北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 80-85. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.01.015
经前庭沟切口的骨膜下隧道技术在治疗MillerⅠ、Ⅱ度单牙牙龈退缩中的应用
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,牙周科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
Vestibular incision subperiosteal tunnel access with connective tissue graft for the treatment of Miller classⅠ and Ⅱ gingival recession
Ke-ang FAN,Jin-sheng ZHONG,Xiang-ying OUYANG( ),Ying XIE,Zi-yuan CHEN,Shuang-ying ZHOU,Yuan ZHANG
),Ying XIE,Zi-yuan CHEN,Shuang-ying ZHOU,Yuan ZHANG
- Department of Periodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
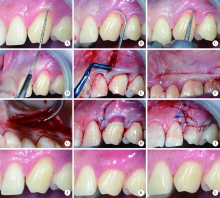
目的:拟评价经前庭沟切口的骨膜下隧道技术(vestibular incision subperiosteal tunnel access,VISTA)联合上皮下结缔组织移植术(connective tissue graft,CTG)治疗MillerⅠ、Ⅱ度单牙牙龈退缩的效果。方法:采用VISTA联合CTG技术治疗10颗单牙、退缩深度≥2 mm的MillerⅠ、Ⅱ度牙龈退缩,比较术前及术后6个月时的牙龈退缩深度、宽度、角化龈宽度、牙龈生物型、探诊深度和临床附着丧失水平,计算根面覆盖率,用视觉模拟评分法评价患者术中和术后2周内疼痛情况以及对术后6个月美观效果满意度。结果:牙龈退缩深度术前达(2.65±0.82) mm,术后6个月时减少了(2.30±0.98) mm(P<0.001),平均根面覆盖率为86.67%±21.94%,完全根面覆盖率为70%;角化龈宽度增加了(0.90±1.22) mm(P<0.05);患者对美观效果满意,评分为8.30分,患者术中及术后2周内疼痛感较轻,评分在2.40~4.30分。进一步分析发现牙龈退缩改善效果与患牙的牙龈生物型及上、下颌牙位分布无关。结论:VISTA技术联合CTG可以有效地治疗单颗牙Miller Ⅰ、 Ⅱ 度牙龈退缩,增加角化龈宽度;患者的疼痛感较轻,患者对术后6个月时的美学效果较满意。该技术可作为临床上治疗单牙Miller Ⅰ、 Ⅱ 度牙龈退缩的方法之一。
中图分类号:
- R781.4
| [1] | American Academy of Periodontology . Glossary of periodontal terms[M]. 3rd ed. Chicago: The American Academy of Periodontology, 1992: 44. |
| [2] |
Addy M, Griffiths G, Dummer P , et al. The distribution of plaque and gingivitis and the influence of toothbrushing hand in a group of South Wales 11-12 year-old children[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 1987,14(10):564-572.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.1987.tb01517.x pmid: 3480293 |
| [3] | Zucchelli G. Mucogingival esthetic surgery [M]. Italia: Quintessence Publishing, 2013. |
| [4] |
Miller PD . A classification of marginal tissue recession[J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 1985,5(2):8-13.
pmid: 3858267 |
| [5] |
Allen EP, Miller PD Jr . Coronal positioning of existing gingiva: short term results in the treatment of shallow marginal tissue recession[J]. J Periodontol, 1989,60(6):316-319.
doi: 10.1902/jop.1989.60.6.316 |
| [6] |
Zucchelli G, De Sanctis M . Treatment of multiple recession-type defects in patients with esthetic demands[J]. J Periodontol, 2000,71(9):1506-1514.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2000.71.9.1506 pmid: 11022782 |
| [7] |
Modica F, Del Pizzo M, Roccuzzo M , et al. Coronally advanced flap for the treatment of buccal gingival recessions with and without enamel matrix derivative. A split-mouth study[J]. J Periodontol, 2000,71(11):1693-1698.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2000.71.11.1693 pmid: 11128916 |
| [8] |
Amarante ES, Leknes KN, Skavland J , et al. Coronally positioned flap procedures with or without a bioabsorbable membrane in the treatment of human gingival recession[J]. J Periodontol, 2000,71(6):989-998.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2000.71.6.989 pmid: 10914803 |
| [9] |
Jepsen K, Heinz B, Halben JH , et al. Treatment of gingival recession with titanium reinforced barrier membranes versus connective tissue grafts[J]. J Periodontol, 1998,69(3):383-391.
doi: 10.1902/jop.1998.69.3.383 pmid: 9579626 |
| [10] | Ricci G, Silvestri M, Tinti C , et al. A clinical/statistical compa-rison between the subpedicle connective tissue graft method and the guided tissue regeneration technique in root coverage[J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 1996,16(6):539-545. |
| [11] |
Santana RB, Furtado MB, Mattos CM , et al. Clinical evaluation of single-stage advanced versus rotated flaps in the treatment of gingival recessions[J]. J Periodontol, 2010,81(4):485-492.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.090237 pmid: 20367091 |
| [12] | Allen AL . Use of thesupraperiosteal envelope in soft tissue grafting for root coverage. Ⅱ. Clinical results[J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 1994,14(4):302-315. |
| [13] |
Zuhr O, Fickl S, Wachtel H , et al. Covering of gingival recessions with a modified microsurgical tunnel technique: case report[J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 2007,27(5):457-463.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2007.01.025 pmid: 17990442 |
| [14] |
Aroca S, Molnar B, Windisch P , et al. Treatment of multiple adjacent Miller class I and II gingival recessions with a Modified Coronally Advanced Tunnel (MCAT) technique and a collagen matrix or palatal connective tissue graft: a randomized, controlled clinical trial[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2013,40(7):713-720.
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12112 pmid: 23627374 |
| [15] |
Santamaria MP, Neves FL, Silveira CA , et al. Connective tissue graft and tunnel or trapezoidal flap for the treatment of single ma-xillary gingival recessions: A randomized clinical trial[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2017,44(5):540-547.
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12714 pmid: 28231619 |
| [16] |
Cortellini P, Tonetti M, Baldi C , et al. Does placement of a connective tissue graft improve the outcomes of coronally advanced flap for coverage of single gingival recessions in upper anterior teeth? A multi-centre, randomized, double-blind, clinical trial[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2009,36(1):68-79.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01346.x pmid: 19046326 |
| [17] |
Gobbato L, Nart J, Bressan E , et al. Patient morbidity and root coverage outcomes after the application of a subepithelial connective tissue graft in combination with a coronally advanced flap or via a tunneling technique: a randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2016,20(8):2191-2202.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1721-7 pmid: 26814715 |
| [18] |
Chambrone L, Tatakis DN . Periodontal soft tissue root coverage procedures: a systematic review from the AAP Regeneration Workshop[J]. J Periodontol, 2015,86(2 Suppl):52-55.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2015.140376 pmid: 25644300 |
| [19] |
Cairo F, Pagliaro U, Nieri M . Treatment of gingival recession with coronally advanced flap procedures: a systematic review[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2008,35(8 Suppl):136-162.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01267.x pmid: 18724847 |
| [20] |
Cairo F, Nieri M, Pagliaro U . Efficacy of periodontal plastic surgery procedures in the treatment of localized facial gingival recessions. A systematic review[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2014,41(Suppl 15):44-62.
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12182 pmid: 24641000 |
| [21] |
Zadeh HH . Minimally invasive treatment of maxillary anterior gingival recession defects by vestibular incision subperiosteal tunnel access and platelet-derived growth factor BB[J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 2011,31(6):653-660.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2011.05.005 pmid: 22140667 |
| [22] |
Garg S, Arora SA, Chhina S , et al. Multiple gingival recession coverage treated with vestibular incision subperiosteal tunnel access approach with or without platelet-rich fibrin: A case series[J]. Contemp Clin Dent, 2017,8(3):464-468.
doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_142_17 pmid: 5644008 |
| [23] |
Chatterjee A, Sharma E, Gundanavar G , et al. Treatment of multiple gingival recessions with vista technique: A case series[J]. J Indian Soc of Periodontol, 2015,19(2):232-235.
doi: 10.4103/0972-124X.145836 pmid: 4439639 |
| [24] |
Lee CT, Hamalian T, Schulzespäte U . Minimally invasive treatment of soft tissue deficiency around an implant-supported restoration in the esthetic zone: modified VISTA technique case report[J]. J Oral Implantol, 2015,41(1):71-76.
doi: 10.1563/AAID-JOI-D-13-00043 pmid: 23510339 |
| [25] |
Zucchelli G, Mele M, Mazzotti C , et al. Coronally advanced flap with and without vertical releasing incisions for the treatment of multiple gingival recessions: A comparative controlled randomized clinical trial[J]. J Periodontol, 2009,80(7):1083-1094.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090041 pmid: 19563288 |
| [26] |
Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Umezu K , et al. Dimensions of peri-implant mucosa: an evaluation of maxillary anterior single implants in humans[J]. J Periodontol, 2003,74(4):557-562.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2003.74.4.557 pmid: 12747463 |
| [27] |
Ozenci I, Ipci SD, Cakar G , et al. Tunnel technique versus coronally advanced flap with acellular dermal matrix graft in the treatment of multiple gingival recessions[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2015,42(12):1135-1142.
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12477 pmid: 26507452 |
| [28] |
Huang LH, Neiva RE, Wang HL . Factors affecting the outcomes of coronally advanced flap root coverage procedure[J]. J Perio-dontol, 2005,76(10):1729-1734.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2005.76.10.1729 |
| [1] | 陈子圆,钟金晟,欧阳翔英,周爽英,谢颖,娄新哲. 牙龈退缩患牙的牙龈厚度评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 339-345. |
| [2] | 徐莉. 上前牙周围软硬组织重建一例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2008, 40(1): 105-108. |
|
||