北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 467-476. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.03.014
拉洛他赛的波谱解析及高效液相色谱法对其脂质体含量的测定
李雪琦1,李建伟1,2,3,4,李秋红1,4,阎妍1,段嘉伦1,崔一诺1,苏展博1,罗倩1,许佳瑞1,杜亚菲1,王桂玲1,谢英1,吕万良1△( )
)
Spectrometric analyses of larotaxel and larotaxel liposomes quantification by high performance liquid chromatography
Xue-qi LI1,Jian-wei LI1,2,3,4,Qiu-hong LI1,4,Yan YAN1,Jia-lun DUAN1,Yi-nuo CUI1,Zhan-bo SU1,Qian LUO1,Jia-rui XU1,Ya-fei DU1,Gui-ling WANG1,Ying XIE1,Wan-liang LU1△( )
)
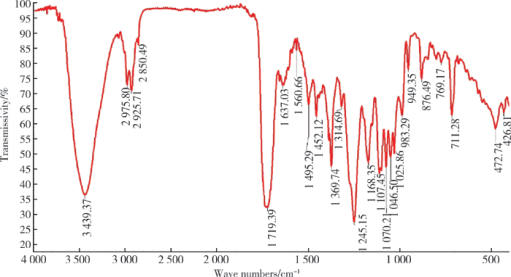
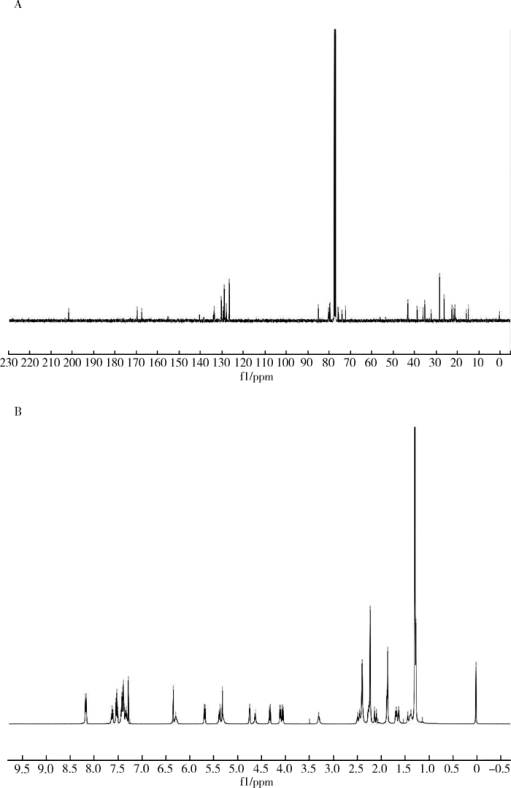
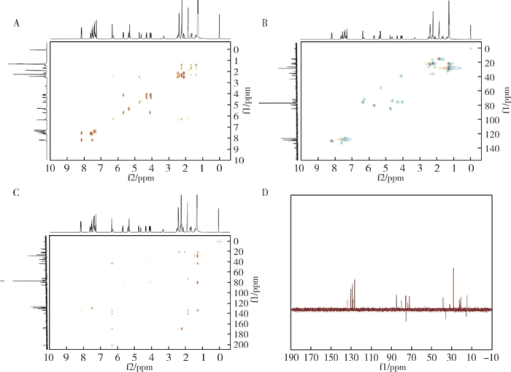
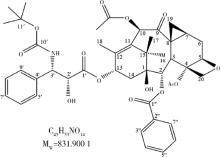
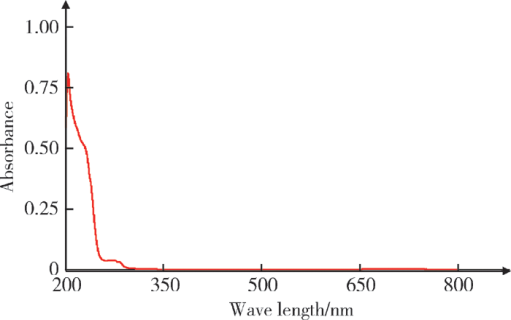
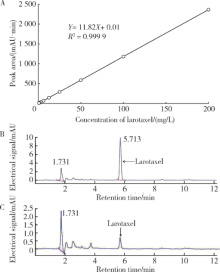
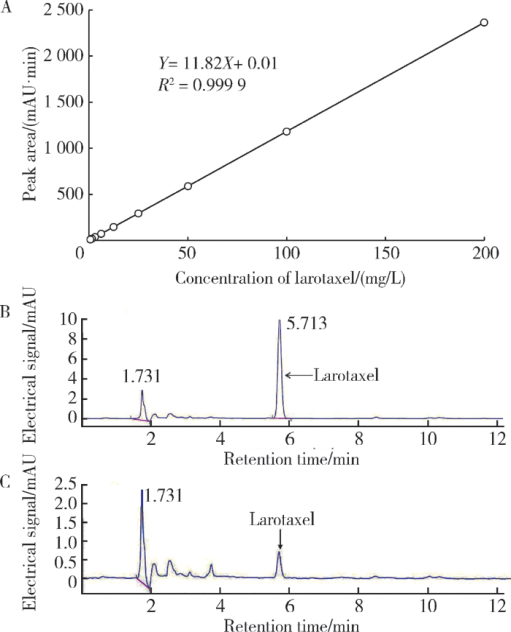
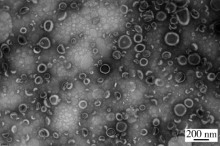
摘要: 目的 拉洛他赛是国内外均未上市的新结构药物,未见质量研究相关报道。对拉洛他赛进行波谱解析以验证其分子式、相对分子质量和化学结构式,同时建立一种定量方法用于拉洛他赛脂质体制剂的含量测定。方法 利用质谱、红外吸收光谱、核磁共振波谱测定方法,对拉洛他赛进行药物结构和光谱学解析;利用紫外-可见分光光度法对拉洛他赛进行全波长扫描,确定其吸收波长;利用高效液相色谱法,建立拉洛他赛定量方法并用于脂质体拉洛他赛包封率的测定。结果 揭示了拉洛他赛的四大光谱学特征并制订相应的标准图谱。确认了拉洛他赛的结构为三环二萜,分子式为C45H53NO14,相对分子质量为831.900 1。建立了拉洛他赛的高效液相色谱定量方法,其色谱柱为C18硅胶反相色谱柱 (5 μm, 250 mm×4.6 mm),流动相为乙腈-水(体积比75 ∶25),检测波长为230 nm,该方法可用于测定脂质体制剂中拉洛他赛的包封率,稳定性、回收率和精密度高。此外,新制备了拉洛他赛脂质体,该脂质体粒径大约105 nm,均一性良好,药物包封率大于80%。结论 制订了拉洛他赛的质谱、红外吸收光谱、核磁共振波谱和紫外-可见光谱图谱,验证了拉洛他赛的分子式、相对分子质量和结构式,建立了拉洛他赛的高效液相色谱定量方法,该方法可用于拉洛他赛脂质体的质量控制。
中图分类号:
- R927
| [1] |
Vallo S, Michaelis M, Rothweiler F , et al. Drug-resistant urothelial cancer cell lines display diverse sensitivity profiles to potential second-line therapeutics[J]. Transl Oncol, 2015,8(3):210-216.
doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2015.04.002 |
| [2] |
Cao YN, Zheng LL, Wang D , et al. Recent advances in microtubule-stabilizing agents[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2018,143(1):806-828.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.11.062 |
| [3] |
Iqbal J, Abbasi BA, Mahmood T , et al. Plant-derived anticancer agents: A green anticancer approach[J]. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed, 2017,7(12):1129-1150.
doi: 10.1016/j.apjtb.2017.10.016 |
| [4] |
Metzger-Filho O, Moulin C, De Azambuja E , et al. Larotaxel: broadening the road with new taxanes[J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2009,18(8):1183-1189.
doi: 10.1517/13543780903119167 |
| [5] |
Ren S, Wang Y, Wang J , et al. Synjournal and biological evaluation of novel larotaxel analogues[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2018,156(5):692-710.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.07.029 |
| [6] |
Zhang H, Qiao Y, Li M , et al. Synjournal and cytotoxicity of two active metabolites of larotaxel[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2016,16(7):875-880.
doi: 10.2174/1871520616666160201151344 |
| [7] |
Khazir J, Mir BA, Pilcher L , et al. Role of plants in anticancer drug discovery[J]. Phytochem Lett, 2014,7(1):173-181.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2013.11.010 |
| [8] |
Dieras V, Limentani S, Romieu G , et al. Phase II multicenter study of larotaxel (XRP9881), a novel taxoid, in patients with metastatic breast cancer who previously received taxane-based the-rapy[J]. Ann Oncol, 2008,19(7):1255-1260.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdn060 |
| [9] |
Zatloukal P, Gervais R, Vansteenkiste J , et al. Randomized multicenter phase II study of larotaxel (XRP9881) in combination with cisplatin or gemcitabine as first-line chemotherapy in nonirradiable stage IIIB or stage IV non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2008,3(8):894-901.
doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31817e6669 |
| [10] |
Sternberg CN, Skoneczna IA, Castellano D , et al. Larotaxel with cisplatin in the first-line treatment of locally advanced/metastatic urothelial tract or bladder cancer: a randomized, active-controlled, phase III trial (CILAB)[J]. Oncology, 2013,85(4):208-215.
doi: 10.1159/000354085 |
| [11] |
Robert F, Harper K, Ackerman J , et al. A phase I study oflarotaxel (XRP9881) administered in combination with carboplatin in chemotherapy-naive patients with stage IIIB or stage IV non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2010,65(2):227-234.
doi: 10.1007/s00280-009-1026-5 |
| [12] |
Singla AK, Garg A, Aggarwal D . Paclitaxel and its formulations[J]. Int J Pharm, 2002,235(1):179-192.
doi: 10.1016/S0378-5173(01)00986-3 |
| [13] |
Che X, Shen L, Xu H , et al. Isolation and characterization of process-related impurities and degradation products in larotaxel[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2011,55(5):1190-1196.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2011.03.036 |
| [14] |
Torchilin VP, Omelyanenko VG, Papisov MI , et al. Poly(ethy-lene glycol) on the liposome surface: on the mechanism of polymer-coated liposome longevity[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1994,1195(1):11-20.
doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90003-5 |
| [15] |
Bertrand N, Wu J, Xu X , et al. Cancer nanotechnology: the impact of passive and active targeting in the era of modern cancer biology[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2014,66(24):2-25.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.11.009 |
| [16] | Sanna V, Pala N, Sechi M . Targeted therapy using nanotechnology: focus on cancer[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2014,9(1):467-483. |
| No related articles found! |
|
||