北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 106-110. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.01.017
应用三维软组织空间线角模板法评价颏部对称性
吕梁1,张铭津1,温奧楠2,3,赵一姣2,3,王勇2,3,李晶1,杨庚辰1,柳大为1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院正畸科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔医学数字化研究中心,口腔修复教研室,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,北京 100081
3. 北京大学医学部医学技术研究院,北京 100191
Preliminary evaluation of chin symmetry with three dimentional soft tissue spatial angle wireframe template
Liang LYU1,Mingjin ZHANG1,Aonan WEN2,3,Yijiao ZHAO2,3,Yong WANG2,3,Jing LI1,Gengchen YANG1,Dawei LIU1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Orthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digi-tal Medical Devices, Beijing 100081, China
2. Center of Digital Dentistry, Faculty of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digi-tal Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry, Beijing 100081, China
3. Institute of Medical Technology, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
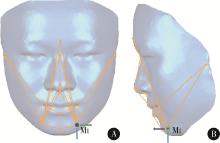
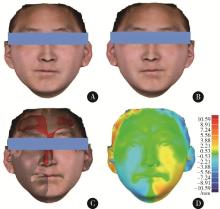
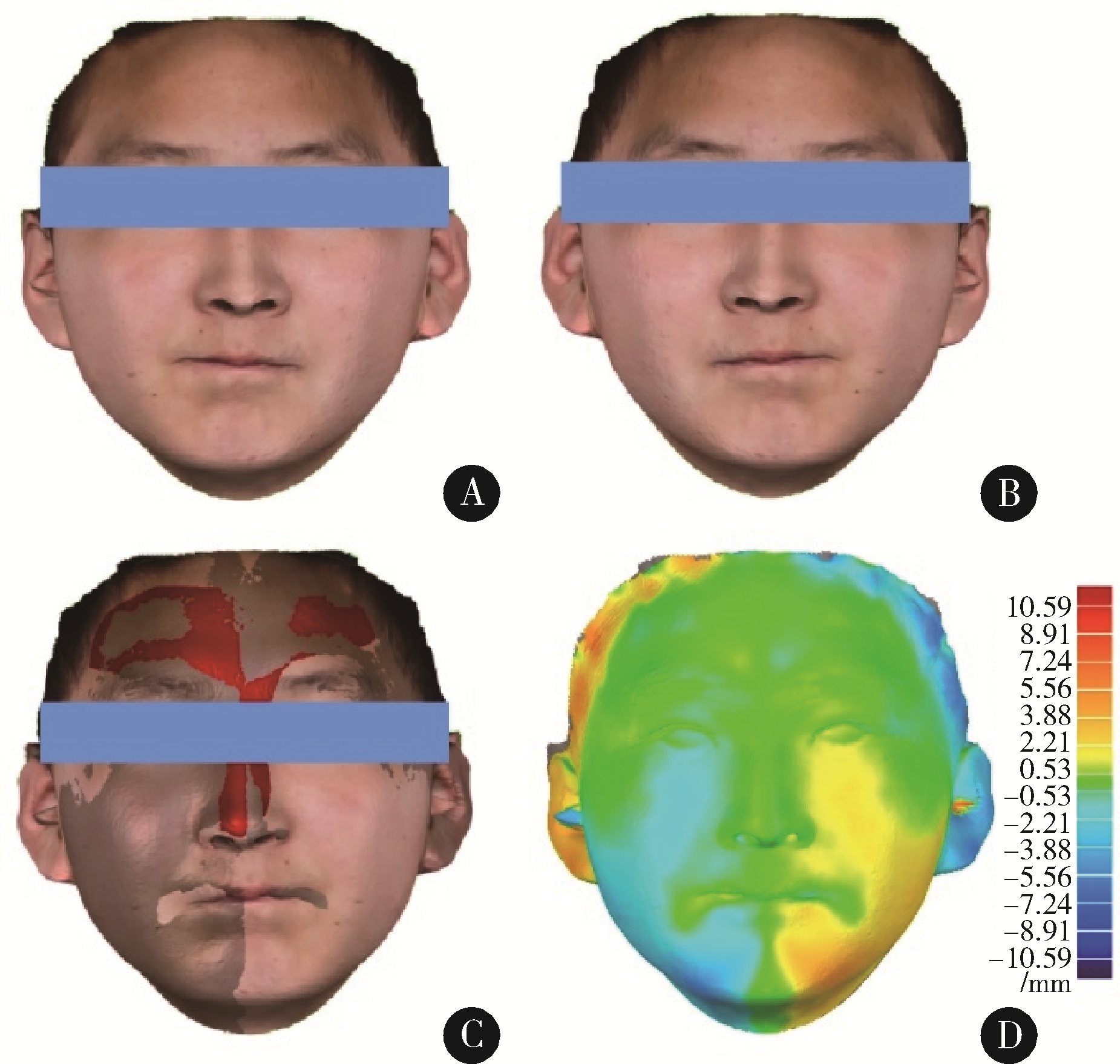
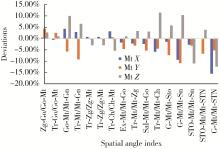
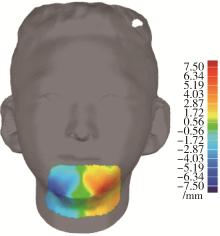
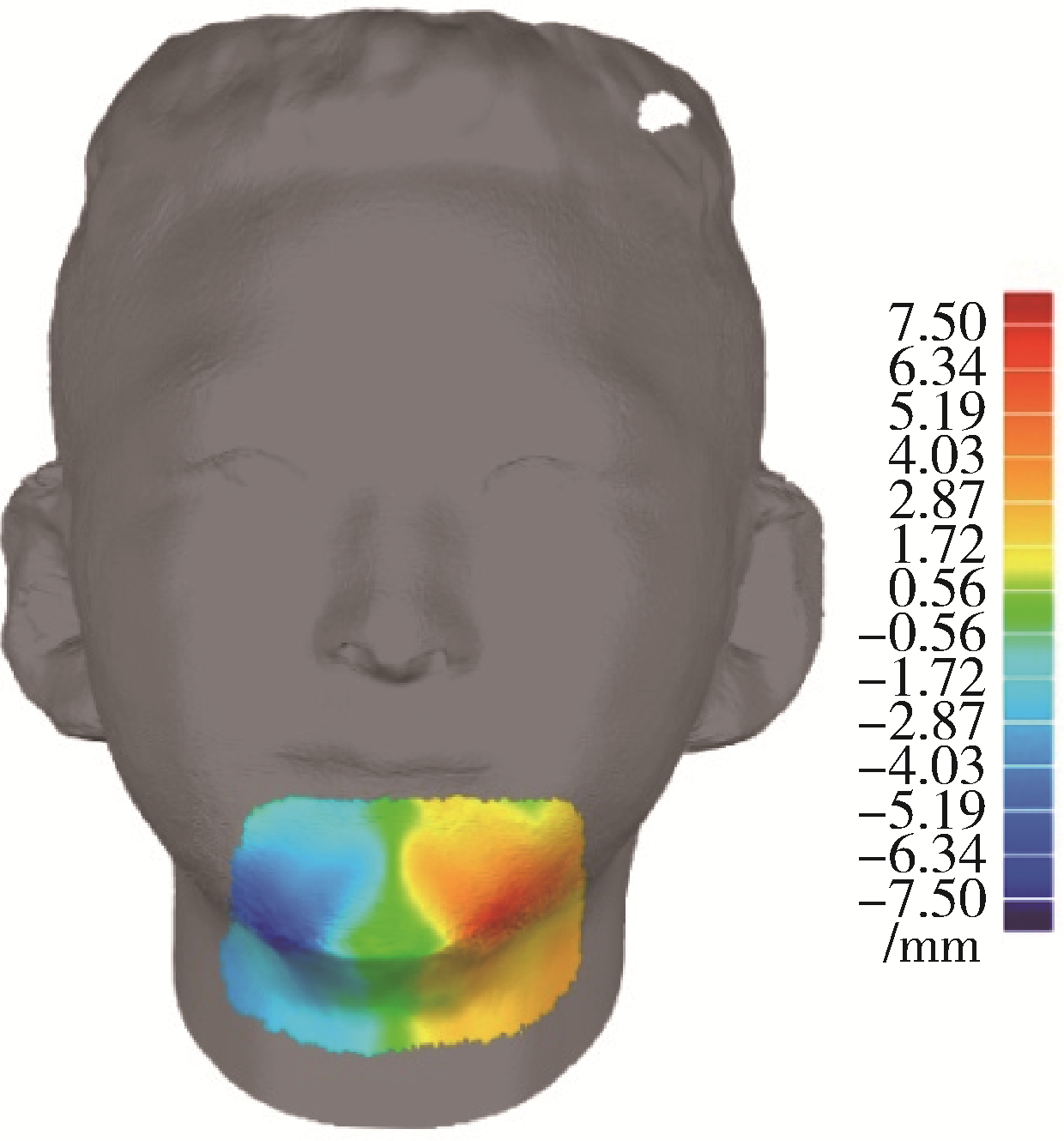
目的: 探讨建立一种基于三维颜面软组织标志点的颏部对称性评价方法, 并对该方法的评价效果进行初步检验。方法: 使用标准对称人脸进行颏结节点坐标变换, 用以筛选软组织三维空间线角并构建相应的三维空间线角模板, 从2021年3月至2022年3月就诊于北京大学口腔医院正畸科的初诊患者中选取10例临床诊断存在颏部不对称的患者, 年龄12~32岁; 收集患者的三维软组织面部扫描数据, 通过MeshMonk非刚性配准算法程序自动确定测试患者面部扫描数据的标志点, 并以此生成三维软组织空间线角模板及相应参数。同时在Geomagic Studio 2015软件中进行人脸镜像重叠分析, 并生成颏部偏差色谱图作为检验参照, 对比三维软组织空间线角模板指标相对于重叠分析的识别率。结果: 通过坐标变换方式筛选三维空间线角指标9项, 在10例患者中对其面部扫描数据进行镜像重叠分析和三维空间线角模板分析, 以镜像重叠为"金标准", 计算用三维软组织空间线角模板分析法评价颏部不对称情况的识别率, 颏部不对称识别率为90%(9/10), 其中X维度识别率为86%, Y维度识别率为89%, Z维度识别率为100%。结论: 应用三维软组织线角模板法在评价颏部软组织不对称上有一定的可行性, 其在三维方向上具有分别识别不同维度不对称的能力, 优于镜像重叠方法, 但在识别率方面稍差, 仍需进一步改进和优化。
中图分类号:
- R783.5
| 1 | Yarosh DB . Perception and deception: Human beauty and the brain[J]. Behav Sci (Basel), 2019, 9 (4): 34. |
| 2 | Matthews H , de Jong G , Maal T , et al. Static and motion facial analysis for craniofacial assessment and diagnosing diseases[J]. Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci, 2022, 10 (5): 19- 42. |
| 3 | 邵祯.颏部美容整形进展在面部轮廓整形中的应用[C].成都: 中国中西医结合学会医学美容学术年会暨第二届泛亚国际医学美容大会, 2016. |
| 4 | 何颖, 郭传瑸, 邓旭亮, 等. 北方正常HE人群颅颌面三维比例测量及面部对称性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47 (4): 708- 713. |
| 5 | 孟宪.青少年临界病例非拔牙矫治前后颏部变化的分析[D].大连: 大连医科大学, 2014. |
| 6 | 沈舜尧.偏突颌畸形患者正颌手术前后软硬组织对称性的三维评价[D].上海: 上海交通大学, 2012. |
| 7 | 沈刚. 偏颌与颜面不对称畸形的诊断, 分类及临床意义[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2021, 30 (1): 1- 6. |
| 8 |
Blasi A , Nucera R , Ronsivalle V , et al. Asymmetry index for the photogrammetric assessment of facial asymmetry[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2022, 162 (3): 394- 402.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2021.04.030 |
| 9 |
Choi JW , Park H , Kim BS , et al. Surgery-first orthognathic approach to correct facial asymmetry: Artificial intelligence-based cephalometric analysis[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2022, 149 (3): 496- 499.
doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000008818 |
| 10 |
Ercan I , Ozdemir ST , Etoz A , et al. Facial asymmetry in young healthy subjects evaluated by statistical shape analysis[J]. J Anat, 2008, 213 (6): 663- 669.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2008.01002.x |
| 11 |
Ferrario VF , Sforza C , Ciusa V , et al. The effect of sex and age on facial asymmetry in healthy subjects: A cross-sectional study from adolescence to mid-adulthood[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2001, 59 (4): 382- 388.
doi: 10.1053/joms.2001.21872 |
| 12 |
Zhu YJ , Zhao YJ , Wang Y . A review of three-dimensional facial asymmetry analysis methods[J]. Symmetry, 2022, 14 (7): 1414.
doi: 10.3390/sym14071414 |
| 13 |
Lum V , Goonewardene MS , Mian A , et al. Three-dimensional assessment of facial asymmetry using dense correspondence, symmetry, and midline analysis[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2020, 158 (1): 134- 146.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2019.12.014 |
| 14 | 温奥楠, 朱玉佳, 郑盛文, 等. 基于三维人脸模板的颜面解剖标志点自动定点方法初探[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2022, 57 (4): 358- 365. |
| 15 |
Fan Y , He W , Chen G , et al. Facial asymmetry assessment in skeletal Class Ⅲ patients with spatially-dense geometric morphometrics[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2022, 44 (2): 155- 162.
doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjab034 |
| 16 | 刘静, 葛胜将, 宋宇. 成年骨性下颌偏斜患者颏部形态对称性的锥形束CT分析[J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2015, 23 (4): 182- 185. |
| 17 | 程家龙.颌骨偏斜的三维分析, 分类及手术模拟研究[D].天津: 天津医科大学, 2017. |
| 18 |
Bollen AM . Cephalometry in orthodontics: 2D and 3D[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop, 2019, 156 (1): 161.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2019.04.021 |
| 19 |
Djordjevic J , Toma AM , Zhurov AI , et al. Three-dimensional quantification of facial symmetry in adolescents using laser surface scanning[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2014, 36 (2): 125- 132.
doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjr091 |
| 20 |
Ferrario VF , Sforza C , Dellavia C , et al. A quantitative three-dimensional assessment of soft tissue facial asymmetry of cleft lip and palate adult patients[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2003, 14 (5): 739- 746.
doi: 10.1097/00001665-200309000-00026 |
| 21 |
Nakamura N , Okawachi T , Nozoe E , et al. Three-dimensional analyses of nasal forms after secondary treatment of bilateral cleft lip-nose deformity in comparison to those of healthy young adults[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2011, 69 (11): e469- e481.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2011.03.041 |
| 22 |
Dong Y , Zhao Y , Bai S , et al. Three-dimensional anthropometric analysis of the Chinese nose[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2010, 63 (11): 1832- 1839.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2009.11.035 |
| 23 |
Dong Y , Zhao Y , Bai S , et al. Three-dimensional anthropometric analysis of chinese faces and its application in evaluating facial deformity[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2011, 69 (4): 1195- 1206.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2010.05.023 |
| 24 |
Zhang MJ , Lyu L , Li J , et al. Subjective evaluation of facial asymmetry with three-dimensional simulated images among the orthodontists and laypersons: A cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2023, 23 (1): 500.
doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03167-9 |
| 25 | Zhu Y , Fu X , Zhang L , et al. A mathematical algorithm of the facial symmetry plane: Application to mandibular deformity 3D facial data[J]. J Anat, 2022, 240 (3): 556- 566. |
| [1] | 唐祖南,胡耒豪,陈震,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 增强现实技术在口腔颌面颈部解剖识别中的应用评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 541-545. |
| [2] | 毛渤淳,田雅婧,王雪东,李晶,周彦恒. 骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后的面部软硬组织变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [3] | 凌晓彤,屈留洋,郑丹妮,杨静,闫雪冰,柳登高,高岩. 牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [4] | 黄莹,吴志远,周行红,蔡志刚,张杰. 股前外侧皮瓣修复上颌骨缺损术后面部软组织对称性感观分级[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [5] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [6] | 欧蒙恩,丁云,唐卫峰,周永胜. 基台边缘-牙冠的平台转移结构中粘接剂流动的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
| [7] | 温奥楠,刘微,柳大为,朱玉佳,萧宁,王勇,赵一姣. 5种椅旁三维颜面扫描技术正确度的初步评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 343-350. |
| [8] | 熊士凯,史尉利,王安鸿,谢兴,郭秦炜. 腓骨远端撕脱骨折的影像学诊断:踝关节X线与CT三维重建的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 156-159. |
| [9] | 高梓翔,王勇,温奥楠,朱玉佳,秦庆钊,张昀,王晶,赵一姣. 基于三维下颌骨平均模型的颌骨标志点自动确定方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 174-180. |
| [10] | 邢海英,陈玉辉,许珂,黄点点,彭清,刘冉,孙葳,黄一宁. 三维超声血管斑块定量分析技术评估颈动脉粥样硬化斑块[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 991-999. |
| [11] | 李志胜,钱浩楠,范田园. 熔融沉积成型3D打印卡托普利与氢氯噻嗪复方片剂的制备与体外评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 572-577. |
| [12] | 刘云松,周倜,叶红强. 前牙美学修复的整体策略及细节剖析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 1-6. |
| [13] | 刘思民,赵一姣,王晓燕,王祖华. 动态导航下不同深度环钻定位精确度的体外评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 146-152. |
| [14] | 邱淑婷,朱玉佳,王时敏,王飞龙,叶红强,赵一姣,刘云松,王勇,周永胜. 姿势微笑位口唇对称参考平面的数字化构建及初步应用验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 193-199. |
| [15] | 邵振兴,宋庆法,赵宇晴,崔国庆. 一种结合线袢固定的关节镜下“嵌入式”喙突移位术:手术技术及术后影像学分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 896-901. |
|
||