北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (6): 1089-1095. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.06.011
中轴型脊柱关节炎合并髋关节终末期受累的长期影像学参数:单中心24年大样本回顾研究
吴昕峰1,*, 满斯亮2,*, 陈大召3, 华勇4, 温锡杰5, 丁盈月2, 张亮3,*( ), 侯秀娟6,*(
), 侯秀娟6,*( )
)
- 1. 首都医科大学附属北京积水潭医院脊柱外科,北京 100035
2. 首都医科大学附属北京积水潭医院风湿免疫科,北京 100035
3. 首都医科大学附属北京积水潭医院矫形骨科,北京 100035
4. 高唐县中医院骨科,山东聊城 252800
5. 河北省沧州中西医结合医院骨科,河北沧州 061000
6. 北京中医药大学东方医院风湿病科,北京 100078
A long-term review for radiographic parameters of hips in axial spondyloarthritis patients with end-stage hip involvement: A 24-year trend analysis from a single high-volume tertiary center
Xinfeng WU1, Siliang MAN2, Dazhao CHEN3, Yong HUA4, Xijie WEN5, Yingyue DING2, Liang ZHANG3,*( ), Xiujuan HOU6,*(
), Xiujuan HOU6,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Spine Surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100035, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100035, China
3. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100035, China
4. Department of Orthopedics, Gaotang County Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Liaocheng 252800, Shandong, China
5. Department of Orthopedics, Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine of Hebei Province, Cangzhou 061000, Hebei, China
6. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100078, China
摘要:
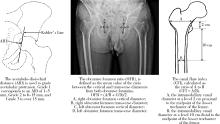
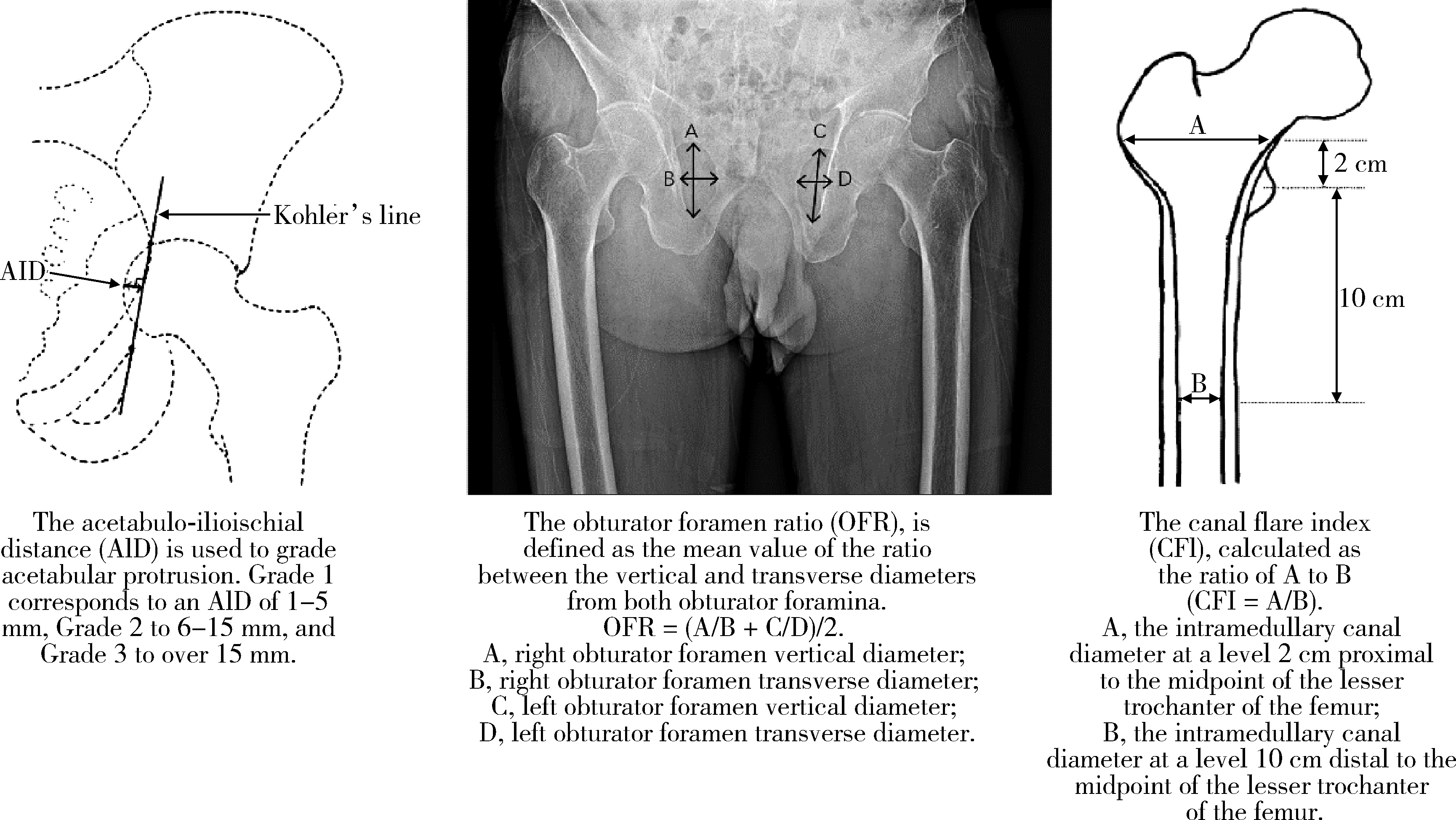
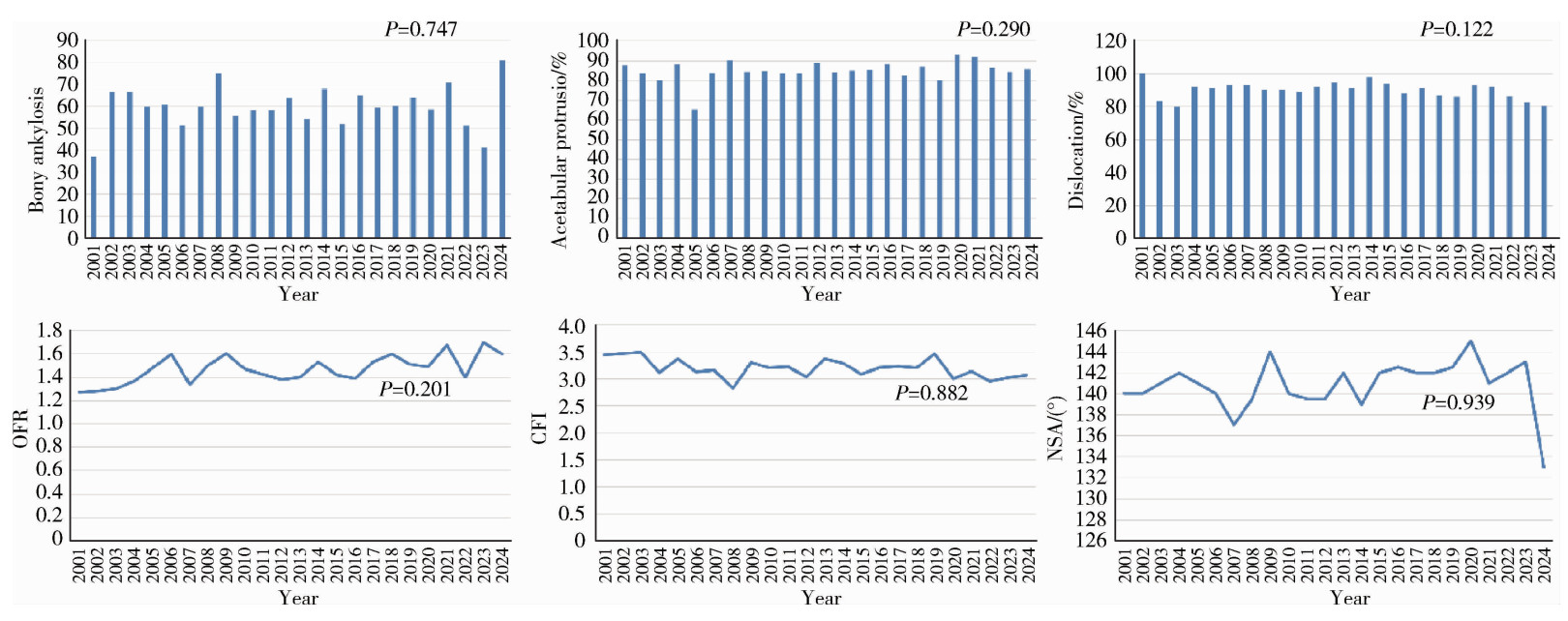
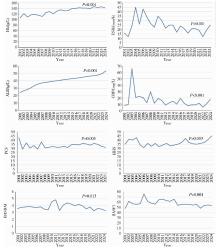
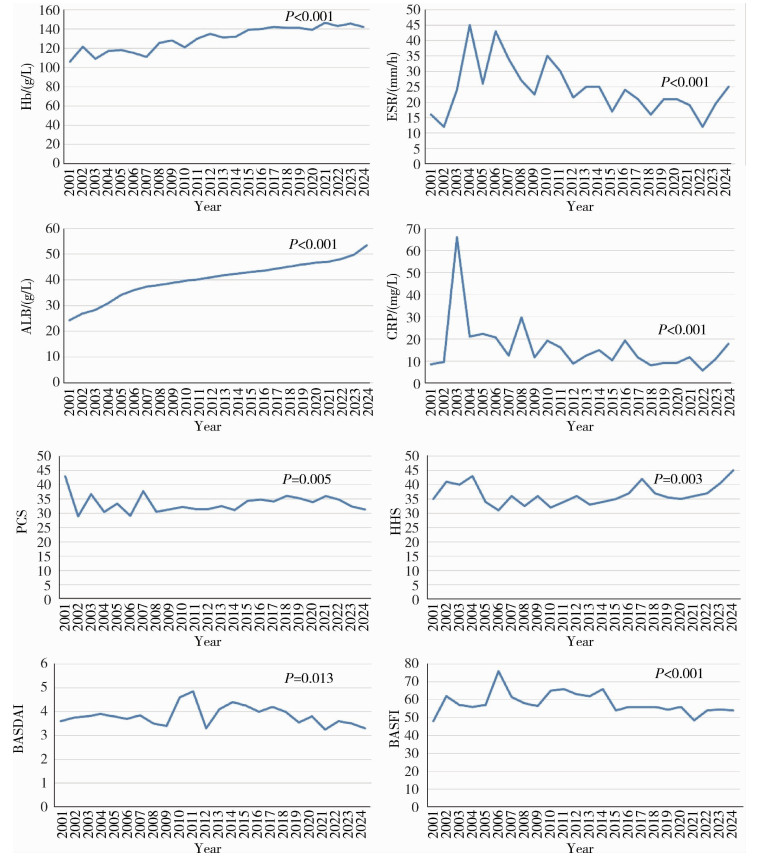
目的: 回顾单中心24年的大样本影像学数据,分析中轴型脊柱关节炎(axial spondyloarthritis, axSpA)终末期髋关节受累的重要影像学参数特点及其变化趋势。方法: 回顾性分析2001—2024年710例接受全髋关节置换术(total hip arthroplasty, THA)的axSpA患者共998例髋关节的术前X线片影像学趋势。测量指标包括:骨性融合、髋臼内陷、脱位(包括半脱位)、闭孔率(obturator foramen ratio,OFR)、髓腔张开指数(canal flare index, CFI)和颈干角(neck shaft angle, NSA),同时收集术前基线人口学参数、疾病相关参数和实验室检查数据。使用Jonkheere-Terpstra检验或Cochran-Armitage检验对临床和影像学参数进行趋势分析。根据axSpA患者手术时间,将998例髋关节分成2001—2012入院组和2013—2024入院组,对两组的临床和影像学参数进行组间比较。结果: axSpA患者术前,基线骨性融合、髋臼内陷和脱位的整体发生率分别为40.2%、14.8%和9.8%;中位OFR、CFI和NSA分别为1.5 (1.2, 1.7)、3.2 (2.6, 3.8)和141.0° (135.0°, 148.0°)。在影像学参数的趋势研究中,仅有OFR呈现显著上升(P=0.001);临床参数中,血红蛋白(hemoglobin, Hb)(P < 0.001)、白蛋白(albumin, ALB)(P < 0.001)、12项健康评估简表(short form 12-item health survey, SF-12)的躯体功能评分(physical component summary, PCS)(P=0.005)和Harris髋关节评分(Harris hip score, HHS)(P=0.003)呈现显著的上升趋势,红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ESR)(P < 0.001)、C反应蛋白(C-reactive protein, CRP)(P < 0.001)、Bath强直性脊柱炎病情活动指数(Bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity index, BASDAI)(P=0.013)和Bath强直性脊柱炎功能指数(Bath ankylosing spondylitis functional index, BASFI)(P < 0.001)呈现显著的下降趋势。在2001—2012入院组(n=421)和2013—2024入院组(n=577)的组间比较中,性别(P=0.004)、体重指数(body mass index,BMI)(P=0.002)、发病年龄(P < 0.001)和HHS(P < 0.001)差异有统计学意义,但两组间的影像学参数差异均无统计学意义。结论: axSpA合并终末期髋关节受累病例的髋关节影像学参数并未随疾病活动度的控制和功能状态的缓解而出现改善趋势,这为后续外科重建提出了诸多技术挑战。
中图分类号:
- R593.23
| 1 |
马祝一, 张亮, 满斯亮, 等. 强直性脊柱炎全髋关节置换术治疗最新研究进展[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2021, 14 (12): 1039- 1045.
|
| 2 |
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221035 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1007/s11926-023-01097-7 |
| 4 |
于志永, 张亮, 边涛, 等. 全髋关节置换术治疗强直性脊柱炎合并髋关节骨性融合的中期随访研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2023, 16 (8): 706- 712.
|
| 5 |
doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07338-7 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.108233 |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2007.06.002 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1097/00003086-197805000-00005 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1016/S0883-5403(00)91155-0 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1097/00003086-198810000-00015 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1002/art.38384 |
| 15 |
马远, 张亮, 郭邵逸, 等. 强直性脊柱炎全髋关节置换术患者基线数据特征分析[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2022, 15 (12): 939- 944.
|
| 16 |
张亮, 李宏超, 张浩天, 等. 类风湿关节炎髋关节终末期受累髋臼内陷临床特征和相关因素分析[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2022, 15 (8): 619- 625.
|
| 17 |
doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001792 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1007/s10067-014-2575-5 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key128 |
| [1] | 王晓林, 郭邵逸, 陈大召, 温锡杰, 华勇, 张亮, 张秦. 全髋关节置换术治疗系统性红斑狼疮继发股骨头缺血性坏死的随访研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(6): 1081-1088. |
| [2] | 汪琪伟, 包鹏宇, 洪士皓, 杨昕, 王宇, 曹永平. 改良股骨颈截骨术在伴严重屈曲畸形强直性脊柱炎患者手术治疗过程中的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 884-889. |
| [3] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [4] | 柯岩,张蔷,马云青,李儒军,陶可,桂先革,李克鹏,张洪,林剑浩. 全髋关节置换术治疗脊柱骨骺发育不良患者Tönnis 3级髋关节骨关节炎的早期疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 175-182. |
| [5] | 李森磊,杨先腾,田晓滨,孙立. 直接前入路和前外侧入路全髋关节置换术后的早期功能恢复对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 268-272. |
| [6] | 张翠平,刘佩佩,傅强,高冠英,崔立刚,徐雁,王健全. 超声引导下髋关节药物注射在关节镜盂唇修复术后康复中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 265-267. |
| [7] | 刘晓东,崔立刚,徐雁,孙洋,郝云霞,宋琳. 超声在髋关节前上盂唇撕裂中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(6): 1014-1018. |
| [8] | 刘蕊, 孙琳, 李常虹, 翟佳羽, 刘湘源. 强直性脊柱炎的脊柱手术原因分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 835-839. |
| [9] | 吕明, 张金庆, 王兴山, 黄野, 李为, 张春雨. 直接前入路髋关节置换术及其早期临床疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2): 206-213. |
| [10] | 张永进,李甲,綦珂,薛晨晨,徐卫东. 全髋关节置换术中直接前方入路与后外侧入路的疗效及安全性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2): 201-205. |
| [11] | 周靖, 党育, 张培训, 王静, 付中国, 张殿英, 王天兵, 徐海林, 薛峰, 陈建海, 杨明, 王钢, 沈惠良, 王光林, 吴新宝, 姜保国, . 60岁以下股骨颈骨折手术治疗术后功能及影响因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(5): 703-706. |
|
||