北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1182-1184. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.037
• 病例报告 • 上一篇
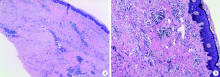
类脂质渐进性坏死1例
- 山西白求恩医院风湿免疫科,太原 030032
Progressive necrosis of lipid: A case report
Jiao-niu DUAN,Wei DU,Rui-hong HOU,Ke XU,Gai-lian ZHANG,Li-yun ZHANG( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Taiyuan 030032, China
中图分类号:
- R593.3
| [1] | Reid SD, Ladizinski B, Lee K , et al. Update on necrobiosis lipoidica: A review of etiology, diagnosis, and treatment options[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2013,69(5):783-791. |
| [2] | Chung CG, Rosengrant A, Helm KF , et al. Necrobiosis lipoidica occurring in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis on concurrent tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor therapy[J]. Int J Dermatol, 2015,54(11):1294-1296. |
| [3] | Valecha N, Bennett G, Yip L . A granulomatous conundrum: concurrent necrobiosis lipoidica, cutaneous sarcoidosis and erythema nodosum in a nondiabetic patient[J]. Australas J Dermatol, 2017,58(4):1232-1235. |
| [4] | 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 显微镜下多血管炎诊断及治疗指南[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2011,15(4):259-261. |
| [5] | Peckruhn M, Tittelbach J, Elsner P . Update: Treatment of necrobiosis lipoidica[J]. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges, 2017,15(2):151-157. |
| [6] | Motolese A, Vignati F, Antelmi A , et al. Effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma in healing necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum ulcers[J]. Clin Exp Dermatol, 2015,40(1):39-41. |
| [1] | 张培恒, 高莹, 吴红花, 张健, 张俊清. 暴发性1型糖尿病合并急性胰腺炎1例及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 923-927. |
| [2] | 马雨佳,卢燃藜,周泽宸,李晓怡,闫泽玉,武轶群,陈大方. 基于两样本孟德尔随机化的失眠与2型糖尿病关联研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 174-178. |
| [3] | 鲍雷,蔡夏夏,张明远,任磊磊. 维生素D3对2型糖尿病小鼠轻度认知障碍的改善作用及机制研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 587-592. |
| [4] | 张晓悦,林雨欣,蒋莹,张蓝超,董芒艳,池海谊,董浩宇,马利军,李智婧,常春. 自我效能在2型糖尿病患者自我管理能力和自我管理行为间的中介效应[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 450-455. |
| [5] | 于欢,杨若彤,王斯悦,吴俊慧,王梦莹,秦雪英,吴涛,陈大方,武轶群,胡永华. 2型糖尿病患者使用二甲双胍与缺血性脑卒中发病风险的队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 456-464. |
| [6] | 俞光岩,宿骞,张艳,吴立玲. 唾液腺疾病与全身系统性疾病的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 1-7. |
| [7] | 陈阳阳,周玉博,杨静,花语蒙,原鹏波,刘爱萍,魏瑗. 双胎妊娠孕期体质量对血清高敏C反应蛋白与妊娠期糖尿病关联的影响:一项队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 427-433. |
| [8] | 王佳敏,刘秋萍,张明露,巩超,刘舒丹,陈暐烨,沈鹏,林鸿波,高培,唐迅. 基于马尔可夫模型的社区人群糖尿病筛查预防心血管病的效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 450-457. |
| [9] | 吴俊慧,武轶群,吴瑶,王紫荆,吴涛,秦雪英,王梦莹,王小文,王伽婷,胡永华. 北京城镇职工2型糖尿病患者缺血性脑卒中发病率及主要危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 249-254. |
| [10] | 徐欣然,霍芃呈,和璐,孟焕新,朱筠轩,靳东思奇. 伴与不伴糖尿病的牙周炎患者牙周基础治疗的疗效比较及其与白细胞水平的相关分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 48-53. |
| [11] | 朱忆颖,闵赛南,俞光岩. 局部注射环孢素A对非肥胖糖尿病小鼠下颌下腺分泌功能及炎症的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 750-757. |
| [12] | 尹雪倩, 张晓玄, 文婧, 刘思奇, 刘欣然, 周若宇, 王军波. 荞麦、燕麦、豌豆复配对糖尿病大鼠血糖的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 447-452. |
| [13] | 郭洪萍,赵艾,薛勇,马良坤,张玉梅,王培玉. 孕期营养素摄入与妊娠期糖尿病孕妇血糖控制效果的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 467-472. |
| [14] | 吴俊慧,陈泓伯,武轶群,吴瑶,王紫荆,吴涛,王梦莹,王斯悦,王小文,王伽婷,于欢,胡永华. 2015—2017年北京市2型糖尿病患者骨关节炎患病的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 518-522. |
| [15] | 樊理诗,高敏,Edwin B.FISHER,孙昕霙. 北京市通州区和顺义区747例2型糖尿病患者生存质量影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 523-529. |
|
||