北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 89-98. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.012
单侧磨牙咬合干扰的口颌肌表面肌电指标体系构建与判别模型验证
李文博1,*, 沈玉凤2,*, 杨咏涛1, 单珅瑶1, 高梓翔3, 温奥楠3, 商相宜1, 田淯文1, 郭殊玮3, 王艺蓁1, 王勇3,*( ), 赵一姣1,*(
), 赵一姣1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学医学部医学技术研究院, 北京 100191
2. 石河子大学第一附属医院口腔科, 新疆石河子 832008
3. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔医学数字化研究中心, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 国家卫生健康委口腔数字医学重点实验室, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
Development of a surface electromyography index system for orofacial muscles and validation of a discriminant model in unilateral molar occlusal interference
Wenbo LI1, Yufeng SHEN2, Yongtao YANG1, Shenyao SHAN1, Zixiang GAO3, Aonan WEN3, Xiangyi SHANG1, Yuwen TIAN1, Shuwei GUO3, Yizhen WANG1, Yong WANG3,*( ), Yijiao ZHAO1,*(
), Yijiao ZHAO1,*( )
)
- 1. Institute of Medical Technology, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Stomatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang, China
3. Center for Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & NHC Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
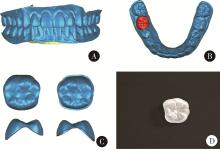
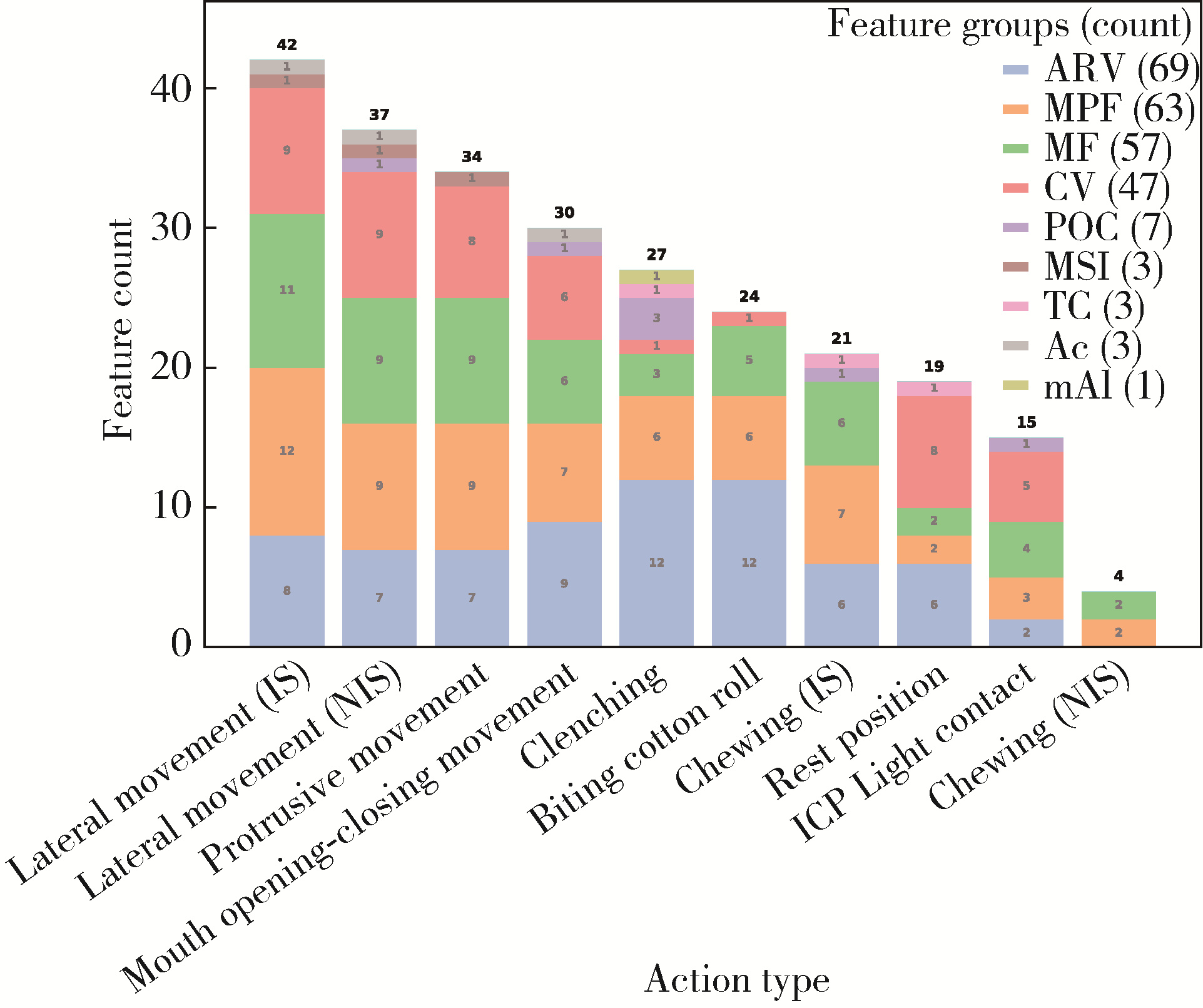
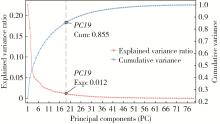
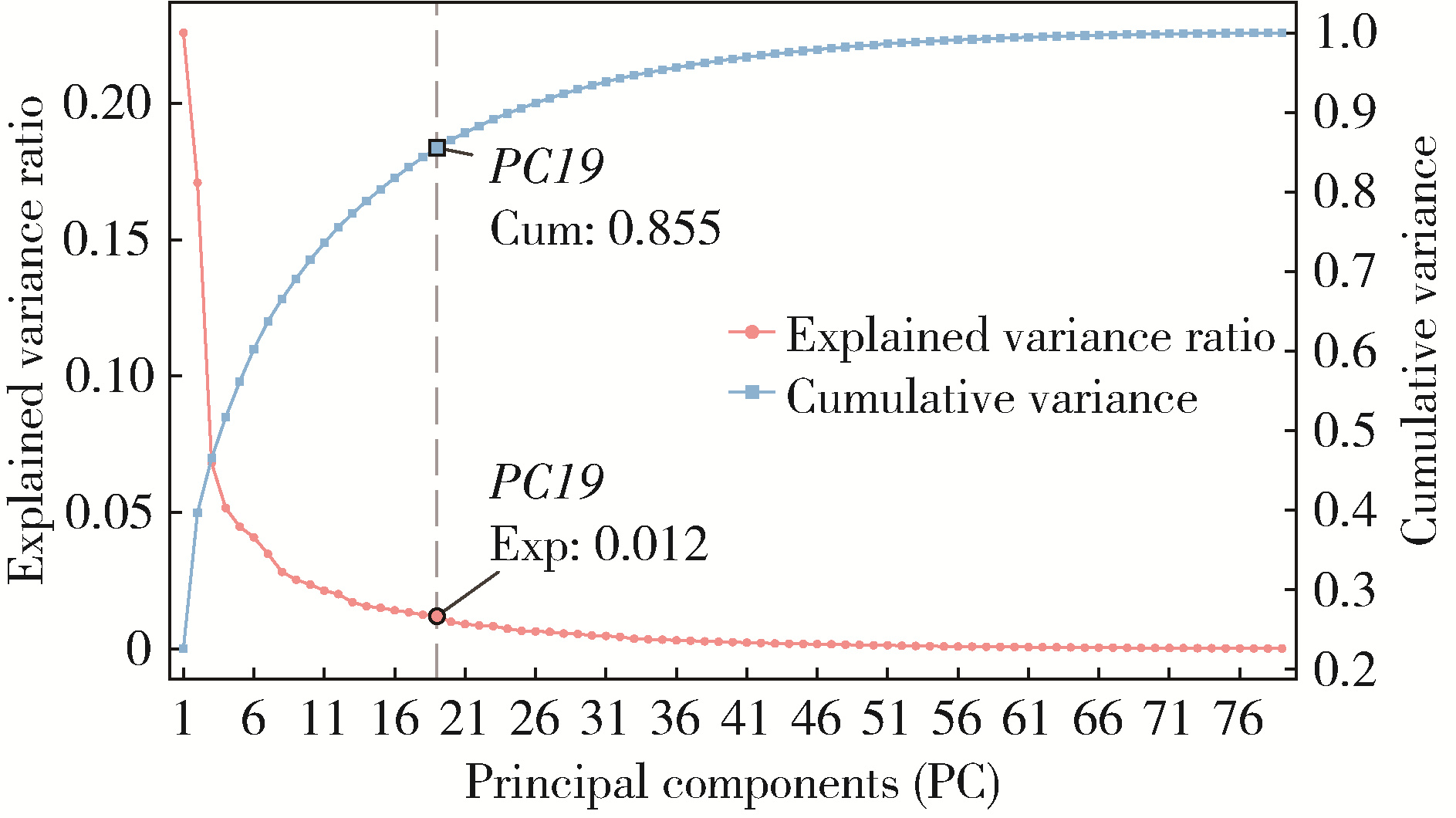
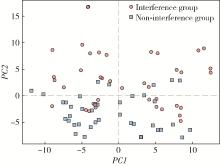
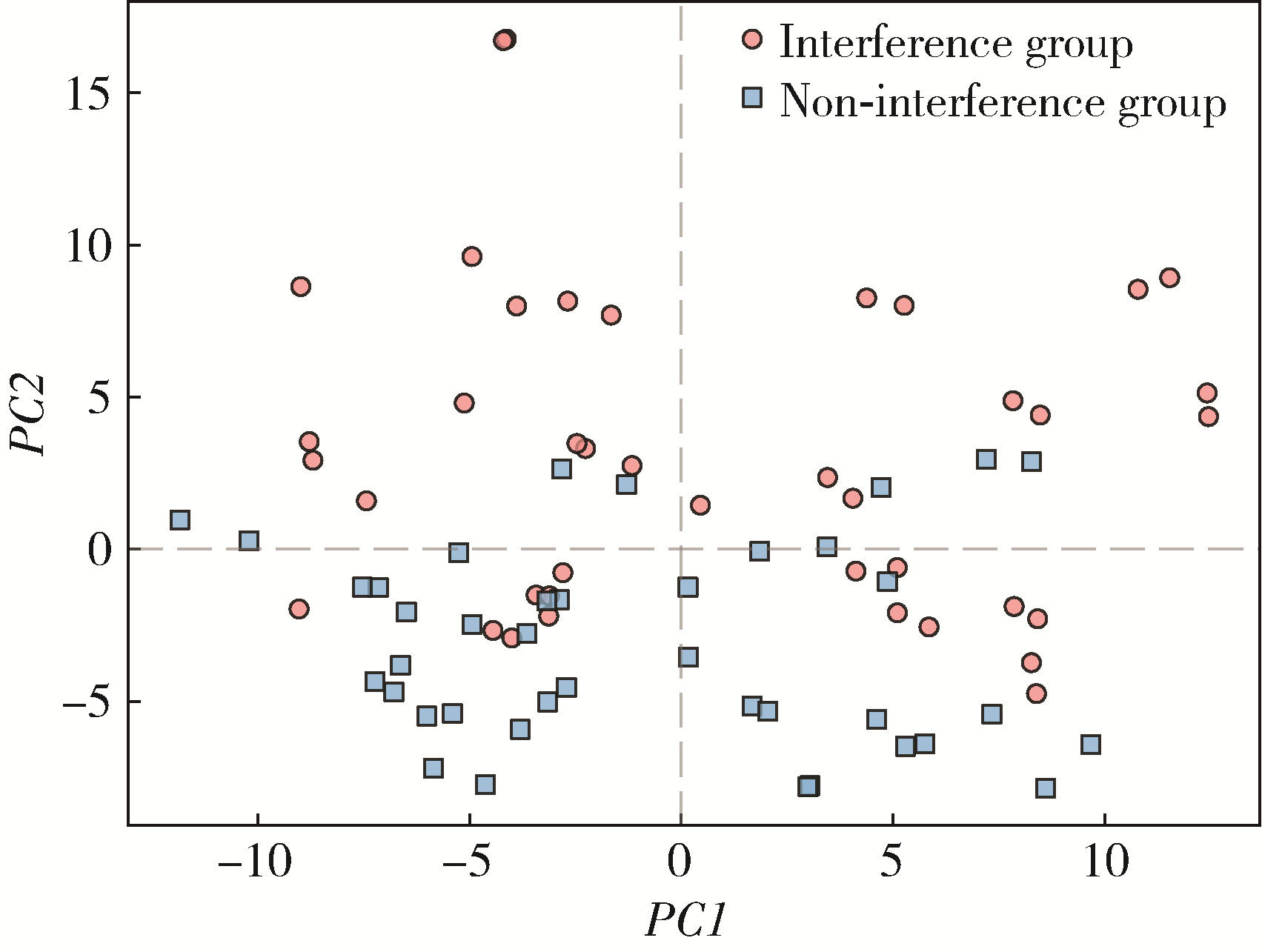
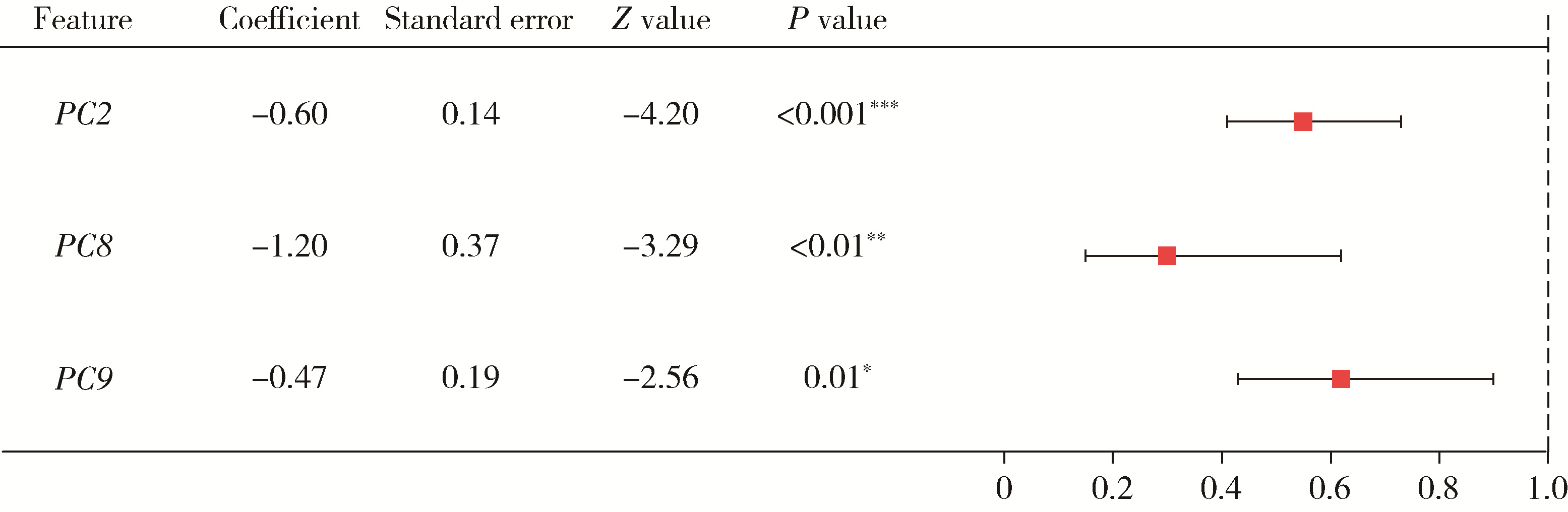
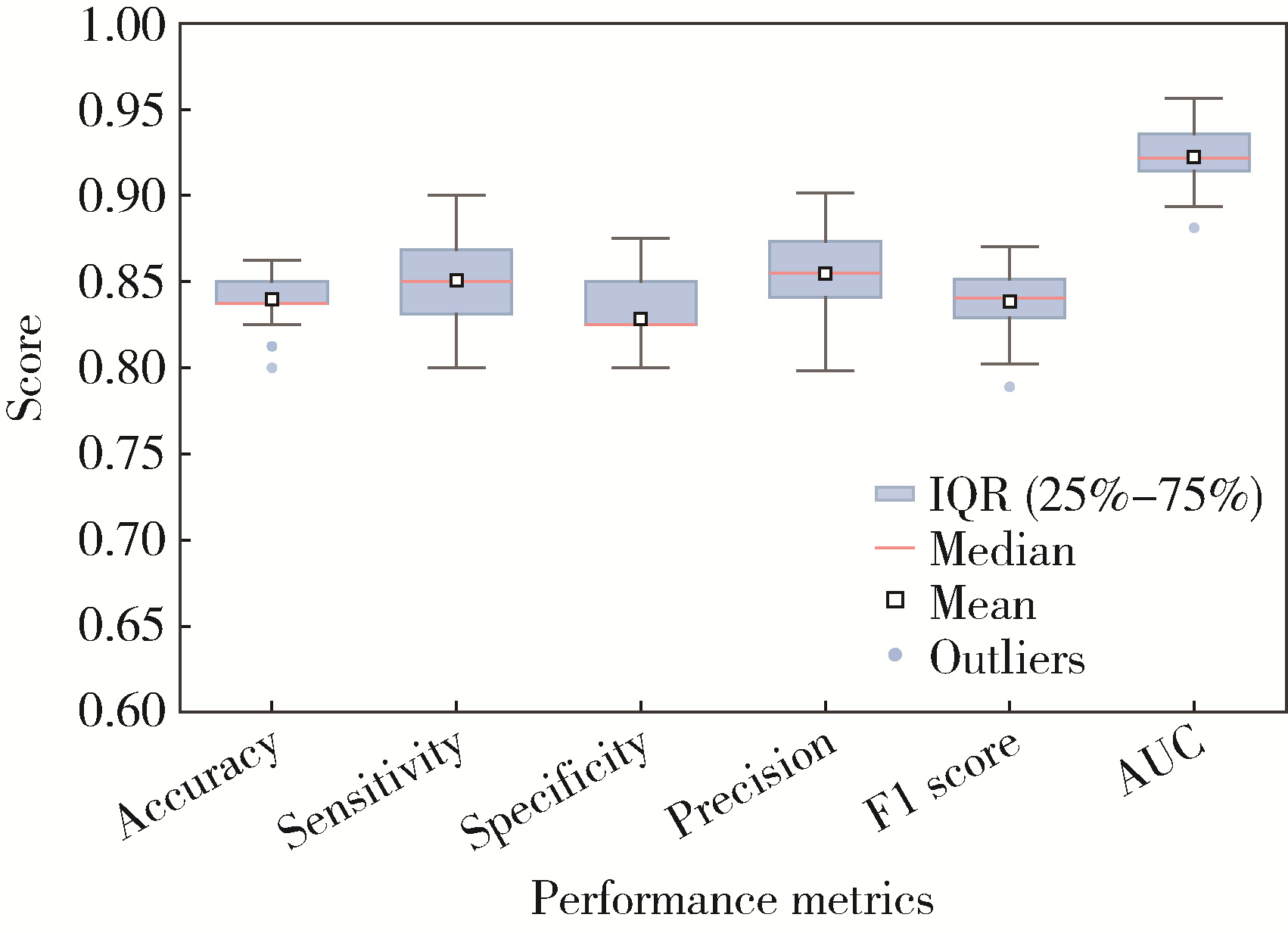
目的: 构建标准化的单侧磨牙咬合干扰模型, 建立基于表面肌电的口颌肌功能指标体系, 并开发咬合干扰的判别模型, 为咬合干扰的客观诊断提供电生理学参考。方法: 招募到26名志愿者, 采用口内扫描、计算机辅助设计及增材制造技术制作标准化咬合干扰贴片, 于下颌第一磨牙处构建可逆性单侧咬合干扰模型。使用自主研发的多通道无线表面肌电系统采集干扰前后10种下颌功能活动时双侧颞肌前束、咬肌及二腹肌前腹的肌电信号, 构建包含56项指标的多维度表面肌电指标体系。通过配对t检验或Wilcoxon符号秩检验、主成分分析和Logistic回归分析, 筛选特征变量并建立判别模型。结果: 共构建40例有效干扰模型, 253项表面肌电信号指标干扰前后比较差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 其中侧方运动相关指标对咬合干扰的敏感性最高。主成分分析共提取19个主成分(principal component, PC), 累计方差贡献率85.5%, 其中PC1(肌肉疲劳程度)和PC2(功能性运动幅度)为主要解释成分。Logistic回归模型最终纳入3项主成分, 交叉验证结果表明模型平均准确率为0.840, 平均灵敏度与特异度分别为0.851和0.828, 平均曲线下面积为0.923。结论: 研究构建的单侧磨牙咬合干扰Logistic回归判别模型能有效识别本实验条件下的咬合干扰状态, 具有较好的诊断潜力。
中图分类号:
- R78
| 1 |
doi: 10.1080/08869634.2020.1764270 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.2007.01750.x |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.1984.tb00583.x |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.1983.tb00114.x |
| 6 |
张磊, 谢秋菲. 牙体解剖与口腔生理学[M]. 3版 北京大学医学出版社, 2022: 206- 207.
|
| 7 |
丁其川, 熊安斌, 赵新刚, 等. 基于表面肌电的运动意图识别方法研究及应用综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42 (1): 13- 25.
|
| 8 |
李文博, 朱玉佳, 秦庆钊, 等. 自主研发无线表面肌电系统对咀嚼肌功能活动的评价研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2025, 43 (3): 346- 353.
|
| 9 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.2005.01558.x |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2842.2000.00490.x |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.1989.tb01318.x |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1016/j.irbm.2024.100866 |
| 13 |
王富, 牛丽娜, 陈吉华. 数字化咬合分析的方案与效能[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2025, 60 (8): 822- 828.
|
| 14 |
孙欣荣, 冯玥, 刘伟才. 多模态数据融合的可视化技术在咬合重建中的应用[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2022, 40 (4): 468- 475.
|
| 15 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.1996.tb00812.x |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1177/154405910508400712 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.1995.tb01197.x |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.2007.01769.x |
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
李宝勇, 周丽娟. TMD患者单侧下颌第三磨牙伸长咬合干扰与升颌肌肌电关系的研究[J/OL]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2025(2025-10-15)[2025-10-16]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/61.1062.R.20251015.1040.002.
|
| 21 |
李雪姣, 徐啸翔, 谢秋菲. 干扰与颞下颌关节紊乱病的复杂关系: 动物实验和临床研究的启示[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2013, 29 (2): 266- 274.
|
| [1] | 范莹莹,刘云,曹烨,谢秋菲. 海马参与雌激素加重咬合干扰致去卵巢大鼠慢性咬肌痛敏[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 40-47. |
| [2] | 闫树东,杨广聚,莫思怡,刘云,谢秋菲. 大鼠后肢长期抗阻训练对慢性咬肌机械痛觉敏感性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 21-27. |
|
||