北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 1-9. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.001
• 论著 • 下一篇
Tribbles同源蛋白3抑制人脂肪间充质干细胞成脂向分化
- 北京大学口腔医学院 ·口腔医院,修复科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Tribbles pseudokinase 3 inhibits the adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Xiang-song BAI,Long-wei LV( ),Yong-sheng ZHOU
),Yong-sheng ZHOU
- Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
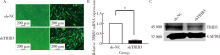
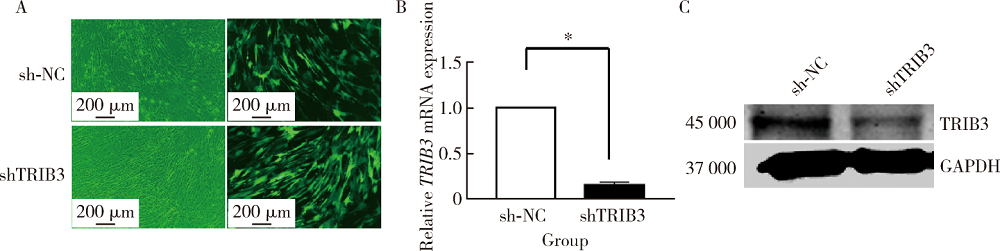
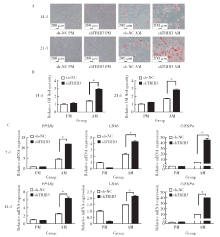
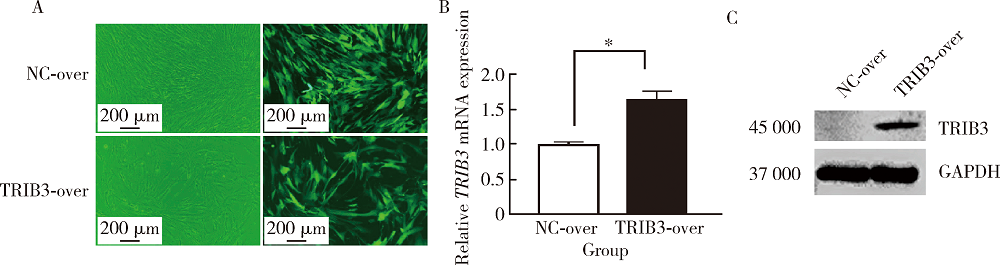
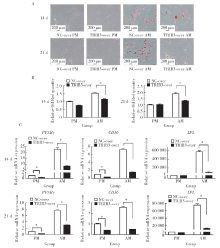
目的:研究Tribbles同源蛋白3(Tribbles pseudokinase 3, TRIB3)在人脂肪间充质干细胞(human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells, hASCs)成脂分化中的调控作用,为提高hASCs成脂向分化能力、并为基于hASCs的脂肪组织工程与软组织缺损修复提供新靶点与新思路。方法:通过慢病毒转染建立TRIB3稳定敲低(TRIB3敲低组)和过表达(TRIB3过表达组)的hASCs细胞系,通过实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction,qRT-PCR)和蛋白质印迹实验(Western blot)检测慢病毒转染hASCs的转染效率和效果。通过油红O染色和定量、qRT-PCR等实验方法,检测敲低、过表达TRIB3对hASCs成脂分化能力的影响。结果:TRIB3敲低慢病毒转染后,TRIB3敲低组hASCs中TRIB3 mRNA表达量较对照组下降84.3%(P<0.01), TRIB3蛋白表达也显著下降,表明成功构建了TRIB3敲低的hASCs细胞系;TRIB3过表达慢病毒转染后,TRIB3过表达组TRIB3 mRNA表达量较对照组增高约1.6倍(P<0.01),TRIB3蛋白表达也显著升高,表明成功构建了TRIB3过表达的hASCs细胞系。在此基础上,油红O染色显示,TRIB3敲低的hASCs成脂诱导后胞浆内红色脂滴明显增多,定量结果表明TRIB3敲低组油红O着色较对照组显著增多(P<0.01)。与之相反,TRIB3过表达的hASCs成脂诱导后胞浆内红色脂滴明显减少,定量结果表明TRIB3敲低组油红O着色较对照组显著减少(P<0.01)。qRT-PCR结果显示,敲低TRIB3的hASCs成脂诱导后,成脂分化相关基因过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, PPARγ)、CCAAT增强子结合蛋白α(CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α, C/EBPα)和白细胞分化抗原36(cluster of differentiation 36, CD36)mRNA水平显著升高(P<0.01);TRIB3过表达的hASCs成脂诱导后成脂分化相关基因PPARγ、CD36和脂蛋白酯酶(lipoprotein lipase, LPL)mRNA水平明显下降。结论:TRIB3能够调控hASCs成脂分化能力,敲低TRIB3促进hASCs成脂分化,过表达TRIB3抑制hASCs成脂分化。
中图分类号:
- R329.2
| [1] | Rubin JP, Marra KG . Adipose stem cell therapy for soft tissue reconstruction[J]. Lancet, 2013,382(9898):1077-1079. |
| [2] | Patrick CJ, Chauvin PB, Hobley J , et al. Preadipocyte seeded PLGA scaffolds for adipose tissue engineering[J]. Tissue Eng, 1999,5(2):139-151. |
| [3] | Paschos NK, Brown WE, Eswaramoorthy R , et al. Advances in tissue engineering through stem cell-based co-culture[J]. J Tissue Eng Regen Med, 2015,9(5):488-503. |
| [4] | Cossu G, Birchall M, Brown T , et al. Lancet Commission: Stem cells and regenerative medicine[J]. Lancet, 2018,391(10123):883-910. |
| [5] | Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H , et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based therapies[J]. Tissue Eng, 2001,7(2):211-228. |
| [6] | Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P , et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells[J]. Mol Biol Cell, 2002,13(12):4279-4295. |
| [7] | Gentile P, Orlandi A, Scioli MG , et al. Concise review: Adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction cells and platelet-rich plasma: Basic and clinical implications for tissue engineering therapies in regenerative surgery[J]. Stem Cells Transl Med, 2012,1(3):230-236. |
| [8] | Lv LW, Liu YS, Zhang P , et al. Transcriptomics and functional analysis of graphene-guided osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chin J Dent Res, 2018,21(2):101-111. |
| [9] | Eyers PA, Keeshan K, Kannan N . Tribbles in the 21st Century: The evolving roles of tribbles pseudokinases in biology and disease[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2017,27(4):284-298. |
| [10] | Ord T, Ord T . Mammalian pseudokinase TRIB3 in normal physi-ology and disease: Charting the progress in old and new avenues[J]. Curr Protein Pept Sci, 2017,18(8):819-842. |
| [11] | Prudente S, Sesti G, Pandolfi A , et al. The mammalian tribbles homolog TRIB3, glucose homeostasis, and cardiovascular diseases[J]. Endocr Rev, 2012,33(4):526-546. |
| [12] | Liu G, Jin S, Hu Y , et al. Disease status affects the association between rs4813620 and the expression of Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility gene TRIB3[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018,115(45):E10519-E10520. |
| [13] | Hua F, Li K, Yu JJ , et al. The TRIB3-SQSTM1 interaction mediates metabolic stress-promoted tumorigenesis and progression via suppressing autophagic and proteasomal degradation[J]. Auto-phagy, 2015,11(10):1929-1931. |
| [14] | Mondal D, Mathur A, Chandra PK . Tripping on TRIB3 at the junction of health, metabolic dysfunction and cancer[J]. Biochimie, 2016,124:34-52. |
| [15] | Kusminski CM, Bickel PE, Scherer PE . Targeting adipose tissue in the treatment of obesity-associated diabetes[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2016,15(9):639-660. |
| [16] | Picon-Ruiz M, Morata-Tarifa C, Valle-Goffin JJ , et al. Obesity and adverse breast cancer risk and outcome: Mechanistic insights and strategies for intervention[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2017,67(5):378-397. |
| [17] | Bezy O, Vernochet C, Gesta S , et al. TRB3 blocks adipocyte differentiation through the inhibition of C/EBPbeta transcriptional activity[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2007,27(19):6818-6831. |
| [18] | Wang X, Gao L, Han Y , et al. Silicon-enhanced adipogenesis and angiogenesis for vascularized adipose tissue engineering[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2018,5(11):1800776. |
| [19] | Levi B, Longaker MT . Concise review: Adipose-derived stromal cells for skeletal regenerative medicine[J]. Stem Cells, 2011,29(4):576-582. |
| [20] | Zhu Y, Zhang P, Gu RL , et al. Origin and clinical applications of neural crest-derived dental stem cells[J]. Chin J Dent Res, 2018,21(2):89-100. |
| [21] | Lu Z, Yuan Y, Gao J , et al. Adipose tissue extract promotes adipose tissue regeneration in an adipose tissue engineering chamber model[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2016,364(2):289-298. |
| [22] | Volz AC, Huber B, Kluger PJ . Adipose-derived stem cell differentiation as a basic tool for vascularized adipose tissue engineering[J]. Differentiation, 2016,92(1/2):52-64. |
| [23] | Gomillion CT, Burg KJ . Stem cells and adipose tissue engineering[J]. Biomaterials, 2006,27(36):6052-6063. |
| [24] | Scott MA, Nguyen VT, Levi B , et al. Current methods of adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2011,20(10):1793-1804. |
| [25] | Saltiel AR . Putting the brakes on insulin signaling[J]. N Engl J Med, 2003,349(26):2560-2562. |
| [26] | Qi L, Heredia JE, Altarejos JY , et al. TRB3 links the E3 ubi-quitin ligase COP1 to lipid metabolism[J]. Science, 2006,312(5781):1763-1766. |
| [27] | Brazil DP, Hemmings BA . Ten years of protein kinase B signalling: A hard Akt to follow[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2001,26(11):657-664. |
| [28] | Cho H, Mu J, Kim JK , et al. Insulin resistance and a diabetes mellitus-like syndrome in mice lacking the protein kinase Akt2 (PKB beta)[J]. Science, 2001,292(5522):1728-1731. |
| [29] | Du K, Herzig S, Kulkarni RN , et al. TRB3: A tribbles homolog that inhibits Akt/PKB activation by insulin in liver[J]. Science, 2003,300(5625):1574-1577. |
| [30] | Park JS, Kim M, Song NJ , et al. A reciprocal role of the Smad4-Taz axis in osteogenesis and adipogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Stem Cells, 2019,37(3):368-381. |
| [31] | Hyvari L, Ojansivu M, Juntunen M , et al. Focal adhesion kinase and ROCK signaling are switch-like regulators of human adipose stem cell differentiation towards osteogenic and adipogenic lineages[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2018, 9(2018-09-12)[2018-12-12]. . |
| [32] | Liu X, He J, Zhang S , et al. Adipose stem cells controlled by surface chemistry[J]. J Tissue Eng Regen Med, 2013,7(2):112-117. |
| [33] | Furuhata Y, Yoshitomi T, Kikuchi Y , et al. Osteogenic lineage commitment of adipose-derived stem cells is predetermined by three-dimensional cell accumulation on micropatterned surface[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017,9(11):9339-9347. |
| [34] | Takahashi Y, Ohoka N, Hayashi H , et al. TRB3 suppresses adipocyte differentiation by negatively regulating PPARgamma transcriptional activity[J]. J Lipid Res, 2008,49(4):880-892. |
| [35] | Chan MC, Hilyard AC, Wu C , et al. Molecular basis for antagonism between PDGF and the TGFbeta family of signalling pathways by control of miR-24 expression[J]. EMBO J, 2010,29(3):559-573. |
| [36] | Roy L, Bikorimana E, Lapid D , et al. MiR-24 is required for hematopoietic differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells[J]. PLoS Genet, 2015,11(1):e1004959. |
| [37] | Kim S, Hata A, Kang H . Down-regulation of miR-96 by bone morphogenetic protein signaling is critical for vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype modulation[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2014,115(5):889-895. |
| [38] | Eom HJ, Chatterjee N, Lee J , et al. Integrated mRNA and micro RNA profiling reveals epigenetic mechanism of differential sensiti-vity of Jurkat T cells to AgNPs and Ag ions[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2014,229(1):311-318. |
| [39] | Liu X, Zhao J, Liu Q , et al. MicroRNA-124 promotes hepatic triglyceride accumulation through targeting tribbles homolog 3[J]. Sci Rep, 2016,6:37170. |
| [1] | 姜蔚然,张晓,刘云松,吴刚,葛严军,周永胜. 骨形态发生蛋白-2-磷酸钙共沉淀支架与人脂肪间充质干细胞构建新型组织工程化骨[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 6-015. |
|
||