北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 111-119. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.01.018
骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后的面部软硬组织变化
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院正畸科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,北京 100081
Soft and hard tissue changes of hyperdivergent class Ⅱ patients before and after orthodontic extraction treatment
Bochun MAO,Yajing TIAN,Xuedong WANG*( ),Jing LI*(
),Jing LI*( ),Yanheng ZHOU
),Yanheng ZHOU
- Department of Orthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digi-tal Medical Devices, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
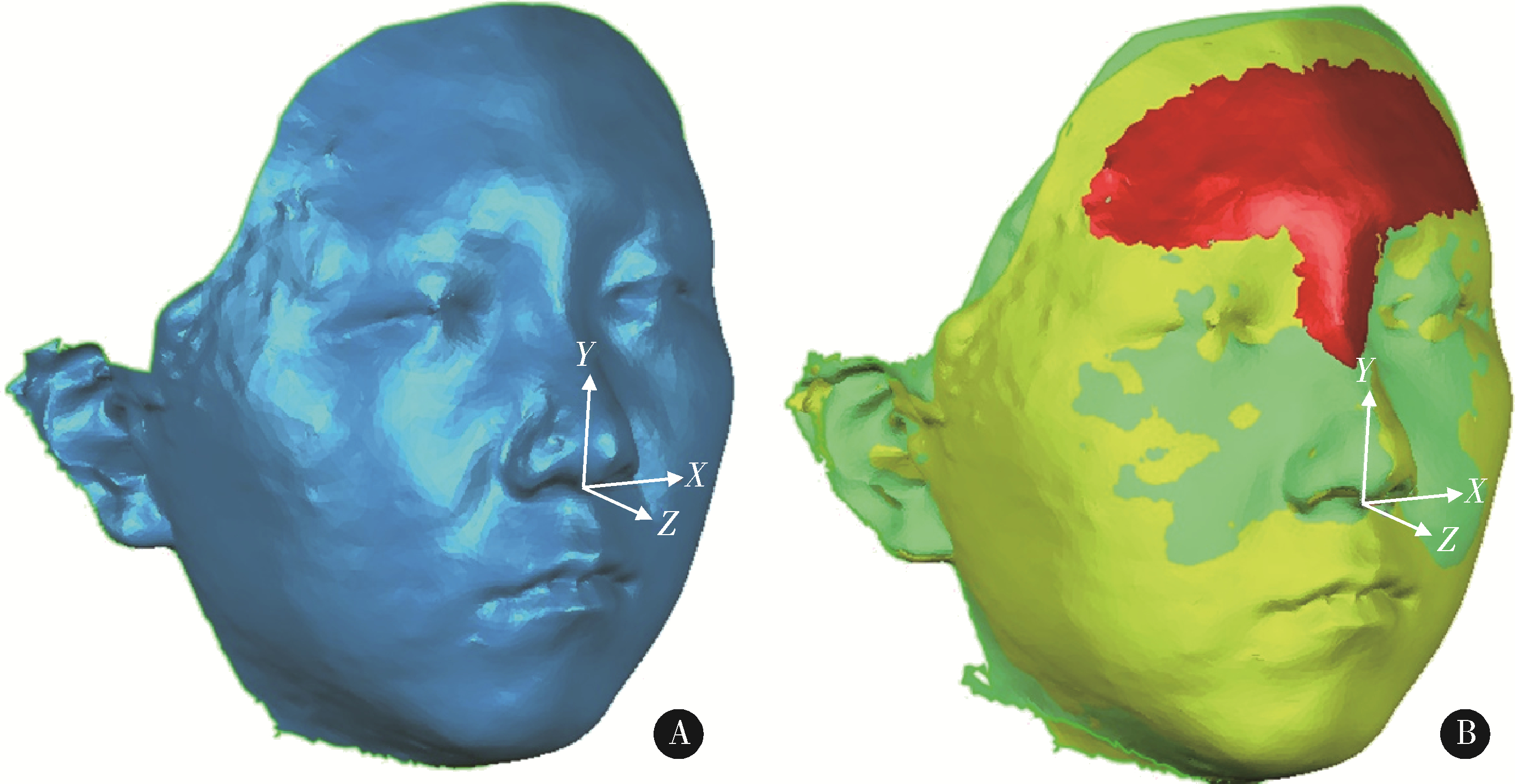
目的: 通过对骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后面部三维扫描模型与头颅侧位片进行测量分析, 探讨软硬组织变化趋势、影响因素及其作用。方法: 选取18例骨性Ⅱ类高角行单纯拔牙矫治的成人女性患者, 对矫治前后的头颅侧位片定点描记并进行硬组织测量, 同时获得纳入患者矫治前后三维颜面数据, 在完成模型重定位及模型重叠后, 对三维软组织标志点标定并测量相应三维软组织。硬组织测量包括17个测量指标(蝶鞍点-鼻根点-上齿槽座点的夹角、蝶鞍点-鼻根点-下齿槽座点的夹角、上齿槽座点-鼻根点-下齿槽座点间的夹角、面角、颌凸角、眶耳平面-下领平面角、Y轴角、前颅底平面-下颌平面角、颏前点到鼻根点-下齿槽座点连线的垂直距离、上中切牙到鼻根点-上齿槽座点连线的垂直距离、上中切牙与鼻根点-上齿槽座点的夹角、下中切牙到鼻根点-下齿槽座点连线的垂直距离、下中切牙与鼻根点-下齿槽座点连线交角、上下中切牙角、上切牙倾斜度、下中切牙-下颌平面角和Z角), 其中11个指标测量其治疗前后变化量。测量20个软组织标志点(左/右颧骨点、左/右口角点、左/右唇峰点、软组织颏顶点、左/右下颌角点、额点、下唇下缘点、上唇上缘点、软组织颏下点、左/右下颌边缘中点、软组织颏前点、口裂点、唇下点、鼻下点和上唇点)治疗前后三维位移量, 并取9项软组织测量指标(下唇高、面突角、下唇红高、下颌轮廓角、鼻唇角、人中长度、人中宽度、上唇高和上唇红高)。对矫治前后各指标变化量进行线性回归分析, 并运用Pearson系数分析各指标间相关性。结果: 矫治前后的硬组织及软组织20个测量指标中有18个测量值变化量差异有统计学意义(P<0.05), 主要变化表现为唇部的整体内收, 软组织颏前点存在垂直向的明显上移[(1.88±2.61) mm, P<0.05], 同时左/右口角点[(-2.95±1.9) mm、(-2.90±1.92) mm]、上下唇缘点[(-4.94±1.95) mm、(-3.25±1.44) mm]、唇下点[(-3.10±3.5) mm]、鼻下点[(-1.23±1.06) mm]在矢状向明显内收(P<0.05), 其他点差异无统计学意义; Z角平均增加4.10°±2.57°(P<0.05), 其他差异无统计学意义; 矫治后颏下点移动量与眶耳平面-下领平面角(比例为:-0.183 :1)、与前颅底平面-下领平面角(比例为:-0.157 :1)呈高度相关(r>0.7), 其余存在相关性的测量指标间呈中度相关(0.7≥r>0.4), 且差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论: 骨性Ⅱ类高角患者通过单纯拔牙矫治也可得到一定的面型改善, 主要表现为鼻、唇、颏三者矢状方向上关系的改善, 其软组织移动量与硬组织移动量间存在着一定的线性比例关系。
中图分类号:
- R783.5
| 1 |
Reis PMP , Lima P , Garcia FCP , et al. Effect of maxillary median diastema on the esthetics of a smile[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2020, 158 (4): E37- E42.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2020.07.028 |
| 2 | 施丹妮, 杨鑫, 吴建勇. 锥形束CT三维头影测量参考坐标系的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2021, 48 (4): 398- 404. |
| 3 |
Ferrario VF , Sforza C , Schmitz JH , et al. A three-dimensional computerized mesh diagram analysis and its application in soft tissue facial morphometry[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 1998, 114 (4): 404- 413.
doi: 10.1016/S0889-5406(98)70185-4 |
| 4 |
Xiao Z , Liu Z , Gu Y . Integration of digital maxillary dental casts with 3D facial images in orthodontic patients: A three-dimensional validation study[J]. Angle Orthod, 2020, 90 (3): 397- 404.
doi: 10.2319/071619-473.1 |
| 5 |
Janson G , Mendes LM , Junqueira CHZ , et al. Soft-tissue changes in class Ⅱ malocclusion patients treated with extractions: A systematic review[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2016, 38 (6): 631- 637.
doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjv083 |
| 6 |
Konstantonis D , Vasileiou D , Papageorgiou SN , et al. Soft tissue changes following extraction vs. nonextraction orthodontic fixed appliance treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Oral Sci, 2018, 126 (3): 167- 179.
doi: 10.1111/eos.12409 |
| 7 | 谢天伊, 贾绮林. 成年女性正畸患者颊颞部软组织变化的三维测量研究[J]. 中华口腔正畸学杂志, 2020, 27 (4): 181- 186. |
| 8 |
Lu WX , Zhang X , Mei L , et al. Orthodontic incisor retraction caused changes in the soft tissue chin area: A retrospective study[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2020, 20 (1): 108.
doi: 10.1186/s12903-020-01099-2 |
| 9 |
Tadic N , Woods MG . Incisal and soft tissue effects of maxillary premolar extraction in class Ⅱ treatment[J]. Angle Orthod, 2007, 77 (5): 808- 816.
doi: 10.2319/081706-336 |
| 10 |
Veltkamp T , Buschang PH , English JD , et al. Predicting lower lip and chin response to mandibular advancement and genioplasty[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2002, 122 (6): 627- 634.
doi: 10.1067/mod.2002.128864 |
| 11 |
Choi SH , Lee H , Hwang JJ , et al. Differences in soft-tissue thickness changes after bimaxillary surgery between patients with vertically high angle and normal angle[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2021, 159 (1): 30- 40.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2019.10.028 |
| 12 |
Holdaway RA . A soft-tissue cephalometric analysis and its use in orthodontic treatment planning. Part Ⅰ[J]. Am J Orthod, 1983, 84 (1): 1- 28.
doi: 10.1016/0002-9416(83)90144-6 |
| 13 |
Hodges A , Rossouw PE , Campbell PM , et al. Prediction of lip response to four first premolar extractions in white female adolescents and adults[J]. Angle Orthod, 2009, 79 (3): 413- 421.
doi: 10.2319/050208-247.1 |
| 14 |
Upadhyay M , Yadav S , Nagaraj K , et al. Treatment effects of mini-implants for en-mass eretraction of anterior teeth in bialveolar dental protrusion patients: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2008, 134 (1): 18- 29.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2007.03.025 |
| 15 |
Sivakumar A , Valiathan A . Cephalometric assessment of dentofacial vertical changes in class Ⅰ subjects treated with and without extraction[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2008, 133 (6): 869- 875.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.05.041 |
| [1] | 雷玥,杨颖婷,雷海华. 异位萌出诱导矫治器在第一恒磨牙异位萌出治疗中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 766-封三. |
| [2] | 付玉,胡鑫浓,崔圣洁,施捷. 骨性Ⅱ类高角错 |
| [3] | 高娟,吕航苗,马慧敏,赵一姣,李小彤. 锥形束CT三维体积测量评估骨性Ⅲ类错 |
| [4] | 杨雨卉,黄一平,李巍然. 骨皮质切开加速正畸牙齿移动对牙根吸收的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 434-437. |
| [5] | 周境,刘怡. 不同垂直骨面型骨性Ⅱ类青少年女性颞下颌关节锥形束CT测量分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 109-119. |
| [6] | 王高南,焦剑,周彦恒,施捷. 正畸牙齿位置的移动对角化龈宽度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 931-936. |
| [7] | 戴帆帆,刘怡,许天民,陈贵. 探索成人正畸前后下颌三维数字化模型的重叠方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 271-278. |
| [8] | 张又文,辛天艺,焦剑,周彦恒,施捷. 慢性牙周炎的减数正畸治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 308-313. |
| [9] | 柳玉树,李峥,赵一姣,叶红强,周彦秋,胡文杰,刘云松,寻春雷,周永胜. 数字化正畸修复联合治疗设计在前牙美学重建中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 78-84. |
| [10] | 柳大为,李晶,郭亮,荣起国,周彦恒. 舌侧矫治器关闭间隙上前牙牙周膜应力变化的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 141-147. |
| [11] | 张达,王林川,周彦恒,刘晓默,李晶. 3D打印间接粘接托槽精度[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 704-708. |
| [12] | 沈潇,施捷,徐莉,焦剑,路瑞芳,孟焕新. 伴错牙合畸形的侵袭性牙周炎患者牙周-正畸联合治疗的临床评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 60-066. |
| [13] | 郑旭,胡兴学,马宁,陈晓红. 正畸矫治牙性牙合平面倾斜的新方法——波浪形弓[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 176-180. |
| [14] | 温馥嘉,陈贵,刘怡. 基于锥形束CT的强支抗内收上前牙病例牙根及牙槽骨的形态学分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 702-708. |
| [15] | 黄俊强, 刘施瑶, 江久汇. Tweed-Merrifield技术矫治成人严重双颌前突的疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(3): 555-561. |
|
||