北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 678-683. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.015
脱细胞异体补片移植阴茎增粗术后患者决策后悔分析
- 北京大学人民医院泌尿外科,北京 100081
Decision regret analysis among Chinese patients receiving penile girth enhancement with acellular dermal matrix
Chun-long ZHANG,He LI,Qing LI,Wen-jun BAI,Tao XU,Xiao-wei ZHANG( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
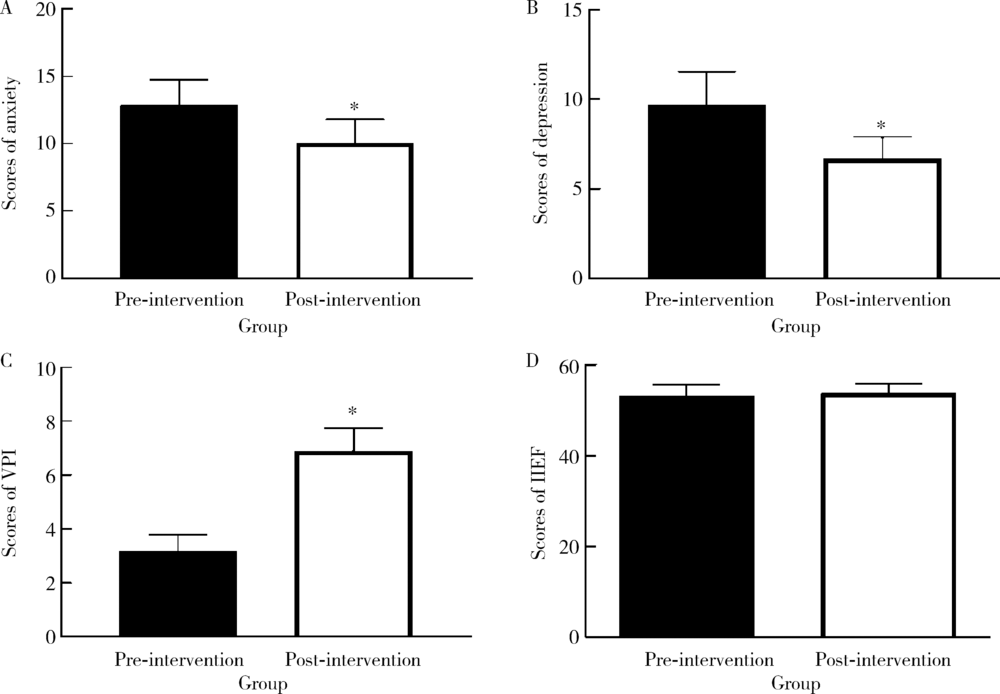
目的: 探究接受脱细胞异体补片移植阴茎增粗术(penile girth enhancement with acellular dermal matrix, PGE with ADM)的患者术后决策后悔现状及潜在预测指标,为优化该类患者决策制定过程提供依据。方法: 纳入78例在2016年6月至2019年1月于北京大学人民医院及协作医院接受PGE with ADM手术的患者。由同一名医师在术前1周测量患者阴茎周长,并以住院焦虑和抑郁量表(hospital anxiety and depression scale,HAD)、国际勃起功能指数(international index of erectile function, IIEF)和视觉化模拟阴茎印象评分(visualized penile image, VPI)评估患者心理负担、勃起功能和阴茎外观。所有患者于术后3个月接受随访,采用决策后悔量表(decision regret scale, DRS)评价患者决策后悔情况。应用多因素方差分析探究决策后悔预测指标,数据使用SPSS 24.0软件进行分析。结果: 术前患者平均阴茎周长为(8.29±0.30) cm,术后平均阴茎周长增至(9.46±0.29) cm(t=76.28, P< 0.01)。术后患者焦虑及抑郁子量表得分均显著下降,分别为2.8±1.3和3.0±1.2(t=19.28, P< 0.05; t=20.67, P< 0.05)。术后患者VPI平均得分增加3.7±1.1(t=30.63, P< 0.05)。用IIEF来评价勃起功能,干预前后IIEF得分无明显变化(t=1.60, P=0.11)。29例(38.2%)患者在一定程度上出现决策后悔,平均DRS评分为27.6±38.2。DRS评分与VPI评分呈负相关(r=-0.348, P< 0.01), 与Anxiety 得分(r=0.760,P< 0.01)和Depression得分呈正相关(r=0.471, P< 0.01), 与IIEF量表得分不具备相关性(r=0.02, P=0.867),多因素方差分析提示年收入高(> 120 000元)和本科以上教育水平的患者更容易发生术后决策后悔(P< 0.01)。结论: 脱细胞异体补片移植阴茎增粗术可以增加患者阴茎周长并减轻患者的心理负担,但术后决策后悔率相对较高。高收入、高教育水平的患者更易产生决策后悔,提示该人群在术前沟通时需要额外的决策支持。
中图分类号:
- R699.8
| [1] |
Tiggemann M, Martins Y, Churchett L. Beyond muscles: unexplored parts of men's body image[J]. J Health Psychol, 2008,13(8):1163-1172.
pmid: 18987089 |
| [2] | Lever J, Frederick DA, Peplau LA. Does size matter? Men’s and women’s views on penis size across the lifespan[J]. Psychol Men Masc, 2006,7(3):129. |
| [3] | Hehemann MC, Towe M, Huynh LM, et al. Penile girth enlargement strategies: What’s the evidence[J]. Sex Med Rev, 2019,7(3):535-547. |
| [4] | Svenson O. Differentiation and consolidation theory of human decision making: a frame of reference for the study of pre- and post-decision Processes[J]. Acta Psychol (Amst), 1992,80(1):143-168. |
| [5] | Zeelenberg M, Pieters R. A Theory of regret regulation 1.0[J]. J Consum Psychol, 2007,17(1):3-18. |
| [6] |
Wilson A, Ronnekleiv-Kelly SM, Pawlik TM. Regret in surgical decision making: a systematic review of patient and physician perspectives[J]. World J Surg, 2017,41(6):1454-1465.
pmid: 28243695 |
| [7] |
Yamauchi K, Nakao M, Nakashima M. Correlates of regret with treatment decision-making among Japanese women with breast cancer: results of an internet-based cross-sectional survey[J]. BMC Womens Health, 2019,19(1):86.
doi: 10.1186/s12905-019-0783-5 pmid: 31266493 |
| [8] |
Wang AW, Chang SM, Chang CS, et al. Regret about surgical decisions among early-stage breast cancer patients: Effects of the congruence between patients’ preferred and actual decision-making roles[J]. Psychooncology, 2018,27(2):508-514.
doi: 10.1002/pon.4522 pmid: 28792651 |
| [9] | Spyropoulos E, Christoforidis C, Borousas D, et al. Augmentation phalloplasty surgery for penile dysmorphophobia in young adults: considerations regarding patient selection, outcome evaluation and techniques applied[J]. Eur Urol, 2005,48(1):121-128 |
| [10] |
Xu T, Zhang G, Bai W, et al. Complications and management of penile girth enhancement with acellular dermal matrix[J]. J Sex Med, 2019,16(12):2011-2017.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2019.09.010 pmid: 31668731 |
| [11] |
Brehaut JC, O'Connor AM, Wood TJ, et al. Validation of a decision regret scale[J]. Med Decis Making, 2003,23(4):281-292.
doi: 10.1177/0272989X03256005 pmid: 12926578 |
| [12] |
Zhong T, Bagher S, Jindal K, et al. The influence of dispositional optimism on decision regret to undergo major breast reconstructive surgery[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2013,108(8):526-530.
doi: 10.1002/jso.23437 pmid: 24105811 |
| [13] |
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale[J]. Acta Psychiatr Scand, 1983,67(6):361-370.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb09716.x pmid: 6880820 |
| [14] |
Bjelland I, Dahl AA, Haug TT, et al. The validity of the hospital anxiety and distress scale[J]. J Psychosom Res, 2002,52(2):69-77.
pmid: 11832252 |
| [15] | Leung CM, Ho S, Kan CS, et al. Evaluation of the Chinese version of the hospital anxiety and depression scale. A cross-cultural perspective[J]. Int J Psychosom, 1993,40(1/2/3/4):29-34. |
| [16] |
Yafi FA, Huynh LM, Ahlering T, et al. What is a “Validated Questionnaire”? A critical review of erectile function assessment[J]. J Sex Med, 2020,17(5):849-860.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2020.02.005 pmid: 32146130 |
| [17] |
Chen XB, Li RX, Yang HN, et al. A comprehensive, prospective study of penile dimensions in Chinese men of multiple ethnicities[J]. Int J Impot Res, 2014,26(5):172-176.
doi: 10.1038/ijir.2014.9 |
| [18] |
Vardi Y, Har-Shai Y, Gil T, et al. A critical analysis of penile enhancement procedures for patients with normal penile size: surgical techniques, success, and complications[J]. Eur Urol, 2008,54(5):1042-1050.
pmid: 18760874 |
| [19] |
Sheehan J, Sherman KA, Lam T, et al. Association of information satisfaction, psychological distress and monitoring coping style with post-decision regret following breast reconstruction[J]. Psychooncology, 2007,16(4):342-351.
doi: 10.1002/pon.1067 pmid: 16874745 |
| [20] |
Calderon C, Ferrando PJ, Lorenzo-Seva U, et al. Validity and reliability of the decision regret scale in cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy[J]. J Pain Symptom Manage, 2019,57(4):828-834.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2018.11.017 pmid: 30639730 |
| [21] |
Shaverdian N, Kishan AU, Veruttipong D, et al. Impact of the primary information source used for decision making on treatment perceptions and regret in prostate cancer[J]. Am J Clin Oncol, 2018,41(9):898-904.
doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000387 pmid: 28537990 |
| [22] |
Schumacher JR, Taylor LJ, Tucholka JL, et al. Socioeconomic factors associated with post-mastectomy immediate reconstruction in a contemporary cohort of breast cancer survivors[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2017,24(10):3017-3023.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-017-5933-0 pmid: 28766209 |
| [23] | 谌绍林, 丁敏, 朱健华, 等. 护士评判性思维能力的调查及其相关因素分析[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2011,17(11):1241-1244. |
| [24] | 石霞, 刘玉玲, 封锡玲. 护理人员获取网络资源信息的能力调查[J]. 护理学杂志, 2008,23(2):14-15. |
| [1] | 张展奕,张帆,颜野,曹财广,李长剑,邓绍晖,孙悦皓,黄天亮,管允鹤,李楠,陆敏,胡振华,张树栋. 近红外荧光靶向探针用于前列腺神经血管束术中成像[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
| [2] | 张帆,张树栋,肖春雷,黄毅,马潞林. 80岁及以上前列腺癌患者行腹腔镜前列腺根治性切除术围手术期参数及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 822-827. |
|
||