北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 887-892. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.05.016
改良猪小肠黏膜下层可吸收膜在兔下颌骨缺损早期愈合中的作用
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,修复科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Barrier effect of improved porcine small intestinal submucosa absorbable membrane on early healing of mandibular defects in rabbits
Bo-wen LI,Wei-yi WU,Lin TANG,Yi ZHANG,Yu-hua LIU( )
)
- Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
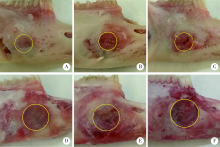
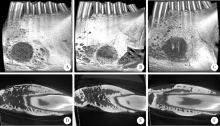
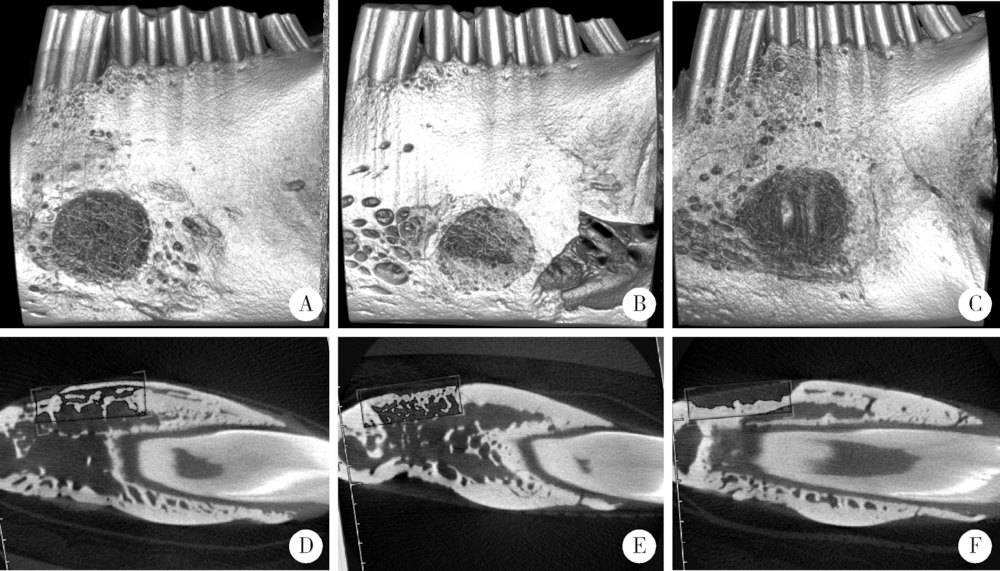
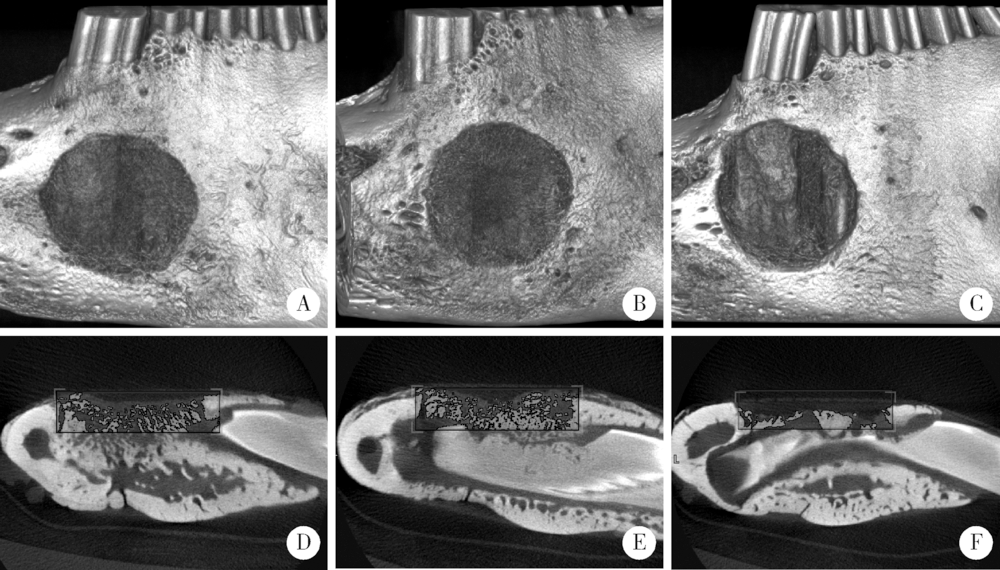
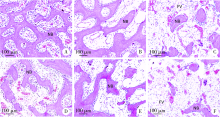
目的:建立两种尺寸兔下颌骨骨缺损模型,研究改良猪小肠黏膜下层(small intestinal submucosa,SIS)可吸收膜在骨缺损早期愈合中的屏障作用。方法:将12只新西兰大白兔随机分组,于双侧下颌骨各制备一个深度均为2 mm、直径为5 mm或8 mm的A、B两种圆形骨缺损,并分别给予以下处理:覆盖SIS膜(简称S)、覆盖Bio-Gide膜(简称G)和不做任何处理(简称O), 得到AS、AG、AO、BS、BG和BO共6组(n=4)24个样本。术后4周取材,进行大体、微型CT(Micro-CT)和组织学观察,采用单因素方差分析法对数据进行统计学分析,评估各组骨缺损早期愈合的情况。结果:大体标本观察显示术后4周SIS膜完整,未见明显降解,Bio-Gide不完整,与周围组织融合;AS、BS和AG三组中屏障膜均平整覆盖于骨面,下方骨质较硬,BG组Bio-Gide向中央凹陷,下方骨质相对松软;AO、BO两组骨面明显凹陷,有大量纤维结缔组织。Micro-CT三维重建图显示,AS、BS、AG和BG四组均可见大量新生骨小梁,BG组中央凹陷区新生骨小梁稀疏,AO、BO组仅在缺损底部有少量新生骨小梁。Micro-CT定量结果显示,AS组骨体积分数(new bone percentage,BV/TV)(39.10%±0.79%)和骨密度(bone mineralized density,BMD)[(517.73±11.22) mg/cm 3]显著高于AO组[26.67%±1.12%,(319.81±8.00) mg/cm 3,P<0.05],但与AG组[38.15%±0.91%,(518.65±7.48) mg/cm 3]差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。BS组BV/TV(34.90%±1.35%)和BMD[(409.09±8.14) mg/cm 3]显著高于BO组[23.63%±2.07%,(171.00±16.24) mg/cm 3,P<0.05],但与BG组[33.40%±1.06%,(412.70±8.6) mg/cm 3]差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。组织学观察显示,AO和BO组有大量脂肪空泡,仅有少许散在新生骨组织,相对稀疏,未形成岛状,与天然骨组织界限清楚。AS和AG两组可见大量新生骨组织形成,骨小梁呈岛状,表面衬有成排的成骨细胞,可见血管形成,与周围自体骨组织界限不清。BS和BG组也可见大量新生骨组织,但较AS、AG组稀疏,与周围自体骨组织界限清晰。结论:在下颌骨骨缺损早期愈合中,SIS可吸收膜和Bio-Gide可吸收膜均发挥良好的屏障作用,其效果无明显差异,但本实验中SIS膜在一定程度上对于下颌骨缺损修复空间的维持能力更好。
中图分类号:
- R738.4
| [1] | Retzepi M, Donos N . Guided bone regeneration: biological principle and therapeutic applications[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2010,21(6):567-576. |
| [2] | Dimitriou R, Mataliotakis GI, Calori GM , et al. The role of bar-rier membranes for guided bone regeneration and restoration of large bone defects: Current experimental and clinical evidence[J]. BMC Med, 2012,10(1):81. |
| [3] | Wessing B, Urban I, Montero E , et al. Guided bone regeneration using collagen membranes simultaneous to implant placement at compromised sites leads to reproducible results and high success rates[J]. Musculoskelet Regen, 2017,3:e1537. |
| [4] | Cen L, Liu W, Cui L , et al. Collagen tissue engineering: Deve-lopment of novel biomaterials and applications[J]. Pediatr Res, 2008,63(5):492-496. |
| [5] | Zitzmann NU, Schärer P, Marinello CP . Long-term results of implants treated with guided bone regeneration: A 5-year prospective study[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2001,16(3):355-366. |
| [6] | Tal H, Kozlovsky A, Artzi Z , et al. Long-term bio-degradation of cross-linked and non-cross-linked collagen barriers in human guided bone regeneration[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2008,19(3):295-302. |
| [7] | Lee JH, Lee JS, Baek WS , et al. Assessment of dehydrothermally cross-linked collagen membrane for guided bone regeneration around peri-implant dehiscence defects: A randomized single-blinded clinical trial[J]. J Periodontal Implant Sci, 2015,45(6):229-237. |
| [8] | Tu Y, Chen C, Li Y , et al. Fabrication of nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan membrane with asymmetric structure and its applications in guided bone regeneration[J]. Biomed Mater Eng, 2017,28(3):223-233. |
| [9] | Jiménez GJ, Berghezan S, Jmm C , et al. Effect of cross-linked vs. non-cross-linked collagen membranes on bone: A systematic review[J]. J Periodontal Res, 2017,52(6):955-964. |
| [10] | Andrée B, Bär A, Haverich A , et al. Small intestinal submucosa segments as matrix for tissue engineering: review[J]. Tissue Eng Part B Rev, 2013,19(4):279-291. |
| [11] | Mosala Nezhad Z, Poncelet A, de Kerchove L, et al. Small intestinal submucosa extracellular matrix (CorMatrix ®) in cardiovascular surgery: A systematic review [J]. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg, 2016,22(6):839-850. |
| [12] | Mewaldt R, Shi L, Carson D . Enzymatic degradation study of single layer and multi-layer small intestine submucosa (sis) matrices[J]. Wound Repair Regen, 2011,19(2):A39. |
| [13] | 牛睿, 李智峰, 张海燕 , 等. 复合SIS组织修复材料及其制备方法: 北京, CN103877619A[P]. 2014 -06-25. |
| [14] | 陈薇, 李次会, 武术 , 等. 脱细胞处理对小肠黏膜下层细胞残留及生长因子含量影响的实验研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科志, 2010,24(1):94-99. |
| [15] | Olaechea A, Mendoza-Azpur G, Valdivia E , et al. Biodegradation of three different collagen membranes: A histological study[J]. J Osseointegration, 2016,8(2):15-19. |
| [16] | Gottlow J . Guided tissue regeneration using bioresorbable and non-resorbable devices: Initial healing and long-term results[J]. J Periodontol, 1993,64(11 Suppl):1157-1165. |
| [17] | Behring J, Junker R, Walboomers XF , et al. Toward guided tissue and bone regeneration: morphology, attachment, proliferation, and migration of cells cultured on collagen barrier membranes: A systematic review[J]. Odontology, 2008,96(1):1-11. |
| [18] | Rothamel D, Schwarz F, Fienitz T , et al. Biocompatibility and biodegradation of a native porcine pericardium membrane: Results of in vitro and in vivo examinations[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2012,27(1):146-154. |
| [19] | Jung RE, Hälg GA, Thoma DS , et al. A randomized, controlled clinical trial to evaluate a new membrane for guided bone regeneration around dental implants[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2009,20(2):162-168. |
| [20] | de Santana RB, de Mattos CML, Francischone CE , et al. Superficial topography and porosity of an absorbable barrier membrane impacts soft tissue response in guided bone regeneration[J]. J Periodontol, 2010,81(6):926-933. |
| [21] | McPherson TB, Badylak SF . Characterization of fibronectin derived from porcine small intestinal submucosa[J]. Tissue Engineering, 1998,4(1):75-83. |
| [22] | Lindberg K, Badylak SF . Porcine small intestinal submucosa (SIS): A bioscaffold supporting in vitro primary human epidermal cell differentiation and synjournal of basement membrane proteins[J]. Burns, 2001,27(3):254-266. |
| [23] | Ermis R . Comparison of mechanical properties between small intestine submucosa (sis) with varying layers[J]. Wound Repair Regen, 2011,19(2):A21. |
| [24] | 吴唯伊, 李博文, 刘玉华 , 等. 复层猪小肠黏膜下层可吸收膜体内外降解性能的研究[ C]//中华口腔医学会口腔修复学专业委员会. 第十一次全国口腔修复学学术年会论文汇编.北京: 中华口腔医学会口腔修复学专业委员会, 2017: 1. |
| [25] | Schmitz JP, Hollinger JO . The critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1986(205):299-308. |
| [26] | Li M, Zhang C, Cheng M , et al. Small intestinal submucosa: A potential osteoconductive and osteoinductive biomaterial for bone tissue engineering[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Appl, 2017,75:149-156. |
| [1] | 陈晓颖,张一,李雨柯,唐琳,刘玉华. 不同种类聚合物对猪小肠黏膜下层支架仿生矿化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 17-24. |
| [2] | 李雨柯,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华,陈晓颖. 不同pH值对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层海绵支架螯合锶离子的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 44-51. |
| [3] | 邓艺,张一,李博文,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华. 不同交联剂处理对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层多孔支架的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 557-564. |
| [4] | 尤鹏越,刘玉华,王新知,王思雯,唐琳. 脱细胞猪心包膜生物相容性及成骨性能的体内外评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 776-784. |
| [5] | 王梅, 李博文, 王思雯, 刘玉华. 猪小肠黏膜下层海绵的制备及促成骨作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 952-958. |
| [6] | 吴唯伊,李博文,刘玉华,王新知. 复层猪小肠黏膜下层可吸收膜的降解性能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 564-569. |
| [7] | 李菲,乔静,段晋瑜,张勇,王秀婧. 引导性组织再生术对浓缩生长因子联合植骨术治疗下颌磨牙Ⅱ度根分叉病变临床效果的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 346-352. |
|
||