北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 564-569. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.03.025
复层猪小肠黏膜下层可吸收膜的降解性能
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,修复科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
Biodegradation properties of multi-laminated small intestinal submucosa
Wei-yi WU,Bo-wen LI,Yu-hua LIU( ),Xin-zhi WANG
),Xin-zhi WANG
- Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
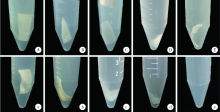
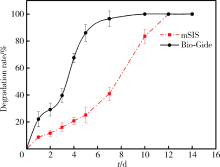
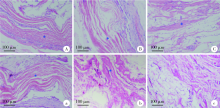
目的 通过体内外实验研究复层猪小肠黏膜下层(multi-laminated small intestinal submucosa,mSIS)可吸收膜的降解性能,并与应用最为广泛的Bio-Gide可吸收生物膜进行比较,为其进一步应用于临床提供实验依据。方法 体外模拟降解采用胶原酶配制降解液,对mSIS膜和Bio-Gide膜进行降解,分别于不同时间点观察二者在降解液中的形态并取出称重,计算降解率。体内皮下埋植采用9只新西兰兔,每只动物背部皮下制备6个皮囊,分别埋入mSIS膜和Bio-Gide膜。于术后4、8、12周取材,通过肉眼观察及HE染色观察不同时间二者的降解程度及组织相容性。结果 体外降解实验显示mSIS膜在第12天降解完全,而Bio-Gide膜在第7天降解完全,且mSIS在降解液中维持形状的时间更长。皮下埋植4周时,mSIS膜和Bio-Gide膜形态相对完整,镜下观二者胶原纤维连续,膜周围少许炎症细胞浸润,Bio-Gide膜部分胶原纤维与周围组织融合。术后8周,mSIS膜形态基本完整,镜下观部分区域与结缔组织融合;肉眼观Bio-Gide膜已破碎,镜下仅可见部分残留纤维与周围组织结合,无完整膜的形态。术后12周时肉眼仅见少量mSIS膜残留碎片,镜下可见mSIS膜残留纤维,与周围结缔组织基本融合;肉眼及镜下观Bio-Gide膜均已消失。结论 mSIS膜皮下埋植降解时间约为12周,Bio-Gide膜约为8周,植入体内生物相容性良好。体外降解mSIS比Bio-Gide膜降解时间延长,且空间维持能力更佳。
中图分类号:
- R318.021
| [1] | Lopez-Martinez F, Gomez Moreno G, Olivares-Ponce P, et al. Implants failures related to endodontic treatment. An observational retrospective study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2015,26(9):992-995. |
| [2] | Palachur D, Prabhakara Rao KV, Murthy KR, et al. A comparative evaluation of bovine-derived xenograft (Bio-Oss collagen) and type Ⅰ collagen membrane (Bio-Gide) with bovine-derived xenograft (Bio-Oss collagen) and fibrin fibronectin sealing system (tisseel) in the treatment of intrabony defects: A clinico-radiographic study[J]. J Indian Soc Periodontol, 2014,18(3):336-343. |
| [3] | Amoian B, Moudi E, Majidi MS, et al. A histologic, histomorphometric, and radiographic comparison between two complexes of cenoboen/cenomembrane and bio-oss/Bio-Gide in lateral ridge augmentation: A clinical trial[J]. Dent Res J (Isfahan), 2016,13(5):446-453. |
| [4] | Oortgiesen DA, Plachokova AS, Geenen C, et al. Alkaline phosphatase immobilization onto Bio-Gide® and Bio-Oss® for periodontal and bone regeneration [J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2012,39(6):546-555. |
| [5] | 詹雅琳, 胡文杰, 甄敏, 等. 去蛋白牛骨基质与可吸收胶原膜的磨牙拔牙位点保存效果影像学评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015,47(1):19-26. |
| [6] | Strietzel FP, Khongkhunthian P, Khattiya R, et al. Healing pattern of bone defects covered by different membrane types: a histologic study in the porcine mandible[J]. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater, 2006,78(1):35-46. |
| [7] |
Owens KW, Yukna RA. Collagen membrane resorption in dogs: A comparative study[J]. Implant Dent, 2001,10(1):49-58.
doi: 10.1097/00008505-200101000-00016 pmid: 11307648 |
| [8] | 吴唯伊, 李博文, 刘玉华, 等. 猪小肠黏膜下层可吸收膜性能及修复骨缺损的效果评价[C]. 中华口腔医学会口腔修复学专业委员会.第十一次全国口腔修复学学术会议论文汇编.南京: 2017. |
| [9] | Olaechea A, Doza-Azpur GM, Valdivia E, et al. Biodegradation of three different collagen membranes: A histological study[J]. Journal of Osseointegration, 2016,8(2):15-19. |
| [10] |
Pilipchuk SP, Plonka AB, Monje A, et al. Tissue engineering for bone regeneration and osseointegration in the oral cavity[J]. Dent Mater, 2015,31(4):317-338.
pmid: 25701146 |
| [11] |
Mcallister BS, Haghighat K. Bone augmentation techniques[J]. J Periodontol, 2007,78(3):377-396.
pmid: 17335361 |
| [12] |
Bresaola MD, Matsumoto MA, Zahoui A, et al. Influence of rapid- and slow-rate resorption collagen membrane in maxillary sinus augmentation[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2017,28(3):320-326.
doi: 10.1111/clr.12801 pmid: 26916561 |
| [13] |
Moses O, Vitrial D, Aboodi G, et al. Biodegradation of three different collagen membranes in the rat calvarium: A comparative study[J]. J Periodontol, 2008,79(5):905-911.
pmid: 18454670 |
| [14] |
Sheikh Z, Hamdan N, Ikeda Y, et al. Natural graft tissues and synthetic biomaterials for periodontal and alveolar bone reconstructive applications: A review[J]. Biomater Res, 2017,21:9.
doi: 10.1186/s40824-017-0095-5 pmid: 28593053 |
| [15] | Bozkurt A, Apel C, Sellhaus B, et al. Differences in degradation behavior of two non-cross-linked collagen barrier membranes: An in vitro and in vivo study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2014,25(12):1403-1411. |
| [16] |
Bozkurt A, Lassner F, O’dey D, et al. The role of microstructured and interconnected pore channels in a collagen-based nerve guide on axonal regeneration in peripheral nerves[J]. Biomaterials, 2012,33(5):1363-1375.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.10.069 pmid: 22082619 |
| [17] | Bozkurt A, Deumens R, Beckmann C, et al. In vitro cell alignment obtained with a schwann cell enriched microstructured nerve guide with longitudinal guidance channels[J]. Biomaterials, 2009,30(2):169-179. |
| [18] |
Verissimo DM, Leitao RF, Ribeiro RA, et al. Polyanionic collagen membranes for guided tissue regeneration: Effect of progressive glutaraldehyde cross-linking on biocompatibility and degradation[J]. Acta Biomater, 2010,6(10):4011-4018.
pmid: 20433958 |
| [19] | Glynn JJ, Polsin EG, Hinds MT. Crosslinking decreases the hemocompatibility of decellularized, porcine small intestinal submucosa[J]. Acta Biomater, 2015,14:96-103. |
| [20] | Moses O, Pitaru S, Artzi Z, et al. Healing of dehiscence-type defects in implants placed together with different barrier membranes: A comparative clinical study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2005,16(2):210-219. |
| [21] |
Valentin JE, Stewart-Akers AM, Gilbert TW, et al. Macrophage participation in the degradation and remodeling of extracellular matrix scaffolds[J]. Tissue Eng Part A, 2009,15(7):1687-1694.
pmid: 19125644 |
| [22] |
Valentin JE, Badylak JS, Mccabe GP, et al. Extracellular matrix bioscaffolds for orthopaedic applications. A comparative histologic study[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2006,88(12):2673-2686.
pmid: 17142418 |
| [23] |
Bai H, Wang D, Delattre B, et al. Biomimetic gradient scaffold from ice-templating for self-seeding of cells with capillary effect[J]. Acta Biomater, 2015,20:113-119.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.04.007 pmid: 25871536 |
| [24] |
Badylak SF, Gilbert TW. Immune response to biologic scaffold materials[J]. Semin Immunol, 2008,20(2):109-116.
pmid: 18083531 |
| [25] |
Yan HJ, Casalini T, Hulsart-Billstrom G, et al. Synthetic design of growth factor sequestering extracellular matrix mimetic hydrogel for promoting in vivo bone formation[J]. Biomaterials, 2018,161:190-202.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.01.041 pmid: 29421555 |
| [26] | Rothamel D, Benner M, Fienitz T, et al. Biodegradation pattern and tissue integration of native and cross-linked porcine collagen soft tissue augmentation matrices: An experimental study in the rat[J]. Head Face Med, 2014(10):10. |
| [27] |
Siar CH, Toh CG, Romanos G, et al. Subcutaneous reactions and degradation characteristics of collagenous and noncollagenous membranes in a macaque model[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2011,22(1):113-120.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.01970.x pmid: 20678135 |
| [28] |
Olde Damink LH, Dijkstra PJ, Van Luyn MJ, et al. In vitro degradation of dermal sheep collagen cross-linked using a water-soluble carbodiimide[J]. Biomaterials, 1996,17(7):679-684.
doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(96)86737-8 pmid: 8672629 |
| [29] |
Li J, Ren N, Qiu J, et al. Carbodiimide crosslinked collagen from porcine dermal matrix for high-strength tissue engineering scaffold[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2013,61:69-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.06.038 pmid: 23820178 |
| [30] | 闫建伟. 牙种植引导骨再生心包胶原膜的制备及理化性能研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017. |
| [31] |
Kozlovsky A, Aboodi G, Moses O, et al. Bio-degradation of a resorbable collagen membrane (Bio-Gide) applied in a double-layer technique in rats[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2009,20(10):1116-1123.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01740.x pmid: 19719734 |
| [32] |
Gilbert TW, Stewart-Akers AM, Simmons-Byrd A, et al. Degradation and remodeling of small intestinal submucosa in canine achilles tendon repair[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2007,89(3):621-630.
doi: 10.2106/JBJS.E.00742 pmid: 17332112 |
| [33] |
Record RD, Hillegonds D, Simmons C, et al. In vivo degradation of c-14-labeled small intestinal submucosa (sis) when used for urinary bladder repair[J]. Biomaterials, 2001,22(19):2653-2659.
doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(01)00007-2 |
| [34] | Mewaldt R, Shi L, Carson D. Enzymatic degradation study of single layer and multi-layer small intestine submucosa (sis) matrices[J]. Wound Repair Regen, 2011,19(2):A39. |
| [1] | 梁晨,张维宇,胡浩,王起,方志伟,许克新. 膀胱扩大术两种不同术式的疗效及并发症比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 293-297. |
| [2] | 詹雅琳,胡文杰,徐涛,甄敏,路瑞芳. 罹患重度牙周炎磨牙拔除后应用去蛋白牛骨基质与可吸收胶原膜进行位点保存的组织学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 169-175. |
| [3] | 宋杨,王晓飞,王宇光,孙玉春,吕培军△. 人脂肪间充质干细胞与生物材料共混物三维打印体的体内成骨[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(1): 45-50. |
| [4] | 詹雅琳, 胡文杰, 甄敏, 徐涛, 路瑞芳. 去蛋白牛骨基质与可吸收胶原膜的磨牙拔牙位点保存效果影像学评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(1): 19-26. |
| [5] | 张培训,安帅,王国强,王艳华,陈博,王振威,韩娜,寇玉辉,王韵,姜保国. 生物套管小间隙套接修复大鼠坐骨神经损伤过程中的疼痛评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(5): 675-678. |
| [6] | 张培训, 寇玉辉, 韩娜, 党育, 薛峰, 王天兵, 徐海林, 陈建海, 杨明, 卢浩, 殷晓峰, . 可降解生物套管小间隙套接法修复周围神经损伤的临床观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(6): 842-846. |
| [7] | 米姗姗, 董艳梅, 高学军. 溶胶-凝胶生物活性玻璃对人牙髓细胞作用的研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(1): 39-42. |
| [8] | 任晓帅, 魏世成, , 苏晓东. 牙种植钛基生物材料表面骨形态发生蛋白修饰的固定与评价方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(5): 604-607. |
|
||