北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 277-282. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.02.015
肱骨近端骨折微创锁定钢板改良内固定的疗效分析
- 北京大学第三医院骨科,北京 100191
Application of the modified internal fixation method of minimally invasive percuta-neous plate osteosynthesis in treatment of proximal humeral fracture
Bing-chuan LIU,Zhong-wei YANG,Fang ZHOU,Hong-quan JI,Zhi-shan ZHANG,Yan GUO,Yun TIAN( )
)
- Department of Orthopedics, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
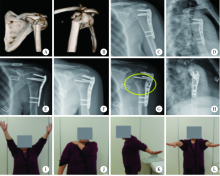
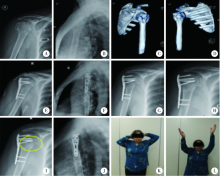
目的: 分析应用微创锁定钢板内固定治疗肱骨近端骨折患者,采用近端4枚锁钉及远端2枚锁钉(简称“近四远二”)的生物力学稳定固定方式的临床疗效及骨折愈合特点。方法: 对北京大学第三医院2010年2月至2016年12月期间的肱骨近端骨折患者进行回顾性研究,入组患者分为微创组与非微创组,微创组采用“近四远二”的内固定方式,非微创组采用传统切开复位内固定方式。为了研究对于不同类型骨折两种手术方式的治疗效果,我们同时进行了不同Neer分型患者的比较。术后复查肩关节X线片,采用视觉模拟评分法(visual analogue scale,VAS)及Constant-Murley评分评估患者肩关节疼痛及功能水平。结果: 符合入组标准的患者共117例,微创组45例,非微创组72例,平均年龄(61.5±16.2)岁。根据Neer分型,二部分骨折46例,三部分骨折63例,四部分骨折8例。微创组患者男17例,女28例,平均年龄(62.2±17.1))岁,包括Neer二部分骨折18例,Neer三部分骨折23例,Neer四部分骨折4例;非微创组患者男27例,女45例,平均年龄(60.1±17.7)岁,包括Neer二部分骨折28例,Neer三部分骨折40例,Neer四部分骨折4例。两组数据在性别(P = 0.975)、年龄(P=0.545)及骨折类型(P=0.756)方面的差异无统计学意义。微创组患者与非微创组的平均住院日分别为(2.8±1.1) d和(4.3±1.3) d (P=0.023),手术时间分别为(67.8±14.9) min和(102.3±34.1) min (P<0.001),失血量分别为(21.3±6.5) mL和(181.5±55.6) mL(P<0.001), 术后1周Constant-Murley评分分别为6.1±0.9及6.5±0.8 (P=0.032),术后3个月Constant-Murley评分分别为66.1±4.3及63.4±4.9(P=0.006),在这些方面微创组具有显著优势。对于Neer二部分及三部分骨折,微创组的术后1周VAS评分(5.9±0.8)及术后3个月的Constant-Murley评分(66.6±3.7)均具有显著优势(P<0.05)。微创组发生骨折延迟愈合1例(2.2%)、外展受限1例(2.2%);非微创组发生骨折延迟愈合3例(4.2%)、外展受限2例(2.8%), 两组均未出现内固定断裂及肱骨头坏死的情况。结论: 应用微创技术结合“近四远二”的内固定方式治疗肱骨近端骨折,术后骨折断端骨痂生长明显,骨折正常愈合且肩关节功能恢复良好,是一种可行的手术方式。
中图分类号:
- R683.4
| [1] |
Roux A, Decroocq L, Batti SE , et al. Epidemiology of proximal humerus fractures managed in a trauma center[J]. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res, 2012,98(6):715-719.
doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2012.05.013 |
| [2] |
Jost B, Spross C, Grehn H , et al. Locking plate fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus: analysis of complications, revision strategies and outcome[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 2013,22(4):542-549.
doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2012.06.008 |
| [3] | Maier D, Jäger M, Strohm PC , et al. Treatment of proximal humeral fractures: a review of current concepts enlightened by basic principles[J]. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech, 2012,79(4):307-316. |
| [4] | Burkhart KJ, Dietz SO, Bastian L , et al. The treatment of proximal humeral fracture in adults[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2013,110(35):591-597. |
| [5] |
Jung SW . Indirect reduction maneuver and minimally invasive approach for displaced proximal humerus fractures in elderly patients[J]. Clin Orthop Surg, 2013,5(1):66-73.
doi: 10.4055/cios.2013.5.1.66 |
| [6] |
Sohn HS, Shin SJ . Minimally invasive plate osteosynjournal for proximal humeral fractures: clinical and radiologic outcomes according to fracture type[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 2014,23(9):1334-1340.
doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2013.12.018 |
| [7] | 赵弟庆, 张丽娜, 杨广忠 , 等. MIPPO技术结合PHILOS治疗老年骨质疏松性肱骨近端骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(6):508-511. |
| [8] |
Gavaskar AS, Muthukumar S, Chowdary N . Biological osteosynjournal of complex proximal humerus fractures: surgical technique and results from a prospective single center trial[J]. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2010,130(5):667-672.
doi: 10.1007/s00402-009-1028-0 |
| [9] | 刘振东, 马梦然 . 骨折愈合理论研究现状[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2010,18(16):87-91. |
| [10] |
Parren SM . Evolution of the internal fixation of long bong fracture. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2002,84(8):1093-1110.
doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.84B8.13752 |
| [11] |
Sonderegger J, Grob KR, Kuster MS . Dynamic plate osteosynjournal for fracture stabilization: how to do it[J]. Orthop Rev, 2010,2(1):e4.
doi: 10.4081/or.2010.e4 |
| [12] | 夏和桃, 李刚 . 现代骨外固定概念的生物学基础及应用原则[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2011,13(10):964-968. |
| [13] |
Koljonen PA, Fang C, Lau TW , et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynjournal for proximal humeral fractures[J]. J Orthop Surg, 2015,23(2):160-163.
doi: 10.1177/230949901502300208 |
| [14] | Gardner MJ, Griffith MH, Dines JS , et al. The extended anterolateral acromial approach allows minimally invasive access to the proximal humerus[J]. Clin Orthop, 2005,434(434):123-129. |
| [15] |
Falez F, Papalia M, Greco A , et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynjournal in proximal humeral fractures: one-year results of a prospective multicenter study[J]. Int Orthop, 2016,40(3):579-585.
doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-3069-z |
| [1] | 蒋艳芳,王健,王永健,刘佳,裴殷,刘晓鹏,敖英芳,马勇. 前交叉韧带翻修重建术后中长期临床疗效及影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 857-863. |
| [2] | 魏菱,邹东,陈虎,潘韶霞,孙玉春,周永胜. 一种数字化全口义齿的临床疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 762-770. |
|
||