北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 853-859. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.016
18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用
- 1. 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科,风湿病机制及免疫诊断北京市重点实验室,北京 100044
2. 北京大学人民医院核医学科,北京 100044
Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases
Hua ZHONG1, Yuan LI2, Liling XU1, Mingxin BAI1, Yin SU1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People's Hospital; Beijing Key Laboratory for Rheumatism Mechanism and Immune Diagnosis, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
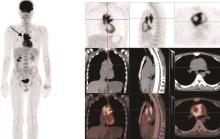
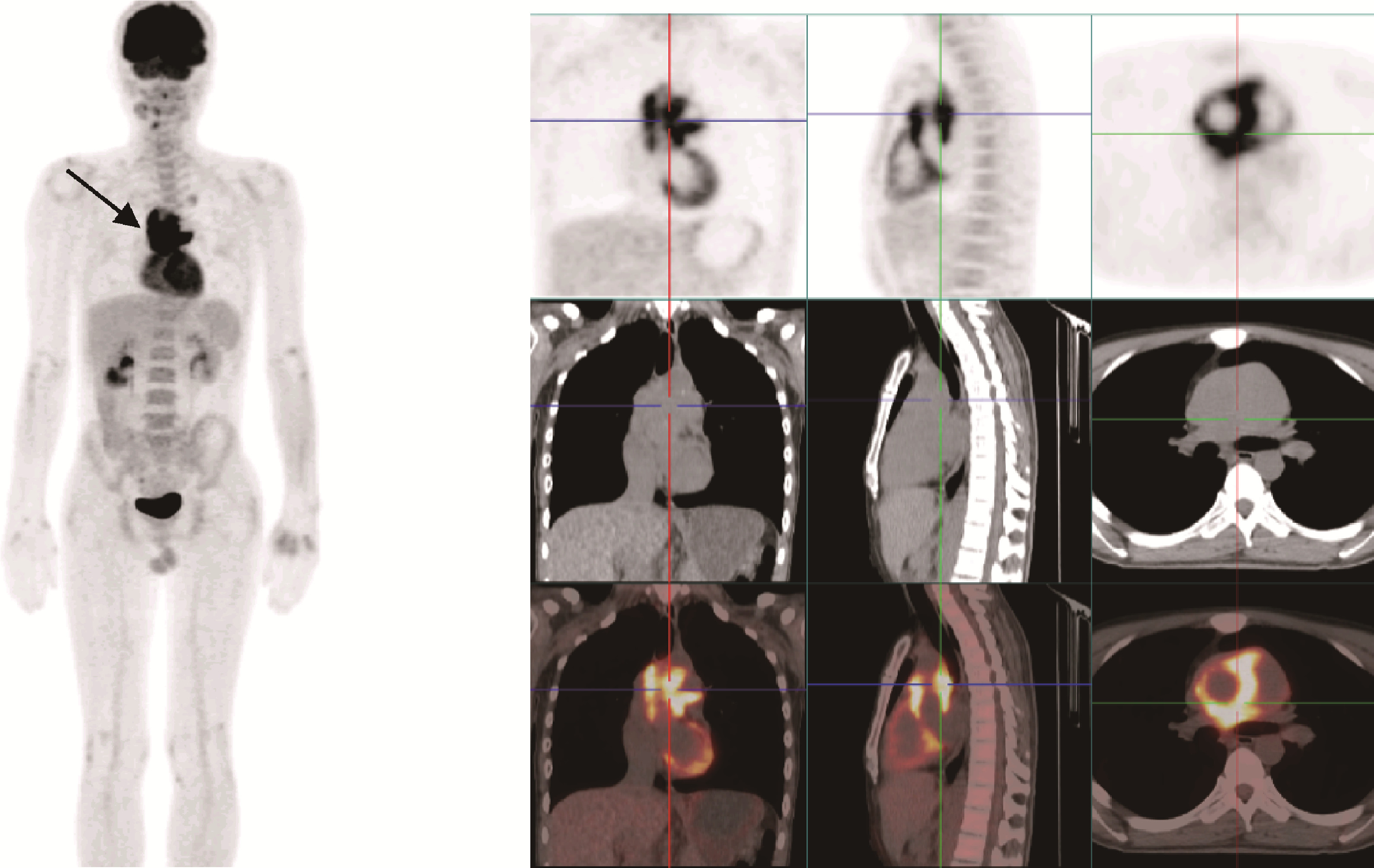
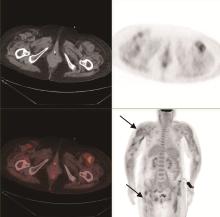
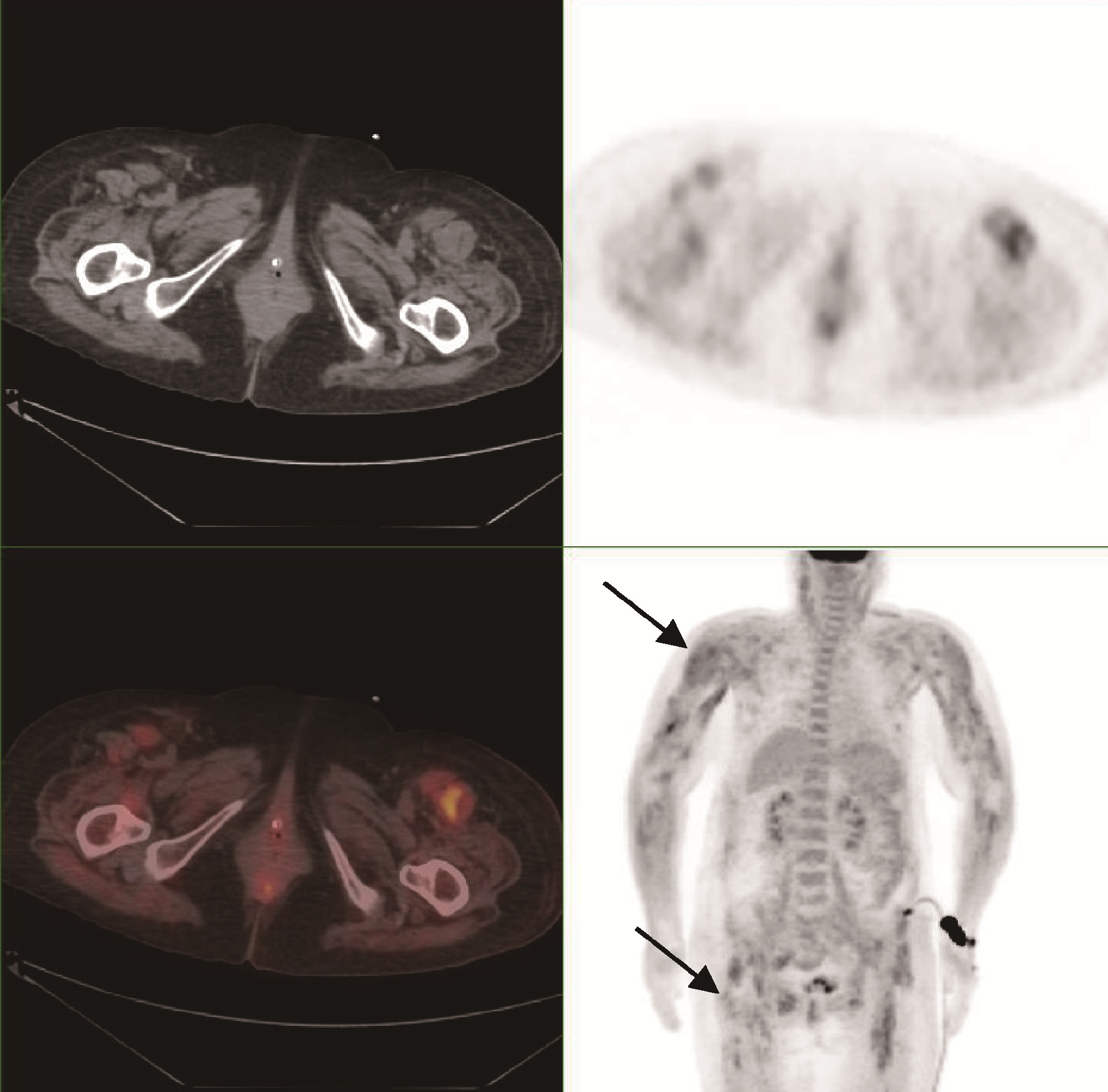
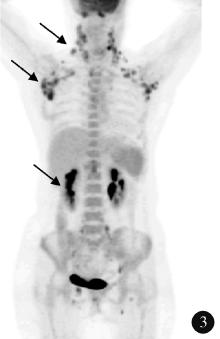
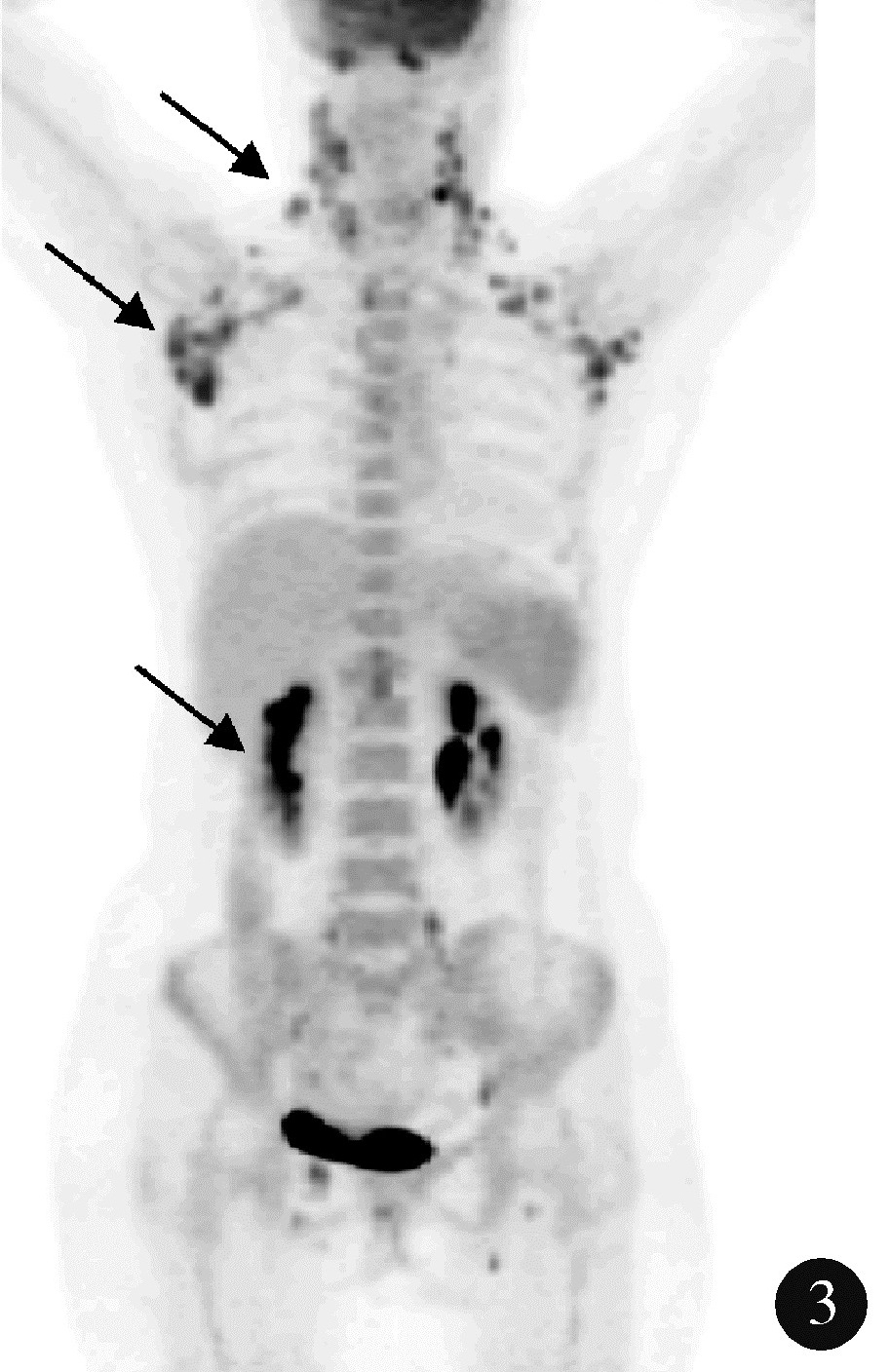
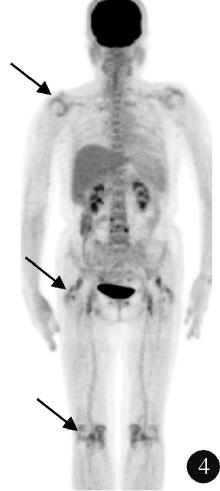
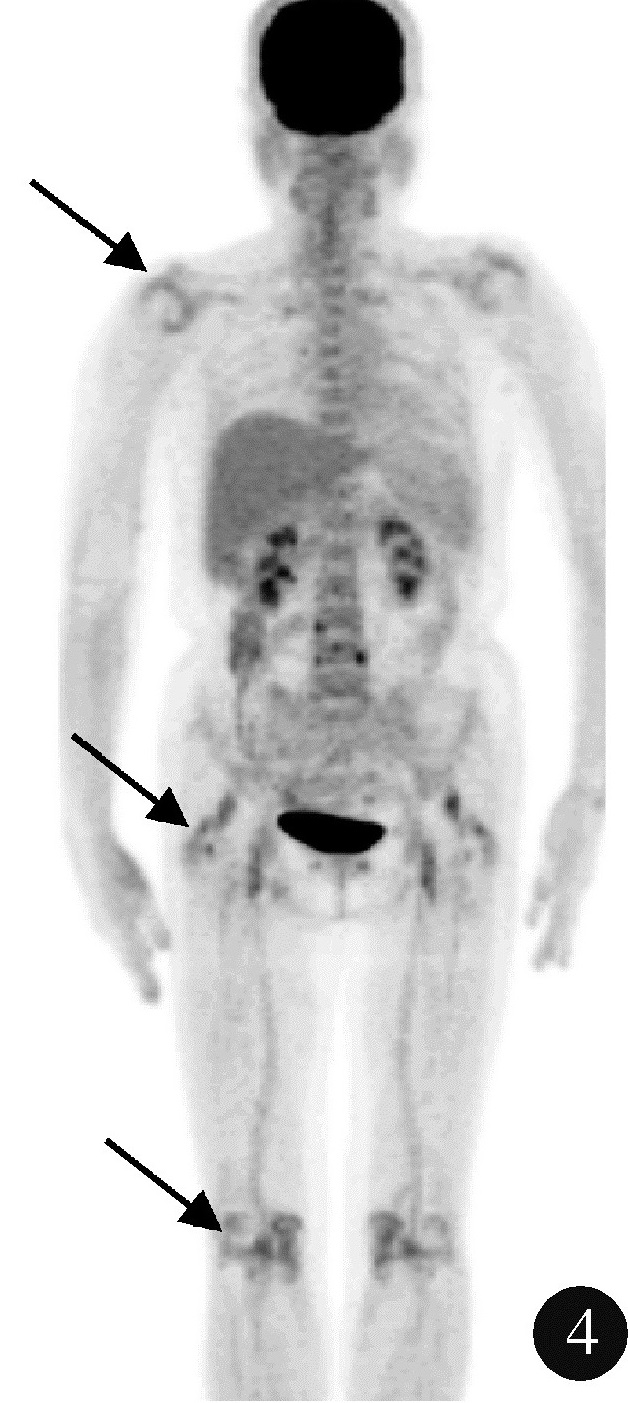
目的: 探索分析 18F-脱氧葡萄糖正电子发射断层显像/计算机体层扫描技术(18F-flurodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography, 18F-FDG PET/CT)在风湿免疫病中的应用现状。方法: 纳入2012年1月至2018年12月期间于北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科住院并进行 18F-FDG PET/CT检查的患者,回顾性分析 18F-FDG PET/CT检查技术在风湿免疫病中的临床应用情况及其影像学特征。结果: 共486例风湿免疫科的住院患者行 18F-FDG PET/CT检查,占全院行PET/CT检查总例数的5.30%,其中女性304例(62.55%),男性182例(37.45%),男女比例为1 ∶1.67,平均年龄(53.21±18.81)岁,45~65岁年龄段患者的比例(227/486,46.71%)最高。风湿免疫科患者行PET/CT检查的主要目的依次为排除肿瘤(55.56%)、协助明确诊断(24.60%)及评估病情(19.84%)。74例患者的PET/CT检查结果提示恶性肿瘤,327例患者提示风湿免疫病,其中292例对疾病的提示诊断具有参考作用,25例患者提示感染性疾病,60例患者的检查结果无明确提示意义。有10例风湿免疫病患者在治疗后复查PET/CT进行了随访,缓解病例的检查结果显示,18F-FDG代谢活性降低以及代谢增高病灶的范围缩小。结论: 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用日益广泛,尤其在排除恶性肿瘤方面具有重要价值,同时对疑难病例的辅助诊断具有一定参考作用。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 | Yamashita H , Kubota K , Mimori A . Clinical value of whole-body PET/CT in patients with active rheumatic diseases[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2014, 16 (5): 423. |
| 2 | Kubota K , Yamashita H , Mimori A . Clinical value of FDG-PET/CT for the evaluation of rheumatic diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, and relapsing polychondritis[J]. Semin Nucl Med, 2017, 47 (4): 408- 424. |
| 3 | 王冬艳, 杨彦松, 邵小南, 等. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿性疾病的初步应用[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2015, 23 (10): 759- 763. |
| 4 | Dejaco C , Ramiro S , Duftner C , et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in large vessel vasculitis in clinical practice[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2018, 77 (5): 636- 643. |
| 5 | Rehak Z , Sprlakova-Pukova A , Kazda T , et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT in polymyalgia rheumatica: A pictorial review[J]. Br J Radiol, 2017, 90 (1076): 20170198. |
| 6 | Ebbo M , Grados A , Guedj E , et al. Usefulness of 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography for staging and evaluation of treatment response in IgG4-related disease: A retrospective multicenter study[J]. Arthritis Care Res, 2014, 66 (1): 86- 96. |
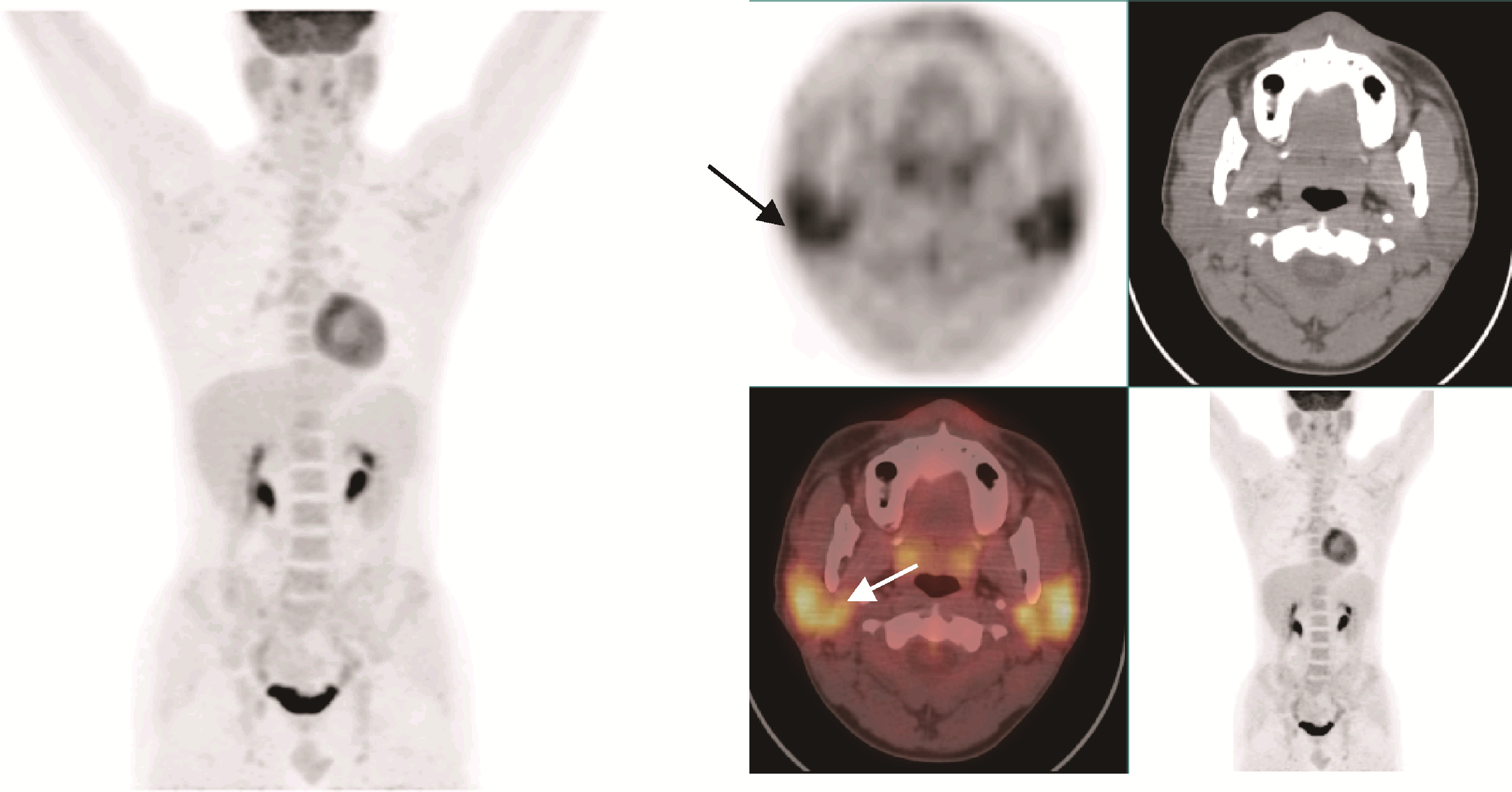
| 7 | Zhang J , Chen H , Ma Y , et al. Characterizing IgG4-related disease with 18F-FDG PET/CT: A prospective cohort study[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2014, 41 (8): 1624- 1634. |
| 8 | Martinez-Pimienta G , Noriega-álvarez E , Simó-Perdigó M . Study of systemic disease IgG4. Usefulness of 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography for staging, selection of biopsy site, evaluation of treatment response and follow-up[J]. Eur J Rheumatol, 2017, 4 (3): 222- 225. |
| 9 | Lee J , Hyun SH , Kim S , et al. Utility of FDG PET/CT for differential diagnosis of patients clinically suspected of IgG4-rela-ted disease[J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2016, 41 (5): 237- 243. |
| 10 | An YS , Suh CH , Jung JY , et al. The role of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the assessment of disease activity of adult-onset Still's disease[J]. Korean J Intern Med, 2017, 32 (6): 1082- 1089. |
| 11 | Yamashita H , Kubota K , Takahashi Y , et al. Clinical value of 18F-fluoro-dexoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in patients with adult-onset Still's disease: A seven-case series and review of the literature[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2014, 24 (4): 645- 650. |
| 12 | Yoo DH . Utility and drawbacks of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the evaluation of adult-onset Still's disease[J]. Korean J Intern Med, 2017, 32 (6): 998- 1001. |
| 13 | Sondag M , Guillot X , Verhoeven F , et al. Utility of 18F-fluoro-dexoxyglucose positron emission tomography for the diagnosis of polymyalgia rheumatica: A controlled study[J]. Rheumatology, 2016, 55 (8): 1452- 1457. |
| 14 | Takahashi H , Yamashita H , Kubota K , et al. Differences in fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography findings between elderly onset rheumatoid arthritis and polymyalgia rheumatica[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2015, 25 (4): 546- 551. |
| 15 | D'Agostino MA , Haavardsholm EA , van der Laken CJ . Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis; What is the current role of established and new imaging techniques in clinical practice?[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol, 2016, 30 (4): 586- 607. |
| 16 | Bhattarai A , Nakajima T , Sapkota S , et al. Diagnostic value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake parameters to differentiate rheumatoid arthritis from other types of arthritis[J]. Medicine, 2017, 96 (25): e7130. |
| 17 | Chaudhari AJ , Ferrero A , Godinez F , et al. High-resolution 18F-FDG PET/CT for assessing disease activity in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis: Findings of a prospective pilot study[J]. Br J Radiol, 2016, 89 (1063): 20160138. |
| 18 | Suto T , Okamura K , Yonemoto Y , et al. Prediction of large joint destruction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using 18F-FDG PET/CT and disease activity score[J]. Medicine, 2016, 95 (7): e2841. |
| 19 | Lee DH , Yoon JK , Yoon SH , et al. Physiologic facial muscle uptake on 18F-FDG PET/CT by chewing-like habitual movement in patient with Sjögren syndrome[J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2015, 40 (3): 268- 269. |
| 20 | Sharma P , Chatterjee P . 18F-FDG PET/CT in multisystem Sjögren syndrome[J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2015, 40 (5): 293- 294. |
| [1] | 彭清,刘佳君,刘焱,尚华,唐果,韩雅欣,龙丽. Padua预测评分和血清白蛋白水平在评估风湿病住院患者静脉血栓栓塞中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 625-630. |
| [2] | 哈雪梅,姚永正,孙莉华,辛春杨,熊焰. 实性肺胎盘样变形1例及文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [3] | 张旭初,张建华,王荣福,范岩,付占立,闫平,赵光宇,白艳霞. 18F-FDG PET/CT联合多种肿瘤标志物在结直肠中分化腺癌术后复发及转移中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1071-1077. |
| [4] | 卢昕,张立宁. 肌活检在特发性炎性肌病诊断和临床分型中的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 949-951. |
| [5] | 康磊, 徐小洁, 范岩, 王荣福, 马超, 付占立, 张建华, 张旭初. 18F-FDG PET/CT在不明原因发热中的诊断价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(1): 175-180. |
| [6] | 张卓莉, 邓雪蓉. 肌肉骨骼超声在风湿性疾病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(6): 828-830. |
| [7] | 栗占国. 风湿性疾病的规范化治疗势在必行[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2006, 38(4): 341-344. |
|
||