北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 975-980. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.006
可溶性白细胞介素2受体α链的检测与类风湿关节炎疾病活动性评估
胥佳佳1,王燕1,△( ),孙贺1,贾汝琳2,张学武1,△(
),孙贺1,贾汝琳2,张学武1,△( ),孟洋1,任丽丽1,孙晓麟2
),孟洋1,任丽丽1,孙晓麟2
- 1. 郑州大学第五附属医院风湿免疫科, 郑州 450000
2. 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科, 北京 100044
Clinical significance of detection of soluble interleukin 2 receptor alpha chain in the assessment of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity
Jia jia XU1,Yan WANG1,△( ),He SUN1,Ru lin JIA2,Xue wu ZHANG1,△(
),He SUN1,Ru lin JIA2,Xue wu ZHANG1,△( ),Yang MENG1,Li li REN1,Xiao lin SUN2
),Yang MENG1,Li li REN1,Xiao lin SUN2
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology,Peking University People’s Hospital,Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
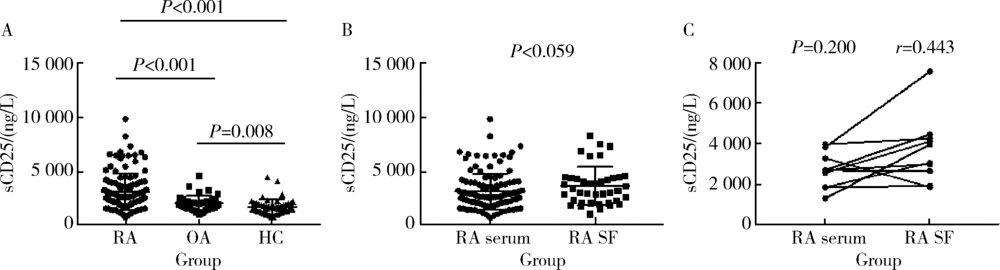
目的: 评价血清可溶性白细胞介素2受体α链(sIL-2Rα、sCD25)对类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)活动度评估的临床意义。方法: 收集RA患者血清108例,RA关节液标本40例,骨关节炎(osteoarthritis,OA)患者血清39例,健康人血清50例,采用酶联免疫吸附(ELISA)检测各组血清、以及RA患者关节液中sCD25浓度,并记录RA患者的各项临床表现和实验室指标,分析其与血清sCD25浓度水平的相关性。结果: RA组血清sCD25(质量)浓度为(2 886±1 333) ng/L,OA组血清sCD25浓度为(2 090±718) ng/L,健康对照组血清sCD25浓度为(1 768±753) ng/L;RA患者的血清sCD25水平显著高于疾病对照组和健康对照组(P< 0.001);血清中sCD25水平与红细胞沉降率(r=0.321,P = 0.001)、C-反应蛋白(r=0.446,P<0.001)、DAS28评分(r=0.324, P<0.001)、关节压痛计数(r = 0.203,P =0.024)、D-二聚体(D-dimer)水平(r=0.383,P<0.001)、年龄(r = 0.24,P = 0.007)、总IgG(r = 0.207,P = 0.028)、类风湿因子IgG(r = 0.345,P = 0.034)呈正相关,与病程呈负相关(r = -0.206,P = 0.021);在RA患者中,低疾病活动度组血清ESR、CRP和sCD25阳性率分别为14.3%(2例),14.3%(2例),71.4%(10例);中疾病活动度组血清ESR、CRP和sCD25阳性率分别为94.2%(49例)、82.7%(43例)和86.5%(45例);高疾病活动度组血清ESR、CRP和sCD25阳性率分别为100%(42例)、95.2%(40例)和90.5%(38例);有36例ESR和/或CRP为阴性(约33.3%),在这36例中有17例(约47.2%)血清sCD5水平升高,并且其中14例(约82.4%)DAS28评分高于3.2。结论: 血清sCD25水平与RA活动性密切相关,表明sCD25可能参与了RA的炎症过程,并有望成为RA患者的一种新的炎症指标;血清sCD25的检测在RA处于病情活动期,但ESR和/或CRP为阴性时更有意义。
中图分类号:
- R593.22
| [1] | Calabresi E, Petrelli F, Bonifacio AF , et al. One year in review 2018: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2018,36(2):175-184. |
| [2] |
Kumar LD, Karthik R, Gayathri N , et al. Advancement in contemporary diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2016,79:52-61.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.02.001 pmid: 27044812 |
| [3] |
Chavele KM, Ehrenstein MR . Regulatory T-cells in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis[J]. FEBS Lett, 2011,585(23):3603-3610.
doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.07.043 pmid: 21827750 |
| [4] |
Boyman O, Kolios AG, Raeber ME . Modulation of T cell responses by IL-2 and IL-2 complexes[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2015,33(4 Suppl 92):S54-S57.
pmid: 26457438 |
| [5] |
Howell MD, Diveley JP, Lundeen KA , et al. Limited T-cell receptor beta-chain heterogeneity among interleukin 2 receptor-positive synovial T cells suggests a role for superantigen in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1991,88(23):10921-10925.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10921 |
| [6] |
Liao W, Lin JX, Leonard WJ . Interleukin-2 at the crossroads of effector responses, tolerance, and immunotherapy[J]. Immunity, 2013,38(1):13-25.
doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.01.004 pmid: 3610532 |
| [7] |
Setoguchi R, Hori S, Takahashi T , et al. Homeostatic maintenance of natural Foxp3(+) CD25(+) CD4(+) regulatory T cells by interleukin (IL)-2 and induction of autoimmune disease by IL-2 neutralization[J]. J Exp Med, 2005,201(5):723-735.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20041982 |
| [8] |
Fulop T, Larbi A, Douziech N , et al. Cytokine receptor signalling and aging[J]. Mech Ageing Dev, 2006,127(6):526-537.
doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2006.01.025 pmid: 16530252 |
| [9] |
Chrobak L . Clinical significance of soluble interleukin-2 receptor[J]. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove), 1996,39(1):3-6.
pmid: 9106384 |
| [10] |
Murakami S . Soluble interleukin-2 receptor in cancer[J]. Front Biosci, 2004,9:3085-3090.
doi: 10.2741/1461 pmid: 15353339 |
| [11] |
Britsemmer K, Ursum J, Gerritsen M , et al. Validation of the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: slight improvement over the 1987 ACR criteria[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2011,70(8):1468-1470.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.148619 pmid: 21586440 |
| [12] |
Zhang W, Doherty M, Peat G , et al. EULAR evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2010,69(3):483-489.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.113100 pmid: 19762361 |
| [13] |
Schett G, Gravallese E . Bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2012,8(11):656-664.
doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2012.153 pmid: 23007741 |
| [14] |
Lee YH, Bae SC, Song GG . Diagnostic accuracy of anti-MCV and anti-CCP antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis[J]. Z Rheumatol, 2015,74(10):911-918.
doi: 10.1007/s00393-016-0134-y pmid: 27312463 |
| [15] | Avouac J, Gossec L, Dougados M . Diagnostic and predictive value of anti-cyclic citrullinated proteinantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2006,65(7):845-851. |
| [16] |
Sun J, Zhang Y, Liu L , et al. Diagnostic accuracy of combined tests of anti cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2014,32(1):11-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.rbre.2014.02.013 pmid: 24050751 |
| [17] |
Tak PP, Bresnihan B . The pathogenesis and prevention of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: advances from synovial biopsy and tissue analysis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2000,43(12):2619-2633.
doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200012)43:123.0.CO;2-V pmid: 11145019 |
| [18] |
Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ . Immunometabolism in early and late stages of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2017,13(5):291-301.
doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.49 pmid: 28360422 |
| [19] |
Malmstrom V, Catrina AI, Klareskog L . The immunopathogenesis of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: from triggering to targeting[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2017,17(1):60-75.
doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.124 pmid: 27916980 |
| [20] |
Dlouhy I, Filella X, Rovira J , et al. High serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL2-R), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) are associated with adverse clinical features and predict poor outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Leuk Res, 2017,59:20-25.
doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2017.05.014 |
| [21] |
Akiyama M, Sasaki T, Kaneko Y , et al. Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor is a useful biomarker for disease activity but not for differential diagnosis in IgG4-related disease and primary Sjögren’s syndrome adults from a defined population[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2018,112(36 Suppl 3):157-164.
pmid: 29465360 |
| [22] |
Gundlach E, Hoffmann M M, Prasse A , et al. Interleukin-2 receptor and angiotensin-converting enzyme as markers for ocular sarcoidosis[J]. PLoS One, 2016,11(1):e147258.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147258 pmid: 4723126 |
| [23] |
Nukui A, Masuda A, Abe H , et al. Increased serum level of soluble interleukin-2 receptor is associated with a worse response of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma to interferon alpha and sequential VEGF-targeting therapy[J]. BMC Cancer, 2017,17(1):372.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3369-3 pmid: 28545581 |
| [24] |
Spadaro A, Taccari E, Riccieri V , et al. Relationship of soluble interleukin-2-receptor and interleukin-6 with class-specific rheumatoid factors during low-dose methotrexate treatment in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Rev Rhum Engl Ed, 1997,64(2):89-94.
doi: 10.1016/S0950-3579(97)80028-3 pmid: 9085442 |
| [25] |
Knevel R, de Rooy DP, Zhernakova A , et al. Association of variants in IL2RA with progression of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2013,65(7):1684-1693.
doi: 10.1002/art.37938 |
| [26] |
van Steenbergen HW, van Nies JA, Ruyssen-Witrand A , et al. IL2RA is associated with persistence of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2015,17:244.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0739-6 pmid: 4563834 |
| [27] |
Turka LA, Walsh PT . IL-2 signaling and CD4+CD25+Foxp3+regulatory T cells[J]. Front Biosci, 2008,13:1440-1446.
doi: 10.2741/2773 pmid: 17981641 |
| [28] |
von Spee-Mayer C, Siegert E, Abdirama D , et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 selectively corrects regulatory T cell defects in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2016,75(7):1407-1415.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207776 pmid: 26324847 |
| [29] |
Matsuoka K, Koreth J, Kim HT , et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 therapy restores regulatory T cell homeostasis in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2013,5(179):143r-179r.
doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005265 pmid: 368651795284151236538681511 |
| [30] |
Gaujoux-Viala C, Mouterde G, Baillet A , et al. Evaluating disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: which composite index is best? A systematic literature analysis of studies comparing the psychometric properties of the DAS, DAS28, SDAI and CDAI[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2012,79(2):149-155.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.04.008 |
| [31] |
Aletaha D, Nell VP, Stamm T , et al. Acute phase reactants add little to composite disease activity indices for rheumatoid arthritis: validation of a clinical activity score[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2005,7(4):R796-R806.
doi: 10.1186/ar1740 pmid: 1175030 |
| [32] |
Stojan G, Fang H, Magder L , et al. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a predictor of renal and overall SLE disease activity[J]. Lupus, 2013,22(8):827-834.
doi: 10.1177/0961203313492578 |
| [33] | Orr C K, Najm A, Young F , et al. The utility and limitations of CRP, ESR and DAS28-CRP in appraising disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2018,5:185. |
| [1] | 刘梦珂,王露辰,胡凡磊. 血清基质金属蛋白酶3水平与早期类风湿关节炎病情评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 981-985. |
| [2] | 陈智滨 ,林琴 , 马长华, 刘凯宁 ,孟焕新. 自然沉降法分离抗凝全血建立生物样本库的特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(1): 111-114. |
| [3] | 张春雨, 刘丽丽, 廖莹, 杜军保, 金红芳. 血浆前白蛋白联合C-反应蛋白对川崎病患儿冠状动脉病变的预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(2): 207-. |
|
||