北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 288-292. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.02.017
滥用一氧化二氮致长节段脊髓病变的临床分析
王云云1,汪仁斌2,洪闻3,焦劲松2,彭丹涛2,刘尊敬2,田朝晖2,金淼2,董明睿2,段晓慧2,刘蕾2,孙青2,孙少杰2,王丽2,∆( )
)
- 1. 中日友好医院 保健部二部, 北京 100029
2. 中日友好医院 神经内科, 北京 100029
3. 中日友好医院 放射诊断科, 北京 100029
Clinical features of long segmental myelopathy caused by nitrous oxide
Yun-yun WANG1,Ren-bin WANG2,Wen HONG3,Jin-song JIAO2,Dan-tao PENG2,Zun-jing LIU2,Zhao-hui TIAN2,Miao JIN2,Ming-rui DONG2,Xiao-hui DUAN2,Lei LIU2,Qing SUN2,Shao-jie SUN2,Li WANG2,∆( )
)
- 1. The Second Health and Medical Department, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
2. Department of Neurology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
3. Department of Radiology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
摘要:
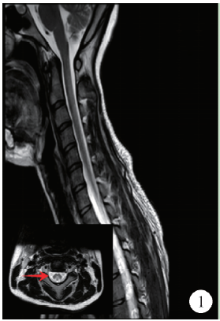
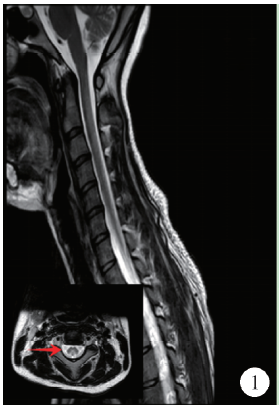
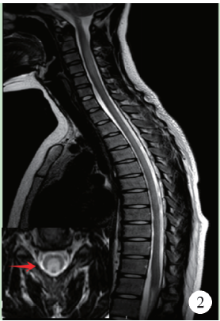
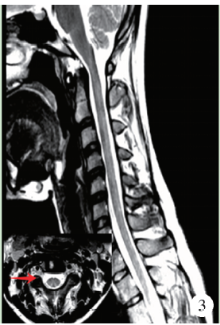
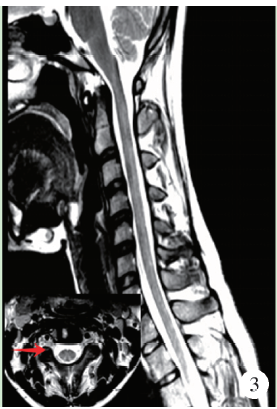
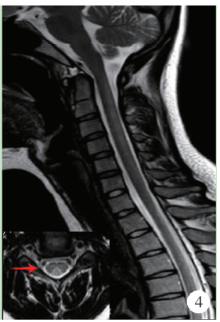
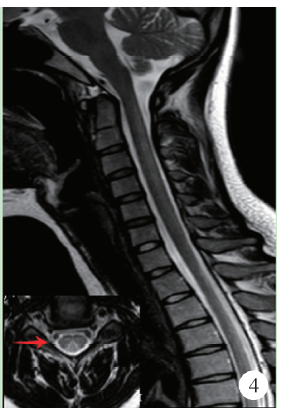
目的: 分析滥用一氧化二氮导致长节段脊髓病变的临床表现和影像学特点。方法: 对2015年10月至2018年2月在中日友好医院神经科就诊的10例滥用一氧化二氮患者的人口学数据、一氧化二氮接触史、临床特点、实验室检查、神经电生理检查、脊髓磁共振成像及治疗效果等进行回顾性分析。结果: 10例患者中男性4例,女性6例,年龄17~26岁[平均年龄(20.80±3.12)岁]。10例患者吸入N2O至起病时间为1个月至1年,平均时间(6.95±4.19)个月。10例均以肢体远端无力为主要症状,9例伴肢体远端麻木,3例伴Lhermitte’s征(+),4例伴尿便障碍。2例血常规提示贫血,1例为巨细胞性贫血,1例为小细胞低色素性贫血。3例曾于外院补充维生素B12治疗,其余7例血清同型半胱氨酸均异常增高。电生理检查示9例患者感觉和运动神经均受累,1例仅运动神经受累,下肢病变严重程度明显重于上肢。脊髓磁共振成像示10例均有颈髓纵行条状T2高信号,3例伴胸髓长节段病变,2例伴脊髓肿胀,6例横轴位呈“倒V”征,1例呈“类月牙”征,3例呈“八字”征。10例均在停止一氧化二氮吸入、积极补充大剂量维生素B12、早期康复锻炼治疗后,症状有不同程度缓解。结论: 一氧化二氮中毒性脊髓病变临床多以肢体远端无力麻木为主,影像学上以颈段脊髓后索受累常见,可伴有胸髓受累,横轴位以“倒V”征多见。停止接触一氧化二氮和补充高剂量维生素B12有效。
中图分类号:
- R744.6
| [1] | 王丽, 范其江, 焦劲松 , 等. 滥用笑气中毒致神经系统损害一例[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2016,16(8):533-537. |
| [2] | 姜季委, 石碧川, 商秀丽 . 笑气中毒致脊髓亚急性联合变性2例报告[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2018,35(4):352-354. |
| [3] | 于文慧, 李德雨, 何志义 . “笑气”中毒导致神经系统损害4例并文献复习[J]. 卒中与神经疾病杂志, 2018,25(5):556-561. |
| [4] |
Gillman MA . Nitrous oxide has a very low abuse potential[J]. Addiction, 1995,90(3):439.
doi: 10.1111/add.1995.90.issue-3 |
| [5] |
Wu LT, Pilowsky DJ, Schlenger WE . Inhalant abuse and depen-dence among adolescents in the United States[J]. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry, 2004,43(10):1206-1214.
doi: 10.1097/01.chi.0000134491.42807.a3 |
| [6] |
Garland EL, Howard MO, Perron BE . Nitrous oxide inhalation among adolescents: prevalence, correlates, and co-occurrence with volatile solvent inhalation[J]. J Psychoactive Drugs, 2009,41(4):337-347.
doi: 10.1080/02791072.2009.10399771 |
| [7] |
Garakani A, Jaffe RJ, Savla D , et al. Neurologic, psychiatric,and other medical manifestations of nitrous oxide abuse: a syste-matic review of the case literature[J]. Am J Addict, 2016,25(5):358-369.
doi: 10.1111/ajad.v25.5 |
| [8] | Dimaio VJ, Garriot JC . Four deaths resulting from abuse of nitrous oxide[J]. J Forensic Sci, 1978,23(1):169-172. |
| [9] |
Potocka-Banas B, Majdanik S, Dutkiewicz G , et al. Death caused by addicitive inhalation of nitrous oxide[J]. Hum Exp Toxicol, 2011,30(11):1875-1877.
doi: 10.1177/0960327111401437 |
| [10] |
Duque MA, Kresak JL, Falchook A , et al. Nitrous oxide abuse and vitamin B12 action in a 20-year-old women: a case report[J]. Lab Med, 2015,46(4):312-315.
doi: 10.1309/LM0L9HAVXCHF1UQM |
| [11] |
Morris N, Lynch K, Greenbery SA . Severe motor neuropathy or neuronopathy due to nirous oxide toxicity after correction of vitamin B12 deficiency[J]. Muscle Nerve, 2015,51(4):614-616.
doi: 10.1002/mus.24482 |
| [12] | 蒋雯巍, 蒋雨平 . 甲钴胺代谢及其相关性疾病[J]. 中国临床神经病学杂志, 2010,18(2):203-207. |
| [13] |
Kumar A, Singh AK . Teaching neuroimage: inverted V sign in subacute combined degeneration of spinal cord[J]. Neurology, 2009,72(1):e4.
doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000338663.59433.9c |
| [14] | 王文超, 丁汉军, 刘明 , 等. MRI对脊髓亚急性联合变性的诊断价值[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2000,34(1):40-42. |
| [15] | 腾才钧, 陈玲, 覃盛宝 , 等. 脊髓亚急性联合变性MRI影像分析[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2016,32(7):1009-1011. |
| [16] | Locatelli ER, Laureno R, Ballard P , et al. MRI in vitamin B12 deficiency myelopathy[J]. Can J Neurol Sci, 1999,26(1):60-63. |
| [17] |
Li HT, Chu CC, Chang KH , et al. Clinical and electrodiagnostic characteristics of nitrous oxide-induced neuropathy in Taiwan[J]. Clin Neurophysiol, 2016,127(10):3288-3293.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2016.08.005 |
| [18] |
Hutto BR . Folate and cobalamin in psycheiatric illness[J]. Compr Psychiatry, 1997,38(6):305-314.
doi: 10.1016/S0010-440X(97)90925-1 |
| [19] |
Brodsky L, Zuniga J . Nitrous oxide: a psychotogenic agent[J]. Compr Psychiatry, 1975,16(2):185-188.
doi: 10.1016/0010-440X(75)90065-6 |
| [20] | Gursoy AE, Kolukisa M, Babacan-Yildiz G , et al. Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord due to different etiologies and improvement of MRI findings[J]. Case Rep Neurol Med, 2013,2013(1):159649. |
| [1] | 孟磊, 高炜, 赵春玉, 薛林. 高同型半胱氨酸血症引起家兔动脉硬化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2001, 33(6): 536-539. |
|
||