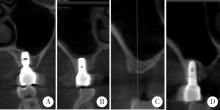
目的:回顾性评价上颌窦底内提升术在植骨与不植骨的情况下同期植入种植体后上颌窦内成骨的效果。方法:共纳入上颌后牙区缺牙的患者26例,根据术式不同分为上颌窦底内提升+植骨组(A组)和上颌窦底内提升+不植骨组(B组), 同期进行种植,术后30~50个月常规复查随访,观察上颌窦内成骨情况。结果:共植入了27枚种植体(其中A组13枚,B组14枚), 随访时间为40.23(36.20,48.07)个月。A组上颌窦底剩余骨高度(residual bone height, RBH)为(6.64±1.21) mm,B组RBH为(6.96±1.36) mm,二者差异没有统计学意义(P = 0.459)。A组随访时上颌窦内成骨高度(sinus bone gain, SBG)为(2.20±1.71) mm,B组随访时SBG为1.77(0.94, 2.05) mm,二者差异没有统计学意义(P = 0.583)。根据随访时种植体尖端附近成骨情况将种植体尖端成骨分为3类,分别为优、良和中。随访时A组有9枚种植体尖端成骨质量为优和良,B组有8枚种植体尖端成骨质量为优和良,二者差异没有统计学意义((Fisher精确检验,P = 0.695)。A组种植体尖端位于新上颌窦底下方(0.09±1.32) mm,B组种植体尖端位于新上颌窦底下方(0.03±0.91) mm,二者差异没有统计学意义(P = 0.898)。随访时两组总体的SBG为1.85(1.10, 2.20) mm,将两组随访时的SBG分别与多个因素进行相关分析,发现其仅与种植体尖端突出于上颌窦底的高度显著相关(r=0.383, P = 0.049)。结论:上颌窦底内提升术在植骨与不植骨的情况下都能取得较好的效果,SBG主要与种植体尖端提升的高度显著相关。
中图分类号:
- R782.1
| [1] | 耿建平 . 上颌窦种植外科学[M]. 江苏: 江苏科学技术出版社, 2010: 1-2. |
| [2] | Boyne PJ, James RA . Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone[J]. J Oral Surg, 1980,38(8):613-616. |
| [3] | Tatum H . Maxillary and sinus implant reconstructions[J]. Dent Clin North Am, 1986,30(2):207-229. |
| [4] | Summers RB . A new concept in maxillary implant surgery: the osteotome technique[J]. Compendium, 1994,15(2):152-162. |
| [5] | 范倩倩, 柳忠豪 . 上颌窦黏膜具有成骨潜能的研究进展[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2014,30(5):475-478. |
| [6] | Srouji S, Ben-David D, Lotan R , et al. The innate osteogenic potential of the maxillary sinus (Schneiderian) membrane: an ecto-pic tissue transplant model simulating sinus lifting[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2010,39(8):793-801. |
| [7] | Lai HC, Zhuang LF, Lv XF , et al. Osteotome sinus floor elevation with or without grafting: a preliminary clinical trial[J]. Clin Oral Impl Res, 2010,21(5):520-526. |
| [8] | Zheng X, Teng M, Zhou F , et al. Influence of maxillary sinus width on transcrestal sinus augmentation outcomes: radiographic evaluation based on cone beam CT[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2016,18(2):292-300. |
| [9] | Nunes LS, Bornstein MM, Sendi P , et al. Anatomical characteristics and dimensions of edentulous sites in the posterior maxillae of patients referred for implant therapy[J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 2013,33(3):337-345. |
| [10] | 山道信之, 系濑正通 . 上颌窦底提升术:依据锥形束牙科CT影像诊断的高成功率植牙手术[M]. 张怡泓, 译.北京: 人民军医出版社, 2012: 6-7. |
| [11] | Brizuela A, Martín N, Fernández-Gonzalez FJ , et al. Osteotome sinus floor elevation without grafting material: results of a 2-year prospective study[J]. J Clin Exp Dent, 2014,6(5):e479-e484. |
| [12] | Jeong SM, Choi BH, Li J , et al. A retrospective study of the effects of sinus membrane elevation on bone formation around implants placed in the maxillary sinus cavity[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2009,107(3):364-368. |
| [13] | Nedir R, Nurdin N, Abi Najm S , et al. Short implants placed with or without grafting into atrophic sinuses: the 5-year results of a prospective randomized controlled study[J]. Clin Oral Impl Res, 2017,28(7):877-886. |
| [14] | Si MS, Shou YW, Shi YT , et al. Long-term outcomes of osteotome sinus floor elevation without bone grafts: a clinical retrospective study of 4-9 years[J]. Clin Oral Impl Res, 2016,27(11):1392-1400. |
| [15] | Spinelli D, DE Vico G, Condò R , et al. Transcrestal guided sinus lift without grafting materials: a 36 months clinical prospective study[J]. Oral Implantol (Rome), 2016,8(2/3):74-86. |
| [16] | Viña-Almunia J, Maestre-Ferrín L, Alegre-Domingo T , et al. Survival of implants placed with the osteotome technique: an update[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2012,17(5):e765-e768. |
| [17] | Rammelsberg P, Mahabadi J, Eiffler C , et al. Radiographic monitoring of changes in bone height after implant placement in combination with an internal sinus lift without graft material[J]. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research, 2015,17(1):e267-e274. |
| [18] | 林国芬, 谭包生, 单志钢 , 等. 冲压式上颌窦底提升术同期种植临床分析[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2012,10(3):231-235. |
| [19] | Borges FL, Dias R, Piattelli A , et al. Simultaneous sinus membrane elevation and dental implant placement without bone graft: a 6-month follow-up study[J]. J Periodontol, 2011,82(3):403-412. |
| [20] | Nedir R, Bischof M, Vazquez L , et al. Osteotome sinus floor elevation without grafting material: a 1-year prospective pilot study with ITI implants[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2006,17(6):679-686. |
| [21] | Zill A, Precht C, Beck-Broichsitter B , et al. Implants inserted with graftless osteotome sinus floor elevation: a 5-year post-loading retrospective study[J]. Eur J Oral Implantol, 2016,9(3):277-289. |
| [22] | Chen HH, Lin YC, Lee SY , et al. Influence of sinus floor configuration on grafted bone remodeling after osteotome sinus floor elevation[J]. J Periodontol, 2017,88(1):10-16. |
| [23] | Qin L, Lin SX, Guo ZZ , et al. Influences of schneiderian membrane conditions on the early outcomes of osteotome sinus floor elevation technique: a prospective cohort study in the healing period[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2017,28(9):1074-1081. |
| [24] | Proussaefs P, Lozada J, Kim J , et al. Repair of the perforated sinus membrane with a resorbable collagen membrane: a human study[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2004,19(3):413-420. |
| [1] | 王聪伟,高敏,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损术后义齿修复的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [2] | 丁茜,李文锦,孙丰博,谷景华,林元华,张磊. 表面处理对氧化钇和氧化镁稳定的氧化锆种植体晶相及断裂强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 721-728. |
| [3] | 孟令玮,李雪,高胜寒,李悦,曹瑞涛,张毅,潘韶霞. 三种方法建立大鼠种植体周炎模型的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 22-29. |
| [4] | 孙菲,刘建,李思琪,危伊萍,胡文杰,王翠. 种植体黏膜下微生物在健康种植体和种植体周炎中的构成与差异:一项横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 30-37. |
| [5] | 梁炜,汤瑶,黄文斌,韩冰,林久祥. 上磨牙颊侧微种植体支抗在安氏Ⅱ类正畸减数拔牙患者垂直向控制中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 340-345. |
| [6] | 孙菲,李思琪,危伊萍,钟金晟,王翠,胡文杰. 种植体周病非手术治疗中联合应用甘氨酸粉喷砂的临床效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 119-125. |
| [7] | 李熠,尉华杰,邱立新. 种植体折裂的临床分型与临床治疗方案[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 126-133. |
| [8] | 梁峰,吴敏节,邹立东. 后牙区单牙种植修复5年后的临床修复疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 970-976. |
| [9] | 岳兆国,张海东,杨静文,侯建霞. 数字化评估CAD/CAM个性化基台与成品基台影响粘接剂残留的体外研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 69-75. |
| [10] | 张众,孟焕新,韩劼,张立,释栋. 软组织垂直厚度对牙周炎患者种植修复临床效果的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 332-338. |
| [11] | 释栋,曹婕,戴世爱,孟焕新. 植体周炎再生治疗短期疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 58-63. |
| [12] | 林春平,卢松鹤,朱浚鑫,胡洪成,岳兆国,唐志辉. 个性化根形种植体的螺纹形态对周围牙槽骨应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1130-1137. |
| [13] | 刘潇倩,陈秋雯,冯海兰,王兵,屈健,孙振,衡墨迪,潘韶霞. 无牙颌患者locator附着体种植覆盖义齿修复后口腔卫生维护的纵向研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 136-144. |
| [14] | 张智勇,孟甜,陈全,刘文曙,陈宇寰. 种植体早期失败病例回顾性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1088-1091. |
| [15] | 吴敏节,邹立东,梁峰. 上前牙即刻种植即刻修复负载3年后软、硬组织变化的临床观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 694-699. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 903
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 1317
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||