北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 500-505. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.03.016
中国中老年人失能状况公平性与影响因素
- 北京大学公共卫生学院全球卫生学系,北京 100191
Research on equity and influencing factors of disability among Chinese middle-aged and old people
- Department of Global Health, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
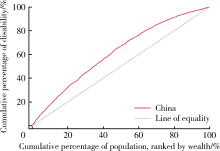
目的 分析中国50岁及以上中老年人失能状况和失能状况公平性,并探究中老年人失能状况不公平的主要影响因素。方法 利用全球老龄化与成人健康研究(Study on Global Ageing and Adult Health,SAGE)中国2007—2010年第一轮调查数据,计算集中指数和集中曲线,并对集中指数进行分解。结果 中国中老年人失能评估量表平均分为7.32,中老年男性平均分为6.37,女性平均分为8.21。中老年人失能状况集中指数为-0.190 9,中老年男性为-0.184 4,中老年女性为-0.196 1。对集中指数进行分解后,社会经济地位对中老年人失能状况不公平的贡献较高,包括经济水平、受教育程度和工作类型,贡献率分别为66.41%、16.45%和13.10%。与社会结构因素相比,中老年人吸烟、饮酒和身体活动情况等个人生活方式因素的贡献率较低。结论 中国存在中老年人失能状况不公平,较好的健康状况集中在经济水平较好的中老年人群中。中老年男性失能状况较女性更轻,且失能状况不公平程度更小。经济水平、受教育程度和工作类型是对中国中老年人失能状况不公平贡献率较高的主要因素,提示仅通过促进中老年人健康生活方式不能够有效减少失能状况在经济水平较好和较差的中老年人群中的差异。政府需要在重视促进中老年人健康的基础上,进一步加强和完善适宜的社会和医疗保障措施,将减少中老年人健康不公平作为政策重点,尤其应该向发展相对滞后、中老年人相对聚集的地区重点分配医疗卫生和其他相关社会资源,同时应该加大对中老年人健康和健康公平相关研究的支持,为积极应对人口老龄化和制定政策收集证据。
中图分类号:
- R197.1
| [1] | World Health Organization. World report on ageing and health [R]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2015: 246. |
| [2] | Jones GW. Ageing in China, India and Indonesia: an overview[M] // Contemporary demographic transformations in China, India and Indonesia. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 325-328. |
| [3] | United Nations. Department of economic and social affairs, population division (2013), world population ageing 2013[M]. New York: United Nations publication, 2013. |
| [4] |
Crimmins EM, Beltrán-Sánchez H. Mortality and morbidity trends: is there compression of morbidity?[J]. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci, 2011,66(1):75-86.
pmid: 21135070 |
| [5] | Wang XQ, Chen PJ. Population ageing challenges health care in China[J]. Lancet, 2014,383(9920):870. |
| [6] | Du P, Wang Y. Population ageing and the development of social care service systems for older persons in China[J]. Int J Ageing Dev C, 2016,1(1):40-52. |
| [7] | Chen X, Huang B, Li S. Population ageing and inequality: Evidence from China[J]. World Economy, 2018,41(8):1976-2000. |
| [8] | Fan C, Ouyang W, Tian L, et al. Elderly health inequality in China and its determinants: a geographical perspective[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2019,16(16):2953. |
| [9] | Zhong Y, Wang J, Nicholas S. Gender, childhood and adult socioeconomic inequalities in functional disability among Chinese older adults[J]. Int J Equity Health, 2017,16(1):165. |
| [10] |
Yang L, Konttinen H, Martikainen P, et al. Socioeconomic status and physical functioning: a longitudinal study of older Chinese people[J]. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci, 2018,73(7):1315-1329.
pmid: 28329825 |
| [11] | International Health Conference. Constitution of the World Health Organization. 1946[J]. Bull World Health Organ, 2002,80(12):983-984. |
| [12] | O’Donnell O, Doorslaer EV, Wagstaff A, et al. Analyzing health equity using household survey data: A guide to techniques and their implementation[J]. World Bank, 2008,86(10):816-816. |
| [13] | Üstuün TB, Ebrary I. Measuring health and disability: manual for WHO Disability Assessment Schedule WHODAS 2.0 [R]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2010. |
| [14] | Murray CJL, Evans DB. Health systems performance assessment: Debates, methods and empiricism[M]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2003. |
| [15] |
Bull FC, Maslin TS, Armstrong T. Global physical activity questionnaire (GPAQ): nine country reliability and validity study[J]. J Phys Act Health, 2009,6(6):790-804.
doi: 10.1123/jpah.6.6.790 pmid: 20101923 |
| [16] | Armstrong T, Bull F. Development of the World Health Organization Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ)[J]. J Public Health, 2006,14(2):66-70. |
| [17] |
van Doorslaer E, Koolman X. Explaining the differences in income—related health inequalities across European countries[J]. Health Econ, 2004,13(7):609-628.
pmid: 15259042 |
| [18] | Macinko J, Harris MJ, Rocha MG. Brazil’s National Program for Improving Primary Care Access and Quality (PMAQ): fulfilling the potential of the world’s largest payment for performance system in primary care[J]. J Ambul Care Manage, 2017,40(2 Suppl):S4-S11. |
| [19] | 赵梓行. 均等化视角下印度医疗服务体系管理研究[D]. 湖南: 湘潭大学, 2018. |
| [20] | Adriano M, Thomas H, Gomes LFA, et al. The Brazilian health system at crossroads: progress, crisis and resilience[J]. BMJ Global Health, 2018,3(4):e000829. |
| [21] |
Balarajan Y, Selvaraj S, Subramanian SV. Health care and equity in India[J]. Lancet, 2011,377(9764):505-515.
pmid: 21227492 |
| [22] | Sharma JK, Narang R. Quality of healthcare services in rural India: the user perspective[J]. Vikalpa, 2011,36(1):51-60. |
| [1] | 张浩宇,石逸雯,潘薇,刘爱萍,孙昕霙,李曼,张旭熙. 基于不同失能水平的老年人照料需求的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 431-440. |
| [2] | 祝春素,连至炜,崔一民. 中国中老年人抑郁和慢性病的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 606-611. |
| [3] | 冯星淋, 沈娟, 郭岩. 儿童健康公平性的社会决定因素研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(3): 252-257. |
|
||