北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 10-17. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.002
可注射羟乙基壳聚糖基水凝胶理化性能及其对人牙髓细胞增殖和成牙本质向分化的作用
曹春玲1,杨聪翀1,屈小中2,韩冰1,△( ),王晓燕1,△(
),王晓燕1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,牙体牙髓科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2. 中国科学院大学材料科学与光电技术学院,北京 100049
Effects of the injectable glycol-chitosan based hydrogel on the proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp cells
Chun-ling CAO1,Cong-chong YANG1,Xiao-zhong QU2,Bing HAN1,△( ),Xiao-yan WANG1,△(
),Xiao-yan WANG1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Cariology and Endodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. College of Materials Science and Opto-electronic Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
摘要:
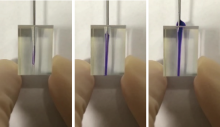
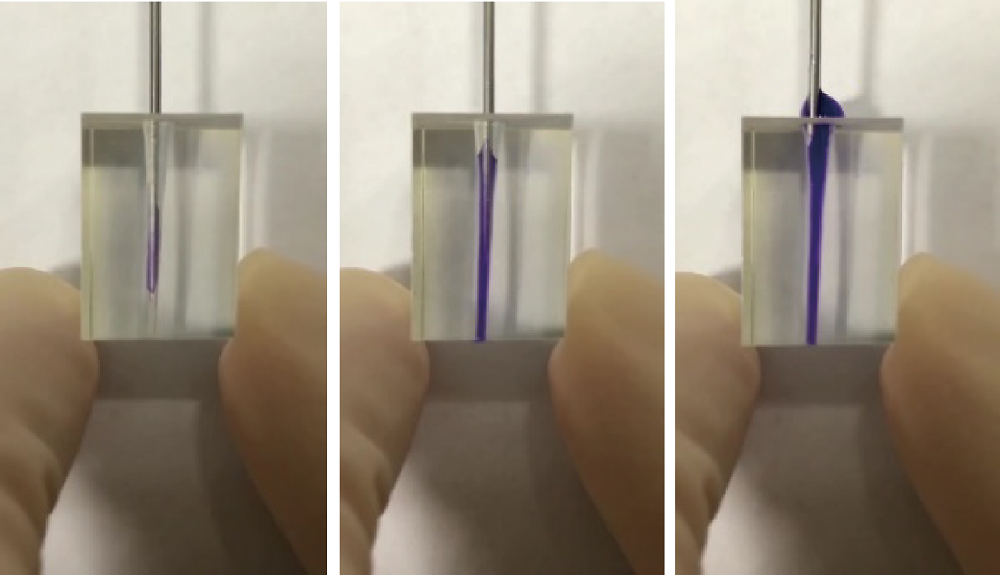
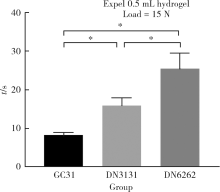
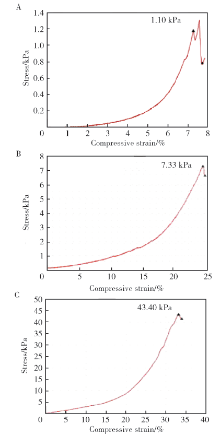
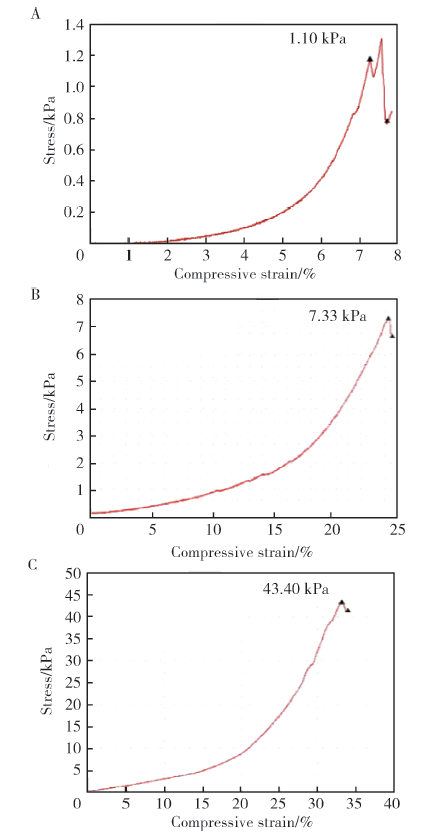
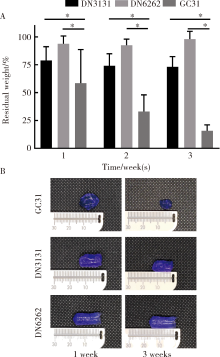
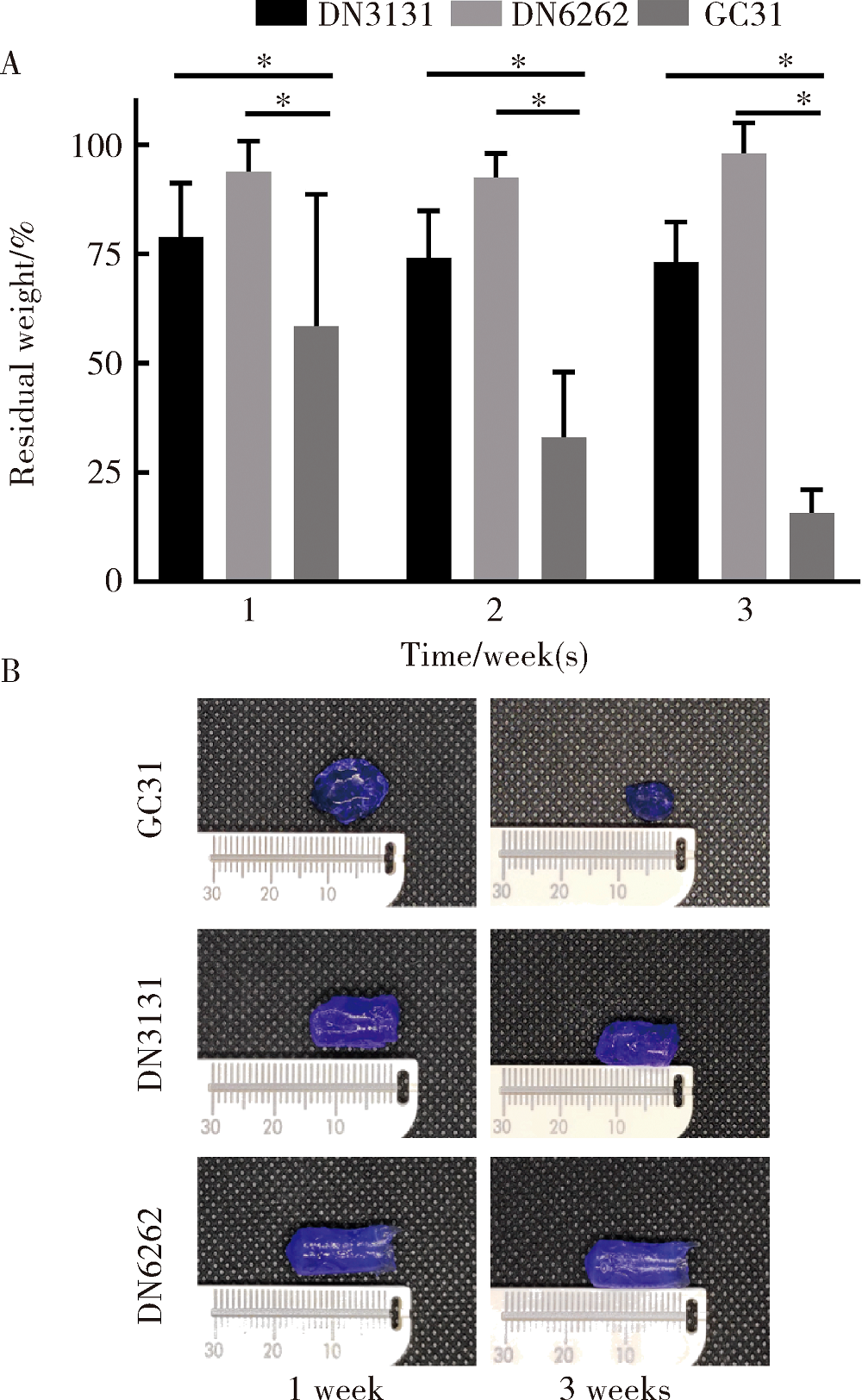
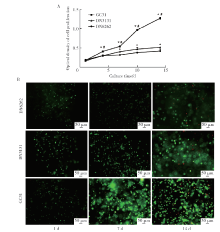
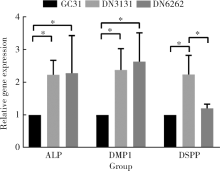
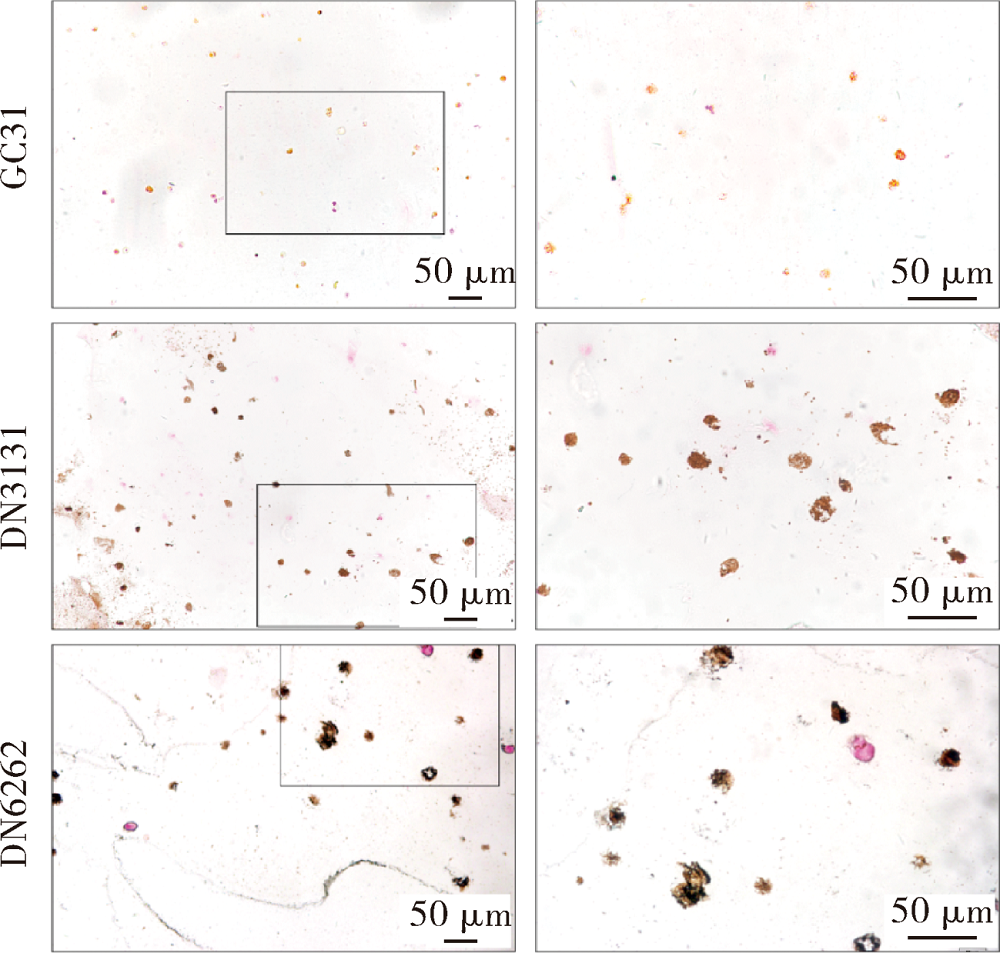
目的:制备羟乙基壳聚糖(glycol-chitosan, GC)基单/双网络水凝胶,比较人牙髓细胞(human dental pulp cells,hDPCs)在水凝胶内三维培养增殖和分化情况,探究GC基单/双网络水凝胶及其理化性能对hDPCs生物学行为的影响。方法:制备不同组成配比的GC基单网络水凝胶(GC31)和GC基双网络水凝胶(DN3131、DN6262)。用双联注射器在恒力下推注GC基单/双网络水凝胶,测定其可注射性能。用失重法测定水凝胶的体外耐降解性能,并用万能力学试验机测定材料断裂应力。在水凝胶内包封hDPCs进行三维培养,用CCK-8法和Calcein-AM/PI活死细胞染色法测定hDPCs的增殖情况。成牙本质向诱导培养14 d后,用实时荧光定量PCR(real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR, RT-PCR)测定各组成牙本质向分化相关基因牙本质涎磷蛋白(dentin sialophosphoprotein, DSPP)、牙本质基质蛋白(dentin matrix protein-1, DMP-1)和矿化相关基因碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase, ALP)的表达变化,用Von Kossa染色法观察矿化结节的形成。结果:3组水凝胶均具有良好的可注射性能,GC31推注时间最短,DN6262推注时间较DN3131长(P<0.05)。GC31水凝胶在体外降解速率高于双网络水凝胶组(P<0.05), DN3131和DN6262的降解速率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。GC31断裂应力为1.10 kPa,DN3131和DN6262断裂应力分别为7.33 kPa和43.30 kPa,双网络水凝胶的抗压缩性能较单网络水凝胶有明显增强。hDPCs在3种水凝胶内均处于良好的增殖状态,GC31组的增殖能力高于DN3131和DN6262组(P<0.05),DN3131组的增殖能力高于DN6262组(P<0.05)。在成牙本质向诱导培养14 d后,DN3131和DN6262组的DSPP、DMP-1、ALP表达水平较GC31组升高(P<0.05), DN3131和DN6262组的DMP-1和ALP表达水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。DN3131和DN6262组体外培养2周后均可见明显生成棕黑色的团块状矿化结节,而GC31组仅观察到浅棕色钙沉积染色,为零星颗粒状散在分布。结论:不同组成配比的GC基单/双网络水凝胶均满足可注射需求,GC单网络水凝胶力学性能较低,hDPCs在其中表现出更好的增殖能力;而双网络水凝胶具备更好的耐降解性能和更高的力学性能,hDPCs在其中表现出更好的成牙本质向分化潜力和矿化潜力。
中图分类号:
- R783.1
| [1] | 孙艳艳, 袁梦桐, 胡伟平 . 牙髓干细胞的研究与应用[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2016,32(3):426-429. |
| [2] | Xuan K, Li B, Guo H , et al. Deciduous autologous tooth stem cells regenerate dental pulp after implantation into injured teeth[J]. Sci Trans Med, 2018,10(455):3227. |
| [3] | Galler KM, Hartgerink JD, Cavender A C , et al. A customized self-assembling peptide hydrogel for dental pulp tissue engineering[J]. Tissue Eng Part A, 2012,18(1/2):176-184. |
| [4] | Qu T, Jing J, Ren Y , et al. Complete pulpodentin complex re-generation by modulating the stiffness of biomimetic matrix[J]. Acta Biomater, 2015,16(1):60-70. |
| [5] | Smith JG, Smith AJ, Shelton RM , et al. Dental pulp cell behavior in biomimetic environments[J]. J Dent Res, 2015,94(11):1552-1559. |
| [6] | Gillette BM, Jensen JA, Wang M , et al. Dynamic hydrogels: switching of 3D microenvironments using two-component naturally derived extracellular matrices[J]. Adv Mater, 2010,22(6):686-691. |
| [7] | Xu X, Gu Z, Chen X , et al. An injectable and thermosensitive hydrogel: Promoting periodontal regeneration by controlled-release of aspirin and erythropoietin[J]. Acta Biomater, 2019,86:235-246. |
| [8] | Yan Y, Li M, Yang D , et al. Construction of injectable double-network hydrogels for cell delivery[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2017,18(7):2128-2138. |
| [9] | Lee KY, Mooney DJ . Hydrogels for tissue engineering[J]. Chem Rev, 2001,101(7):1869-1880. |
| [10] | Jones TD, Kefi A, Sun S, et al. An optimized injectable hydrogel scaffold supports human dental pulp stem cell viability and spreading[J/OL]. Adv Med, 2016, 2016: 7363579(2016-05-16)[2019-09-01]. . |
| [11] | Her GJ, Wu H, Chen M , et al. Control of three-dimensional substrate stiffness to manipulate mesenchymal stem cell fate toward neuronal or glial lineages[J]. Acta Biomater, 2013,9(2):5170-5180. |
| [12] | Slaughter BV, Khurshid SS, Fisher OZ , et al. Hydrogels in regenerative medicine[J]. Adv Mater, 2009,21(32/33):3307-3329. |
| [13] | Dash M, Chiellini F, Ottenbrite RM , et al. Chitosan: a versatile semi-synthetic polymer in biomedical applications[J]. Prog Polym Sci, 2011,36(8):981-1014. |
| [14] | Zou H, Wang G, Song F , et al. Investigation of human dental pulp cells on a potential injectable poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microsphere scaffold[J]. J Endod, 2017,43(5):745-750. |
| [15] | Chrepa V, Austah O, Diogenes A . Evaluation of a commercially available hyaluronic acid hydrogel (restylane) as injectable scaffold for dental pulp regeneration: an in vitro evaluation[J]. J Endod, 2017,43(2):257-262. |
| [16] | Yu L, Ding J . Injectable hydrogels as unique biomedical materials[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2008,37(8):1473. |
| [17] | Malda J, Visser J, Melchels FP , et al. 25th anniversary article: engineering hydrogels for biofabrication[J]. Adv Mater, 2013,25(36):5011-5028. |
| [18] | Smith LR, Cho S, Discher DE . Stem cell differentiation is regu-lated by extracellular matrix mechanics[J]. Physiology, 2018,33(1):16-25. |
| [19] | Sun TL, Kurokawa T, Kuroda S , et al. Physical hydrogels composed of polyampholytes demonstrate high toughness and viscoelasticity[J]. Nat Mater, 2013,12(10):932-937. |
| [20] | Nonoyama T, Wada S, Kiyama R , et al. Double-network hydrogels strongly bondable to bones by spontaneous osteogenesis penetration[J]. Adv Mater, 2016,28(31):6740-6745. |
| [21] | Haque MA, Kurokawa T, Gong JP . Super tough double network hydrogels and their application as biomaterials[J]. Polymer, 2012,53(9):1805-1822. |
| [22] | Bellamy C, Shrestha S, Torneck C , et al. Effects of a bioactive scaffold containing a sustained transforming growth factor-β1-re-leasing nanoparticle system on the migration and differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla[J]. J Endod, 2016,42(9):1385-1392. |
| [23] | Galler KM, Cavender AC, Koeklue U , et al. Bioengineering of dental stem cells in a PE gylated fibrin gel[J]. Regen Med, 2011,6(2):191-200. |
| [24] | Vining KH, Mooney DJ . Mechanical forces direct stem cell be-haviour in development and regeneration[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio, 2017,18(12):728-742. |
| [25] | Caiazzo M, Okawa Y, Ranga A , et al. Defined three-dimensional microenvironments boost induction of pluripotency[J]. Nat Mater, 2016,15(3):344-352. |
| [26] | Duval K, Grover H, Han L , et al. Modeling physiological events in 2D vs. 3D cell culture[J]. Physiology, 2017,32(4):266-277. |
| [27] | Soares DG, Rosseto HL, Basso FG , et al. Chitosan-collagen biomembrane embedded with calcium-aluminate enhances dentinogenic potential of pulp cells[J]. Braz Oral Res, 2016,30(1):e54. |
| [28] | Galler KM, D Souza RN, Hartgerink JD , et al. Scaffolds for dental pulp tissue engineering[J]. Adv Dent Res, 2011,23(3):333-339. |
| [29] | Caliari SR, Burdick JA . A practical guide to hydrogels for cell culture[J]. Nat Methods, 2016,13(5):405-414. |
| [30] | Boland T, Mironov V, Gutowska A , et al. Cell and organ printing 2: Fusion of cell aggregates in three-dimensional gels[J]. Anat Rec Part A, 2003,272A(2):497-502. |
| [31] | Janmey PA, Miller RT . Mechanisms of mechanical signaling in development and disease[J]. J Cell Sci, 2011,124(1):9-18. |
| [32] | Chen CS, Mrksich M, Huang S , et al. Geometric control of cell life and death[J]. Science, 1997,276(5317):1425-1428. |
| [1] | 王明瑞, 王起, 胡浩, 赖金惠, 唐鑫伟, 万春艳, 许克新, 徐涛. 覆膜金属输尿管支架治疗盆腔脂肪增多症所致肾积水的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [2] | 杨文博,余磊,张维宇,徐涛,王强. 带线输尿管支架自排技术在肾移植受者中的效果及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [3] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [4] | 韩金涛,张宇翔,贾子昌,姜除寒,刘恋,栾景源,梁飞,赵彦清. Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞未破裂性颅内宽颈动脉瘤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 139-143. |
| [5] | 李雨柯,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华,陈晓颖. 不同pH值对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层海绵支架螯合锶离子的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 44-51. |
| [6] | 张春龙,王明瑞,王起,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 覆膜金属输尿管支架维持性治疗输尿管镜碎石术后难治性输尿管狭窄的远期疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 674-679. |
| [7] | 邓艺,张一,李博文,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华. 不同交联剂处理对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层多孔支架的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 557-564. |
| [8] | 朱正达,高岩,何汶秀,方鑫,刘洋,魏攀,闫志敏,华红. 红色诺卡氏菌细胞壁骨架治疗糜烂型口腔扁平苔藓的疗效及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 964-969. |
| [9] | 庄金满,李天润,李选,栾景源,王昌明,冯琦琛,韩金涛. Rotarex 旋切导管在下肢动脉硬化闭塞症支架内再狭窄中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 740-743. |
| [10] | 董文敏,王明瑞,胡浩,王起,许克新,徐涛. Allium覆膜金属输尿管支架长期留置治疗输尿管-回肠吻合口狭窄的初期临床经验及随访结果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 637-641. |
| [11] | 贾子昌,李选,郑梅,栾景源,王昌明,韩金涛. 复合手术治疗无残端的症状性长段颈内动脉慢性闭塞[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 177-180. |
| [12] | 赵海燕,樊东升,韩金涛. 重度颈内动脉狭窄伴未破裂动脉瘤的治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 829-834. |
| [13] | 贾子昌,卞焕菊,李选,栾景源,王昌明,刘启佳,韩金涛. Neuroform EZ支架在治疗复杂症状性颅内动脉重度狭窄中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 835-839. |
| [14] | 贾子昌,卞焕菊,韩金涛,赵海燕,栾景源,王昌明,李选. 颈动脉支架成形术后脑高灌注综合征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 733-736. |
| [15] | 贾子昌,李选,李小刚,曾祥柱,栾景源,王昌明,韩金涛. 机械取栓治疗急性缺血性脑卒中单中心研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 256-259. |
|
||