北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 193-199. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.01.031
• 技术方法 • 上一篇
姿势微笑位口唇对称参考平面的数字化构建及初步应用验证
邱淑婷1,朱玉佳1,2,王时敏3,王飞龙1,叶红强1,赵一姣1,2,△( ),刘云松1,△(
),刘云松1,△( ),王勇1,2,周永胜1
),王勇1,2,周永胜1
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院 修复科,北京 100081
2.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院 口腔医学数字化研究中心,北京 100081
3.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院 义齿加工中心,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Preliminary clinical application verification of complete digital workflow of design lips symmetry reference plane based on posed smile
QIU Shu-ting1,ZHU Yu-jia1,2,WANG Shi-min3,WANG Fei-long1,YE Hong-qiang1,ZHAO Yi-jiao1,2,△( ),LIU Yun-song1,△(
),LIU Yun-song1,△( ),WANG Yong1,2,ZHOU Yong-sheng1
),WANG Yong1,2,ZHOU Yong-sheng1
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
3. Center of Dental Laboratory, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
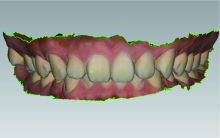
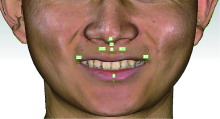
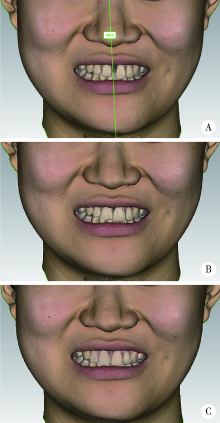
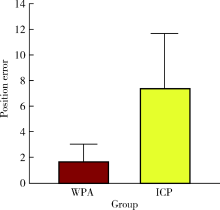
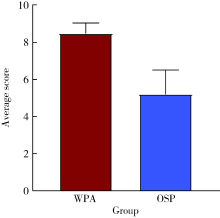
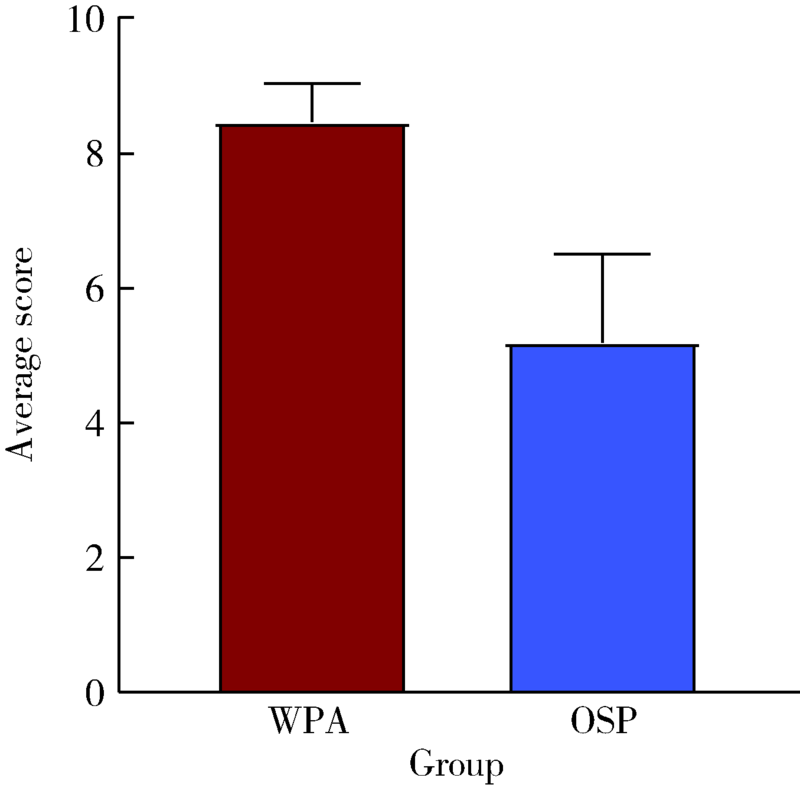
目的: 探索数字化技术构建姿势微笑(posed smile)位口唇对称参考平面(symmetry reference plane, SRP)的方法,实现姿势微笑位口唇SRP的自动化构建,并评价其初步应用效果。方法: 收集18名研究对象的三维面部和牙列数据,基于赋权普氏分析(weighted Procrustes analysis,WPA)算法和区域迭代最近点(iterative closest point,ICP)算法,分别构建每位受试者WPA算法和初学者ICP算法的姿势微笑位口唇SRP作为实验组,以专家定义的“真值平面(truth plane,TP)”作为对照组,比较WPA算法和初学者ICP算法确定的SRP与TP间的角度差异。将姿势微笑位下WPA算法自动获得的口唇SRP应用于前牙美学修复的数字化设计,进行临床初步应用评价。结果: 18名受试者姿势微笑位下WPA算法建立的口唇SRP与TP角度差异为1.78°±1.24°,初学者ICP算法建立的口唇SRP与TP角度差异为7.41°±4.31°,二者差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。在前牙美学设计时,参照姿势微笑位下WPA算法自动获得的口唇SRP进行前牙修复体美学设计,受试者评分为(8.48±0.57)分;常规数字化方案按照原有牙列对称平面进行修复体设计,受试者评分为(5.20±1.31)分,二者差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。结论: WPA算法自动构建的姿势微笑位口唇SRP较初学者ICP算法更准确,与“真值平面”非常相近,可以为口腔美学分析和设计提供重要参考,参照WPA算法自动构建的口唇SRP进行前牙修复体设计,能有效促进医患交流,提高患者对修复效果的满意度。
中图分类号:
- R783
| [1] |
Havens DC, Mcnamara JA, Sigler LM, et al. The role of the posed smile in overall facial esthetics[J]. Angle Orthod, 2010, 80(2):322-328.
doi: 10.2319/040409-194.1 pmid: 19905858 |
| [2] |
van der Geld P, Oosterveld P, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM. Age-related changes of the dental aesthetic zone at rest and during spontaneous smiling and speech[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2008, 30(4):366-373.
doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjn009 |
| [3] |
Kokich V. Esthetics and anterior tooth position: An orthodontic perspective. Part Ⅲ: Mediolateral relationships[J]. J Esthet Dent, 1993, 5(5):200-207.
pmid: 8037970 |
| [4] |
Haraguchi S, Iguchi Y, Takada K. Asymmetry of the face in orthodontic patients[J]. Angle Orthod, 2008, 78(3):421-426.
doi: 10.2319/022107-85.1 pmid: 18416611 |
| [5] |
O’Grady KF, Antonyshyn OM. Facial asymmetry: Three-dimensional analysis using laser surface scanning[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1999, 104(4):928-937.
doi: 10.1097/00006534-199909020-00006 |
| [6] |
Momi ED, Chapuis J, Pappas I, et al. Automatic extraction of the mid-facial plane for cranio-maxillofacial surgery planning[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2006, 35(7):636-642.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2006.01.028 |
| [7] |
Du S, Xu Y, Wan T, et al. Robust iterative closest point algorithm based on global reference point for rotation invariant registration[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(11):e0188039.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188039 |
| [8] |
Verhoeven TJ, Nolte JW, Maal TJJ, et al. Unilateral condylar hyperplasia: A 3-dimensional quantification of asymmetry[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(3):e59391.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059391 |
| [9] |
Gateno J, Jajoo A, Nicol M, et al. The primal sagittal plane of the head: A new concept[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2016, 45(3):399-405.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2015.11.013 |
| [10] |
Chetverikov D, Stepanov D, Krsek P. Robust Euclidean alignment of 3D point sets: The trimmed iterative closest point algorithm[J]. Image Vis Comput, 2005, 23(3):299-309.
doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2004.05.007 |
| [11] | 朱玉佳, 赵一姣, 郑盛文, 等. 基于赋权形态学分析的三维面部对称参考平面构建方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1):220-226. |
| [12] | 李立美, 李风兰, 杨红霞. 140名山西籍青年人微笑美学定性指标初步分析[J]. 口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2021, 22(2):129-133. |
| [13] | 徐成华, 王蕴红, 谭铁牛. 三维人脸建模与应用[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2004, 9(8):1-11. |
| [14] | 刘云松, 叶红强, 谷明, 等. 患者参与的数字化设计在前牙美学修复中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(1):90-94. |
| [15] |
Zhao JM, Ji LL, Han MQ, et al. Lip morphology estimation models based on three-dimensional images in a modern adult population from China[J]. Int J Legal Med, 2021, 135(5):1887-1901.
doi: 10.1007/s00414-021-02559-2 |
| [16] |
Zhu Y, Zheng S, Yang G, et al. A novel method for 3D face symmetry reference plane based on weighted Procrustes analysis algorithm[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2020, 20(1):319.
doi: 10.1186/s12903-020-01311-3 |
| [17] | 叶红强, 柳玉树, 王冠博, 等. 三维数字化仿真设计与实现技术在前牙美学修复中的应用[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2020, 55(10):729-736. |
| [18] | 骆小平. 数字化技术在牙科全瓷美学修复中的应用[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志, 2017, 10(8):449-451. |
| [19] |
McNamara L, McNamara JA Jr, Ackerman MB, et al. Hard- and soft-tissue contributions to the esthetics of the posed smile in growing patients seeking orthodontic treatment[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2008, 133(4):491-499.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.05.042 |
| [20] | 王时敏, 李峥, 王冠博, 等. 全程数字化夜磨牙保护牙合垫的制作和初步应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1):105-110. |
| [21] |
Sun KM, Joo LE, Song IJ, et al. The location of midfacial landmarks according to the method of establishing the midsagittal reference plane in three-dimensional computed tomography analysis of facial asymmetry[J]. Imaging Sci Dent, 2015, 45(4):227-232.
doi: 10.5624/isd.2015.45.4.227 |
| [22] |
Young CK. Analysis of facial asymmetry[J]. Arch Craniofac Surg, 2015, 16(1):1-10.
doi: 10.7181/acfs.2015.16.1.1 pmid: 28913211 |
| [23] | 黄佳梦, 李娟, 林军. 面部不对称畸形评估的研究进展[J]. 中国医疗美容, 2019, 9(6):121-128. |
| [24] | 米雁翎, 西文琼, 邓延伟, 等. 骨性Ⅲ类错伴骨性偏颌的正畸-正颌联合治疗[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2019, 54(6):391-395. |
| [25] | 胡祥莹, 肖燕, 王璧霞, 等. 成人错牙合畸形患者正颌手术治疗决策的质性研究[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2019, 28(5):513-517. |
| [26] |
Silva BP, Jiménez-Castellanos E, Finkel S, et al. Layperson’s preference regarding orientation of the transverse occlusal plane and commissure line from the frontal perspective[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2016, 117(4):513-516.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2016.07.027 |
| [27] |
Silva BP, Mahn E, Stanley K, et al. The facial flow concept: An organic orofacial analysis, the vertical component[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2018, 121(2):189-194.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2018.03.023 |
| [28] | Koseoglu M, Bayindir F. Effect of variations in facial flow curves on the perceptions of smile esthetics by laypeople [J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2021, S0022-3913(21)00320-6. |
| [29] |
Gibelli D, Pucciarelli V, Poppa P, et al. Three-dimensional facial anatomy evaluation: Reliability of laser scanner consecutive scans procedure in comparison with stereophotogrammetry[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2018, 46(10):1807-1813.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2018.07.008 |
| [30] |
Wu J, Heike C, Birgfeld C, et al. Measuring symmetry in children with unrepaired cleft lip: Defining a standard for the three-dimensional midfacial reference plane[J]. Cleft Palate Craniofac J, 2016, 53(6):695-704.
doi: 10.1597/15-053 |
| [31] | 卢长宝, 黄桂艳. 过多选择效应:概念演化、发生前提及行为决策机制[J]. 北京工商大学学报(社会科学版), 2017, 32(5):108-117. |
| [1] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [2] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | 唐祖南,胡耒豪,陈震,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 增强现实技术在口腔颌面颈部解剖识别中的应用评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 541-545. |
| [4] | 吕梁,张铭津,温奧楠,赵一姣,王勇,李晶,杨庚辰,柳大为. 应用三维软组织空间线角模板法评价颏部对称性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [5] | 毛渤淳,田雅婧,王雪东,李晶,周彦恒. 骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后的面部软硬组织变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [6] | 凌晓彤,屈留洋,郑丹妮,杨静,闫雪冰,柳登高,高岩. 牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [7] | 徐心雨,吴灵,宋凤岐,李自力,张益,刘筱菁. 基于下颌运动轨迹的正颌外科术中下颌骨髁突定位方法及初步精度验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [8] | 李穗,马雯洁,王时敏,丁茜,孙瑶,张磊. 上前牙种植单冠修复体切导的数字化设计正确度[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [9] | 刘毅,袁昌巍,吴静云,沈棋,肖江喜,赵峥,王霄英,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 靶向穿刺+6针系统穿刺对PI-RADS 5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [10] | 袁昌巍,李德润,李志华,刘毅,山刚志,李学松,周利群. 多参数磁共振成像中动态对比增强状态在诊断PI-RADS 4分前列腺癌中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [11] | 刘颖,霍然,徐慧敏,王筝,王涛,袁慧书. 磁共振血管壁成像评估颈动脉中重度狭窄患者斑块特征与脑血流灌注的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [12] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [13] | 刘想,谢辉辉,许玉峰,张晓东,陶晓峰,柳林,王霄英. 人工智能对提高放射科住院医生诊断胸部肋骨骨折一致性的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 670-675. |
| [14] | 黄莹,吴志远,周行红,蔡志刚,张杰. 股前外侧皮瓣修复上颌骨缺损术后面部软组织对称性感观分级[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [15] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
|
||