北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 721-728. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.04.025
表面处理对氧化钇和氧化镁稳定的氧化锆种植体晶相及断裂强度的影响
丁茜1,李文锦1,孙丰博2,谷景华3,林元华2,张磊1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院修复科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. 清华大学材料学院, 北京 100084
3. 北京航空航天大学材料科学与工程学院, 北京 100191
Effects of surface treatment on the phase and fracture strength of yttria- and magnesia-stabilized zirconia implants
Qian DING1,Wen-jin LI1,Feng-bo SUN2,Jing-hua GU3,Yuan-hua LIN2,Lei ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Proshodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
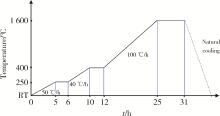
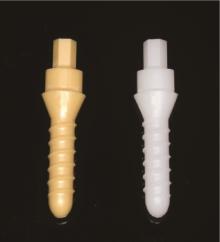
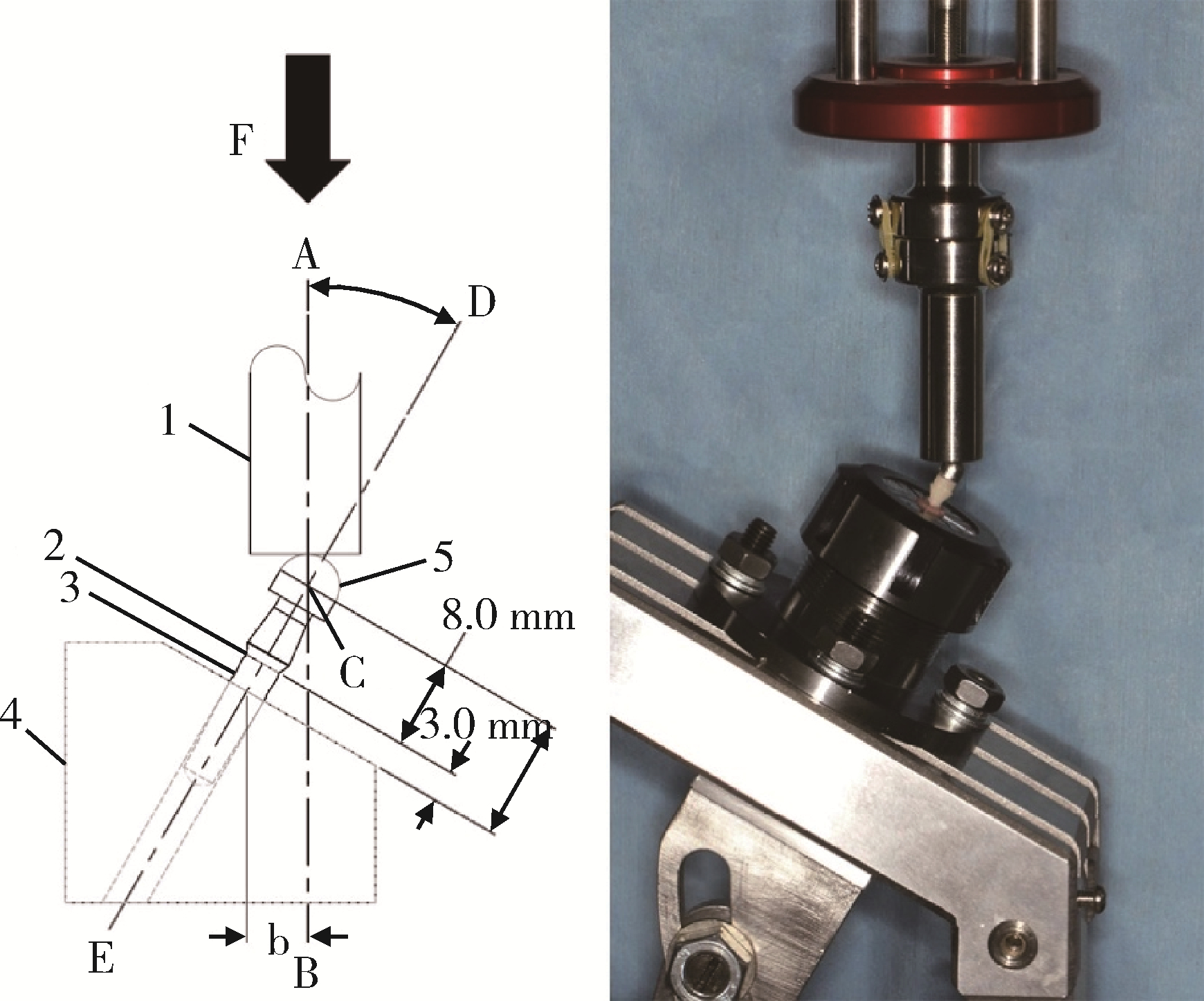
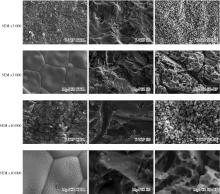
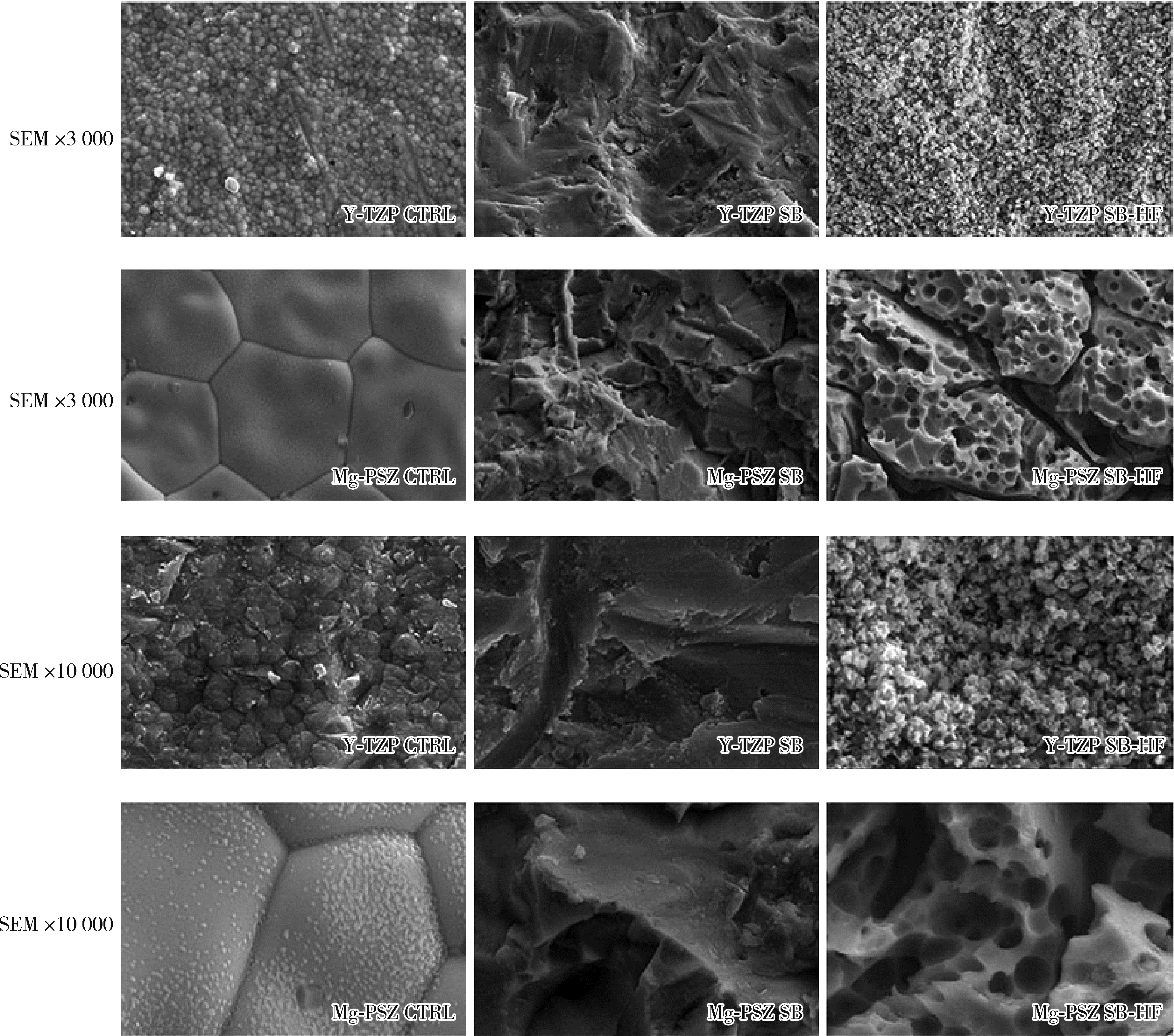
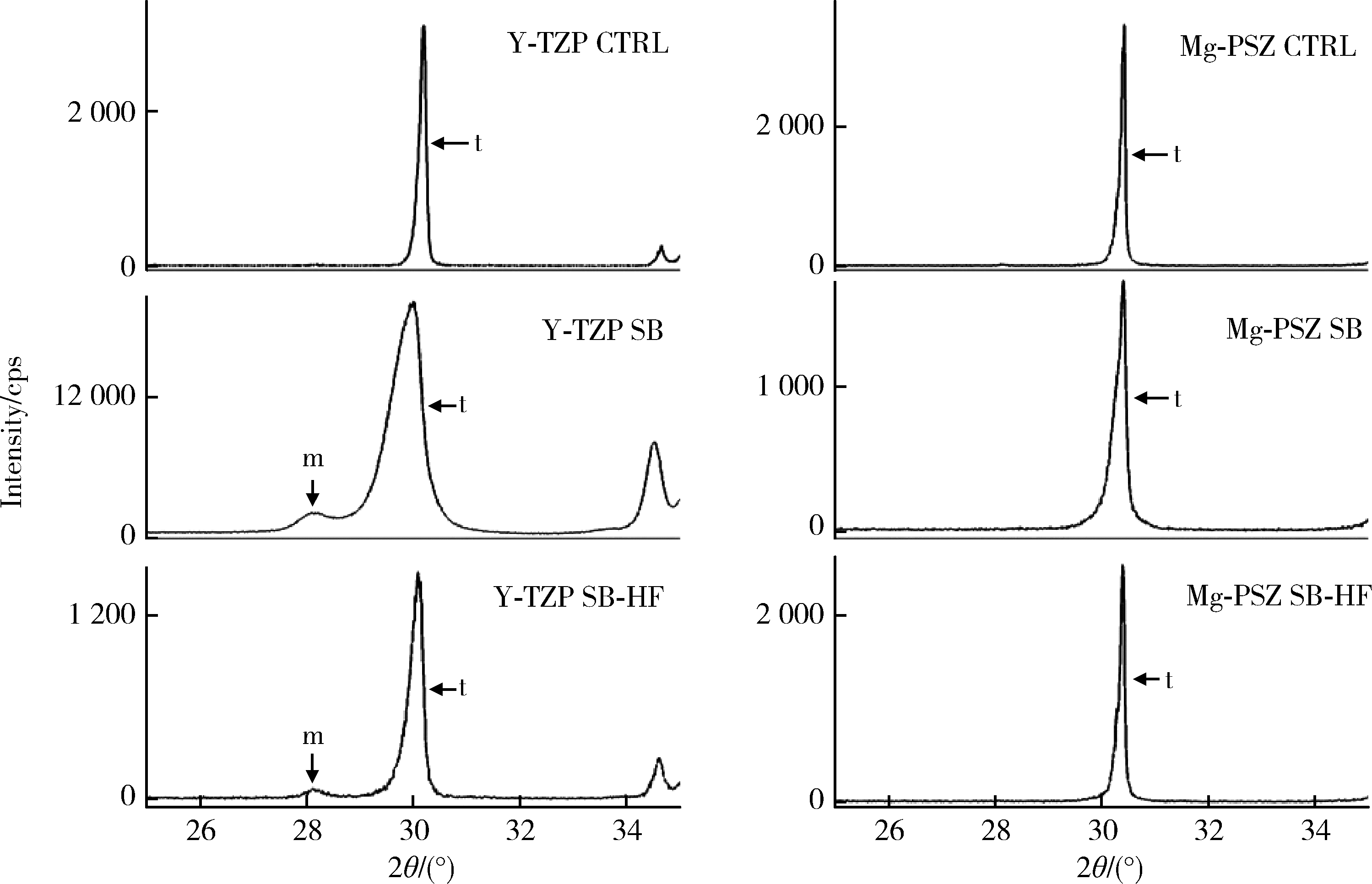
目的: 探索喷砂、喷砂加酸蚀对氧化钇和氧化镁稳定的氧化锆种植体表面晶相和断裂强度的影响。方法: 通过计算机辅助设计(computer aided design, CAD)/计算机辅助制造(computer aided manufacture, CAM)技术, 以氧化钇稳定的多晶四方相氧化锆(yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal, Y-TZP)和氧化镁稳定的氧化锆(magnesia partially stabilized zirconia, Mg-PSZ)两种材料加工标准试件及种植体, 分为不处理组(对照组)、喷砂组和喷砂加酸蚀组3组, 观察表面显微形貌并计算表面粗糙度。采用X射线衍射仪进行物相分析, 通过静力试验获得各组种植体的断裂强度。结果: 喷砂、喷砂加酸蚀处理显著增加了Y-TZP和Mg-PSZ两种种植体的表面粗糙度[轮廓算术平均偏差(Ra)值](P < 0.01)。物相分析结果显示, 表面喷砂和喷砂加酸蚀处理未对Mg-PSZ试件表面的晶相组成造成显著影响, 但导致了Y-TZP试件的单斜相百分数明显升高。喷砂、喷砂加酸蚀处理的Mg-PSZ种植体断裂强度分别为(294.1±3.3) N和(331.3±26.4) N, 与对照组[(458.4±48.7) N]相比均显著下降(P < 0.01)。Y-TZP种植体对照组的断裂强度为(827.3±101.6) N, 喷砂处理后断裂强度为(1 162.9±116.5) N, 与对照组相比显著升高(P=0.03), 喷砂加酸蚀处理后为(867.2±171.0) N, 与对照组相比差异无统计学意义(P>0.99)。结论: 表面喷砂能够提高Y-TZP种植体的断裂强度, 而表面喷砂和喷砂加酸蚀处理均会降低本研究中制备的Mg-PSZ种植体的断裂强度。
中图分类号:
- R783.1
| 1 |
Elnayef B , Lazaro A , Suarez-Lopez DAF , et al. Zirconia implants as an alternative to titanium: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2017, 32 (3): e125- e134.
doi: 10.11607/jomi.5223 |
| 2 |
Roehling S , Astasov-Frauenhoffer M , Hauser-Gerspach I , et al. In vitro biofilm formation on titanium and zirconia implant surfaces[J]. J Periodontol, 2017, 88 (3): 298- 307.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2016.160245 |
| 3 |
Kubasiewicz-Ross P , Hadzik J , Dominiak M . Osseointegration of zirconia implants with 3 varying surface textures and a titanium implant: A histological and micro-CT study[J]. Adv Clin Exp Med, 2018, 27 (9): 1173- 1179.
doi: 10.17219/acem/69246 |
| 4 |
Hanawa T . Zirconia versus titanium in dentistry: A review[J]. Dent Mater J, 2020, 39 (1): 24- 36.
doi: 10.4012/dmj.2019-172 |
| 5 |
Denry I , Kelly JR . State of the art of zirconia for dental applications[J]. Dent Mater, 2008, 24 (3): 299- 307.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2007.05.007 |
| 6 | Toraya H , Yoshimura M , Somiya S . Calibration curve for quantitative analysis of the monoclinic-tetragonal ZrO2 system by X-ray diffraction[J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 1984, 67 (6): 119- 121. |
| 7 | Wennerberg A , Albrektsson T . Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: A systematic review[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2009, 20 (Suppl 4): 172- 184. |
| 8 | Albrektsson T , Wennerberg A . On osseointegration in relation to implant surfaces[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2019, 21 (Suppl 1): 4- 7. |
| 9 |
Pieralli S , Kohal RJ , Lopez HE , et al. Osseointegration of zirconia dental implants in animal investigations: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Dent Mater, 2018, 34 (2): 171- 182.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2017.10.008 |
| 10 |
Soon G , Pingguan-Murphy B , Akbar SA . Modulation of osteoblast behavior on nanopatterned yttria-stabilized zirconia surfaces[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2017, 68, 26- 31.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.01.028 |
| 11 |
Casucci A , Osorio E , Osorio R , et al. Influence of different surface treatments on surface zirconia frameworks[J]. J Dent, 2009, 37 (11): 891- 897.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2009.06.013 |
| 12 |
Smielak B , Klimek L . Effect of hydrofluoric acid concentration and etching duration on select surface roughness parameters for zirconia[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2015, 113 (6): 596- 602.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2015.01.001 |
| 13 | Bergemann C , Duske K , Nebe JB , et al. Microstructured zirconia surfaces modulate osteogenic marker genes in human primary osteoblasts[J]. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 2015, 26 (1): 5350. |
| 14 |
Flamant Q , Marro FG , Rovira J , et al. Hydrofluoric acid etching of dental zirconia. Part 1: Etching mechanism and surface characterization[J]. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2016, 36 (1): 121- 134.
doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.09.021 |
| 15 |
Furuya K , Takemoto S , Yamashita S , et al. Low-temperature degradation of high-strength Y-TZP (yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal)[J]. Dent Mater J, 2020, 39 (4): 577- 586.
doi: 10.4012/dmj.2019-090 |
| 16 | 王晓春, 张希艳. 材料现代分析与测试技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2009: 82. |
| 17 | Warren BE . X-Ray Diffraction[M]. New York: Dover Publications Inc., 1990: 251- 254. |
| 18 | Roy ME , Whiteside LA , Katerberg BJ , et al. Phase transformation, roughness, and microhardness of artificially aged yttria- and magnesia-stabilized zirconia femoral heads[J]. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2007, 83 (4): 1096- 1102. |
| 19 |
Zucuni CP , Dapieve KS , Rippe MP , et al. Influence of finishing/polishing on the fatigue strength, surface topography, and roughness of an yttrium-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystals subjected to grinding[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2019, 93, 222- 229.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.02.013 |
| 20 |
Amaral M , Cesar PF , Bottino MA , et al. Fatigue behavior of Y-TZP ceramic after surface treatments[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2016, 57, 149- 156.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2015.11.042 |
| 21 |
Aurelio IL , Marchionatti AM , Montagner AF , et al. Does air particle abrasion affect the flexural strength and phase transformation of Y-TZP? A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Dent Mater, 2016, 32 (6): 827- 845.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2016.03.021 |
| 22 | Karakoca S , Yilmaz H . Influence of surface treatments on surface roughness, phase transformation, and biaxial flexural strength of Y-TZP ceramics[J]. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater, 2009, 91 (2): 930- 937. |
| 23 |
Egilmez F , Ergun G , Cekic-Nagas I , et al. Factors affecting the mechanical behavior of Y-TZP[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2014, 37, 78- 87.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2014.05.013 |
| 24 |
Sanon C , Chevalier J , Douillard T , et al. A new testing protocol for zirconia dental implants[J]. Dent Mater, 2015, 31 (1): 15- 25.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2014.09.002 |
| 25 |
Ding Q , Zhang L , Bao R , et al. Effects of different surface treatments on the cyclic fatigue strength of one-piece CAD/CAM zirconia implants[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2018, 84, 249- 257.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.05.002 |
| 26 |
Sanon C , Chevalier J , Douillard T , et al. Low temperature degradation and reliability of one-piece ceramic oral implants with a porous surface[J]. Dent Mater, 2013, 29 (4): 389- 397.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2013.01.007 |
| 27 | 牛月月, 王春燕, 舒静媛, 等. 氧化锆基纳米羟基磷灰石功能梯度材料的制备及力学检测[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24 (10): 1528- 1533. |
| 28 |
Bermúdez-Reyes B , Del Refugio Lara-Banda M , Reyes-Zarate E , et al. Effect on growth and osteoblast mineralization of hydroxyapatite-zirconia (HA-ZrO2) obtained by a new low temperature system[J]. Biomed Mater, 2018, 13 (3): 035001.
doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/aaa3a4 |
| [1] | 王聪伟,高敏,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损术后义齿修复的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [2] | 孙菲,刘建,李思琪,危伊萍,胡文杰,王翠. 种植体黏膜下微生物在健康种植体和种植体周炎中的构成与差异:一项横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 30-37. |
| [3] | 李伟伟,陈虎,王勇,孙玉春. 氧化锆陶瓷表面硅锂喷涂层的摩擦磨损性能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 94-100. |
| [4] | 王铮,丁茜,高远,马全诠,张磊,葛兮源,孙玉春,谢秋菲. 氧化锆多孔表面显微形貌对成骨细胞增殖及分化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 31-39. |
| [5] | 梁峰,吴敏节,邹立东. 后牙区单牙种植修复5年后的临床修复疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 970-976. |
| [6] | 李文锦,丁茜,原福松,孙丰博,郑剑桥,鲍蕊,张磊. 飞秒激光表面处理对氧化锆表面特征及弯曲强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 770-775. |
| [7] | 杨欣,李榕,叶红强,陈虎,王勇,周永胜,孙玉春. 不同刃状边缘补偿角度的两种氧化锆全瓷冠断裂强度的评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 402-405. |
| [8] | 释栋,曹婕,戴世爱,孟焕新. 植体周炎再生治疗短期疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 58-63. |
| [9] | 林春平,卢松鹤,朱浚鑫,胡洪成,岳兆国,唐志辉. 个性化根形种植体的螺纹形态对周围牙槽骨应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1130-1137. |
| [10] | 郑苗,詹凌璐,刘志强,李和平,谭建国. 不同等离子体处理氧化锆对人牙龈成纤维细胞黏附能力的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 315-320. |
| [11] | 刘潇倩,陈秋雯,冯海兰,王兵,屈健,孙振,衡墨迪,潘韶霞. 无牙颌患者locator附着体种植覆盖义齿修复后口腔卫生维护的纵向研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 136-144. |
| [12] | 周团锋,王新知. 计算机辅助设计与制作的一体化氧化锆全瓷桩核5年临床观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 680-684. |
| [13] | 吴敏节,邹立东,梁峰. 上前牙即刻种植即刻修复负载3年后软、硬组织变化的临床观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 694-699. |
| [14] | 焦洋, 王继德, 邓久鹏. 不同表面处理对氧化锆晶相结构及性能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 49-52. |
| [15] | 廖宇,刘晓强,陈立,周建锋,谭建国. 不同表面处理方法对氧化锆与树脂水门汀粘接强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 53-57. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 121
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 311
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||