北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 450-455. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.03.010
自我效能在2型糖尿病患者自我管理能力和自我管理行为间的中介效应
张晓悦1,林雨欣1,蒋莹2,张蓝超1,董芒艳3,池海谊4,董浩宇5,马利军6,李智婧1,常春1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学公共卫生学院社会医学与健康教育系,北京 100191
2. 北京一蜂科技有限公司,北京 100020
3. 侯马市人民医院内分泌科,山西侯马 043011
4. 呼和浩特市第一医院内分泌科,呼和浩特 010030
5. 长治医学院附属和平医院内分泌科,山西长治 046000
6. 大同市新荣区人民医院内分泌科,山西大同 037002
Mediating effect of self-efficacy on self-management ability and self-management behavior in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xiao-yue ZHANG1,Yu-xin LIN1,Ying JIANG2,Lan-chao ZHANG1,Mang-yan DONG3,Hai-yi CHI4,Hao-yu DONG5,Li-jun MA6,Zhi-jing LI1,Chun CHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Social Medicine and Health Education, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Bee Technology Limited Company, Beijing 100020, China
3. Department of Endocrinology, Houma People' s Hospital, Houma 043011, Shanxi, China
4. Department of Endocrinology, Hohhot First Hospital, Hohhot 010030, China
5. Department of Endocrinology, Heping Hospital Affiliated to Changzhi Medical College, Changzhi 046000, Shanxi, China
6. Department of Endocrinology, People' s Hospital of Xinrong District, Datong 037002, Shanxi, China
摘要:
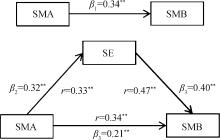
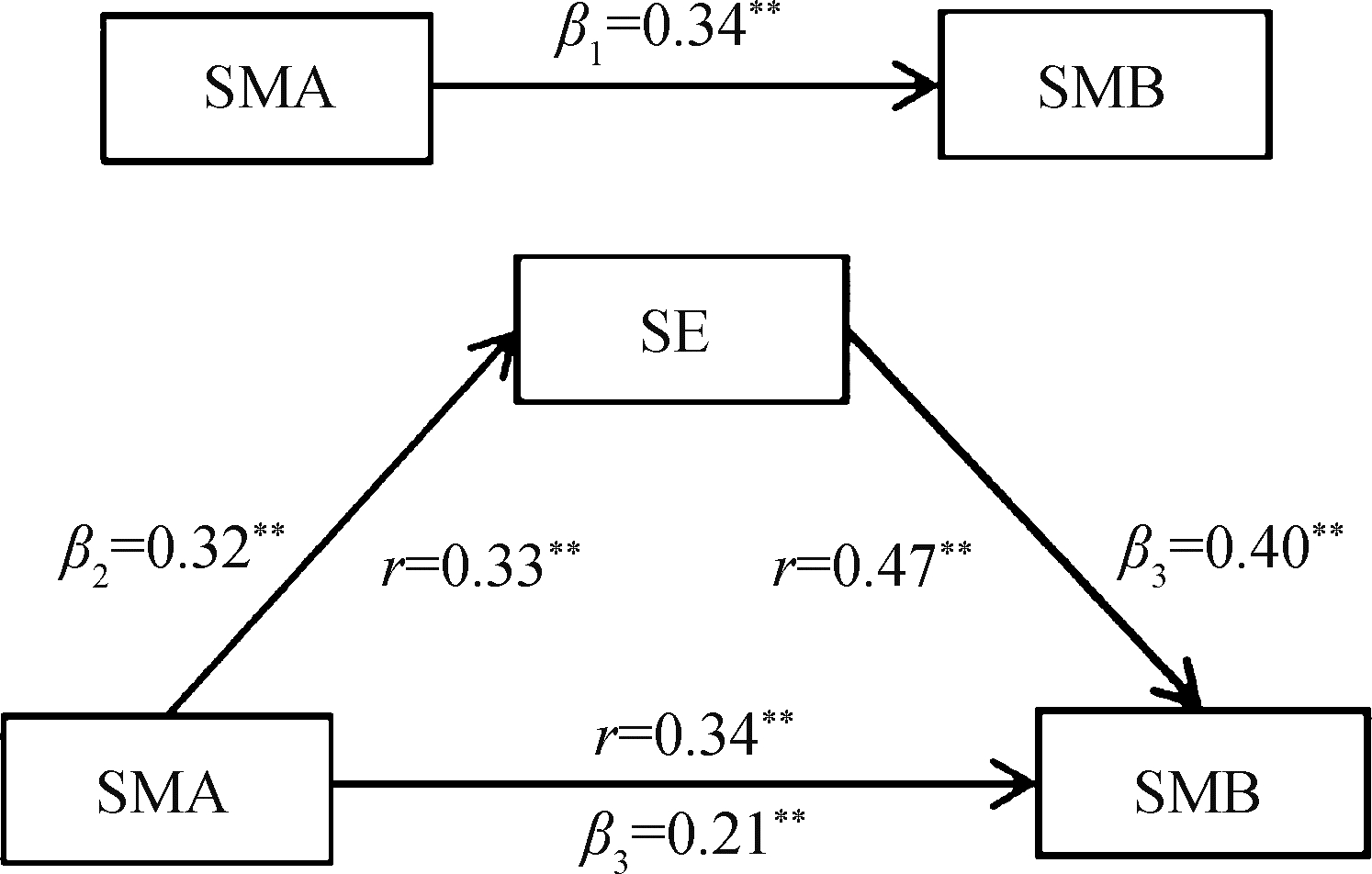
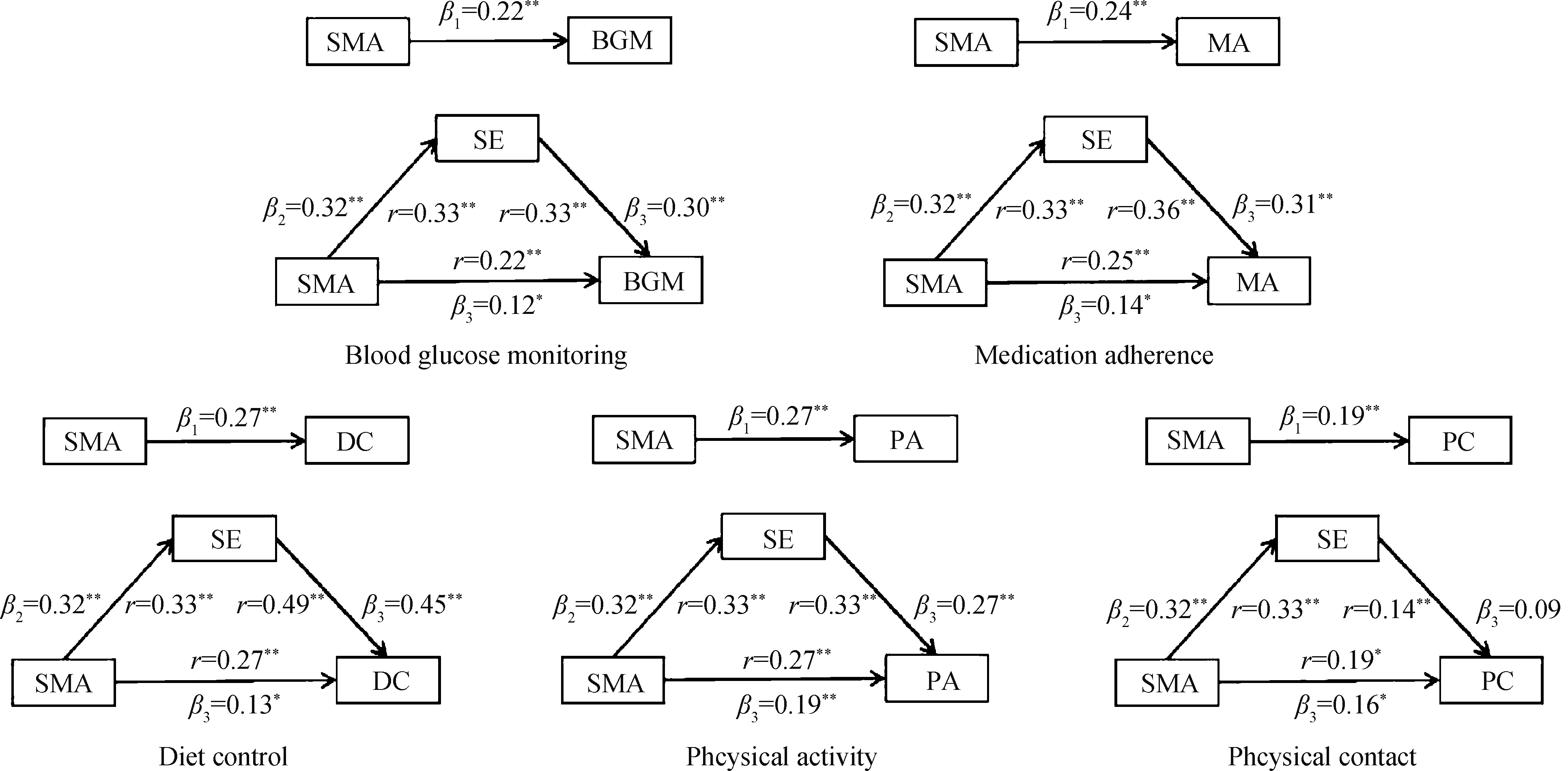
目的: 通过中介检验探究自我效能在自我管理能力和自我管理行为间的作用机制,及其在不同病程患者间的差异。方法: 以2022年7—9月在山西省、内蒙古自治区的四家医院内分泌科就诊的489例2型糖尿病患者为研究对象,通过一般资料调查表、糖尿病自我管理量表、中文版糖尿病授权简化量表、糖尿病自我效能量表进行调查。采用线性回归模型、Sobel检验、Bootstrap检验,在软件Stata 15.0中进行中介检验,并根据病程是否>5年,划分不同病程组别,进行亚组分析。结果: 2型糖尿病患者自我管理行为得分为6.16±1.41,自我管理能力得分为3.99±0.74,自我效能得分为7.05±1.90。自我效能与自我管理能力(r=0.33)以及自我管理行为(r=0.47)呈正相关(P均 < 0.01)。自我效能的中介效应在自我管理能力对自我管理行为的总效应中占38.28%,且在血糖监测(43.45%)和饮食控制(52.63%)行为中占比很高。病程≤ 5年的患者,自我效能的中介效应约占总效应的40.99%,而对于病程> 5年的患者,中介效应占总效应的39.20%。结论: 自我效能增强了自我管理能力对2型糖尿病患者行为的影响,并且对于病程较短患者来说,这种正向影响更显著。应针对患者的患病特征开展有针对性的健康教育,提升患者自我效能与自我管理能力,激发患者的内在行动力,促进其自我管理行为的养成,并形成疾病管理更加稳定、长效的机制。
中图分类号:
- R193.3
| 1 | American Diabetes Association .Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2020[J].Diabetes Care,2020,43(Suppl 1):S32-S36. |
| 2 | American Diabetes Association .Lifestyle management: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2019[J].Diabetes Care,2019,42(Suppl 1):S46-S60. |
| 3 | Burford SJ , Park S , Dawda P .Small data and its visualization for diabetes self-management: Qualitative study[J].JMIR Diabetes,2019,21(8):e10324. |
| 4 | 李至韬, 李玟, 费宇, 等.职业人群的糖尿病及糖尿病前期患病现状及影响因素分析[J].现代预防医学,2021,48(12):2161-2165. |
| 5 | 曹俊, 林琴, 付梦雪, 等.近10年我国糖尿病病人自我管理现状、热点与趋势的可视化分析[J].护理研究,2019,33(6):937-940. |
| 6 |
Funnell MM , Anderson RM , Arnold MS , et al.Empowerment: An idea whose time has come in diabetes education[J].Diabetes Educ,1991,17(1):37-41.
doi: 10.1177/014572179101700108 |
| 7 | 叶会玲.授权理论在糖尿病教育中的应用现状[J].护理研究,2010,24(2):97-100. |
| 8 |
King DK , Glasgow RE , Toobert DJ , et al.Self-efficacy, problem solving, and social-environmental support are associated with diabetes self-management behaviors[J].Diabetes Care,2010,33(4):751-753.
doi: 10.2337/dc09-1746 |
| 9 |
Lee AA , Piette JD , Heisler M , et al.Diabetes self-management and glycemic control: The role of autonomy support from informal health supporters[J].Health Psychol,2019,38(2):122-132.
doi: 10.1037/hea0000710 |
| 10 | 李超群, 井坤娟, 刘昱莹, 等.糖尿病自我管理量表的汉化及信效度评价[J].现代预防医学,2018,45(24):4477-4481. |
| 11 |
Ritter PL , Lorig K , Laurent DD .Characteristics of the Spanish- and English-language self-efficacy to manage diabetes scales[J].Diabetes Educ,2016,42(2):167-177.
doi: 10.1177/0145721716628648 |
| 12 | 刘红云, 温忠麟, 张雷, 等.中介效应检验程序及其应用[J].心理学报,2004,36(5):614-620. |
| 13 | Chiou S , Liao K , Lin K , et al.Using patient health profile evaluation for predicting the likelihood of retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study using latent profile analysis[J].Int J Environ Res Public Health,2022,19(10):6084. |
| 14 | Boussageon R , Pouchain D , Renard V .Prevention of complications in type 2 diabetes: Is drug glucose control evidence based?[J].Br J Gen Pract,2017,67(655):85-87. |
| 15 | 麻倩, 郭玉芳, 井坤娟.糖尿病患者自我管理现状及影响因素研究[J].现代预防医学,2019,46(5):915-920. |
| 16 | Lee Y , Shin S , Wang R , et al.Pathways of empowerment perceptions, health literacy, self-efficacy, and self-care behaviors to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Patient Educ Couns,2016,99(2):287-294. |
| 17 | van Smoorenburg AN , Hertroijs DFL , Dekkers T , et al.Patients' perspective on self-management: Type 2 diabetes in daily life[J].BMC Health Serv Res,2019,19(1):605. |
| 18 | 刘彩云, 尤莉莉.社会认知理论在促进糖尿病和糖尿病前期患者体力活动中的应用[J].中国健康教育,2021,37(11):1037-1040. |
| 19 | 丁贤彬, 张春华, 沈卓之, 等.健康自我管理对糖尿病患者不同自我效能的影响[J].实用预防医学,2016,23(11):1322-1325. |
| 20 | 张洁, 苏丹婷, 陆凤, 等.社区自我管理小组对糖尿病患者自我效能的远期影响研究[J].中国健康教育,2022,38(2):140-144. |
| [1] | 鲍雷,蔡夏夏,张明远,任磊磊. 维生素D3对2型糖尿病小鼠轻度认知障碍的改善作用及机制研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 587-592. |
| [2] | 于欢,杨若彤,王斯悦,吴俊慧,王梦莹,秦雪英,吴涛,陈大方,武轶群,胡永华. 2型糖尿病患者使用二甲双胍与缺血性脑卒中发病风险的队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 456-464. |
| [3] | 陈平,黎泽明,郭怡,孙昕霙,Edwin B.FISHER. 基于大五人格理论应用潜在剖面分析探究2型糖尿病患者的用药依从性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 530-535. |
| [4] | 黎泽明,高敏,陈雪莹,孙昕霙. 2型糖尿病患者大五人格特征与自我管理态度的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 506-513. |
| [5] | 谢江,李菲. 睡眠重叠综合征与糖尿病发病率的横断面调查研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 252-255. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 310
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 500
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||