北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 938-942. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.024
游离腓骨瓣修复重建上颌骨术后腓骨瓣位置变化
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔颌面外科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Postoperative position change of fibular bone after reconstruction of maxillary defect using free fibular flap
Yi-fan KANG,Xiao-feng SHAN,Lei ZHANG,Zhi-gang CAI( )
)
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
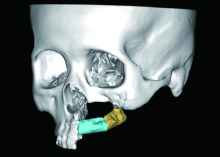
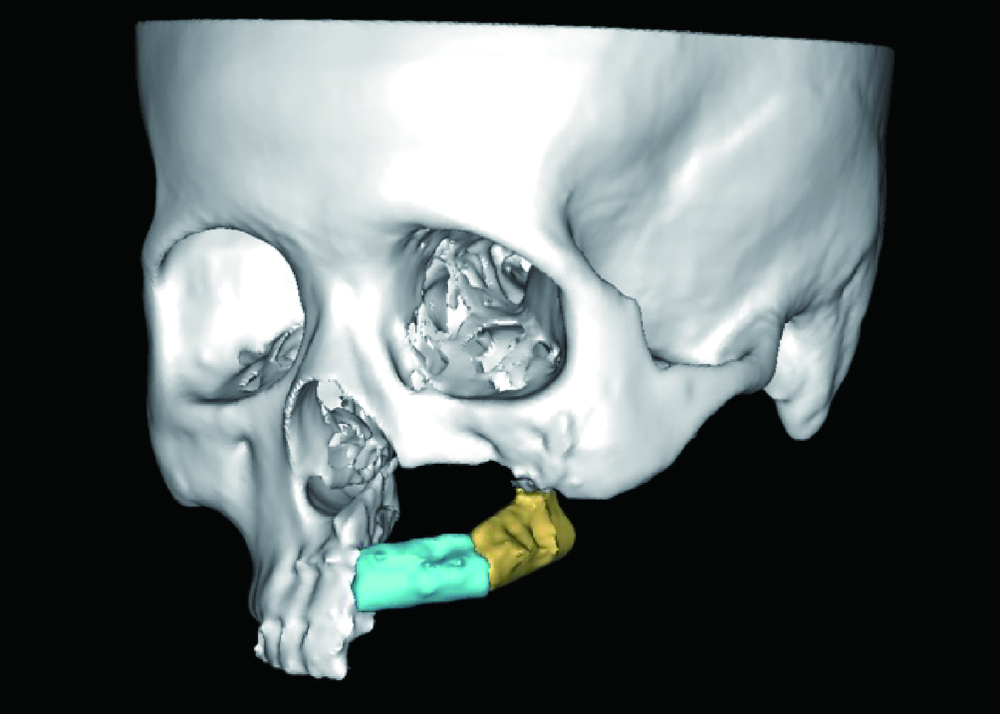
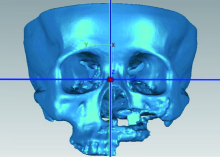
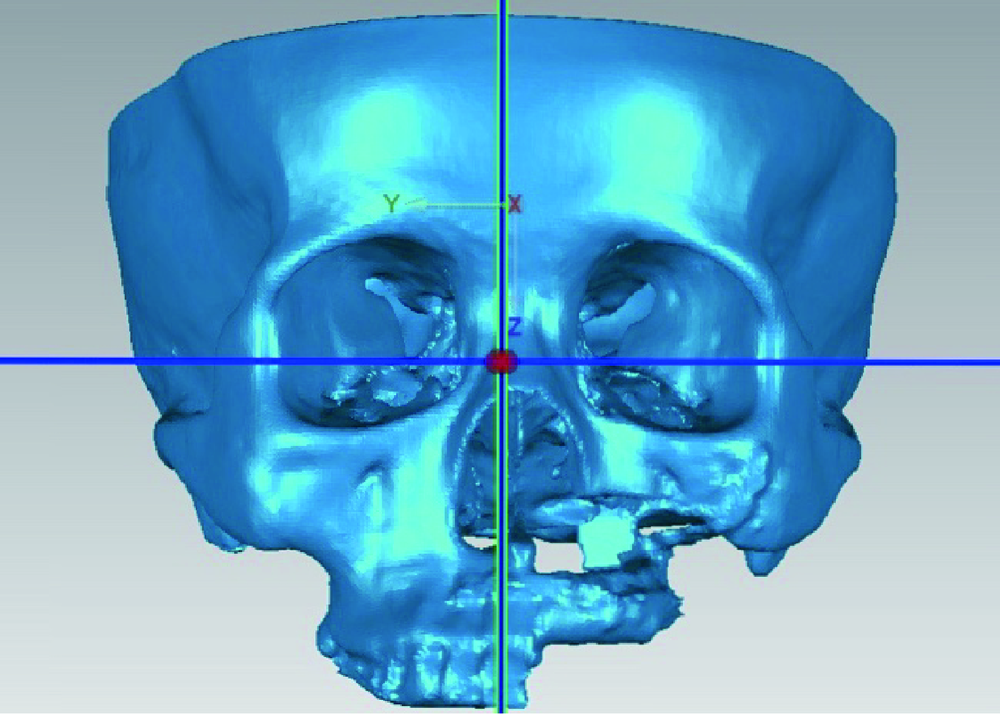
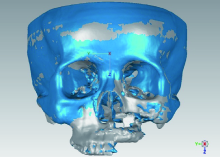
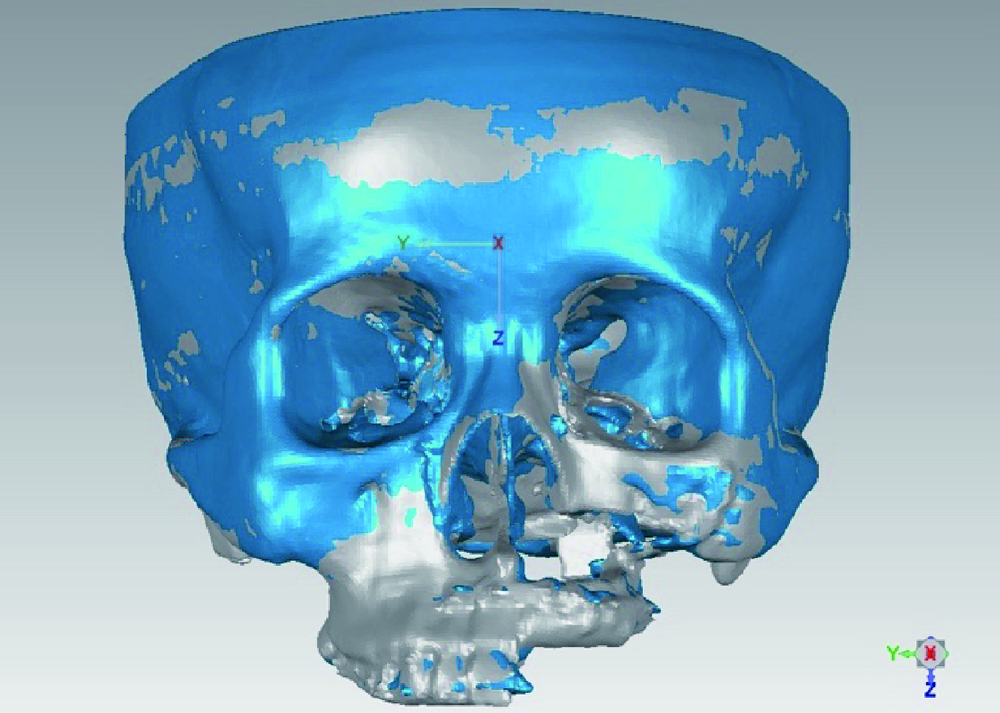
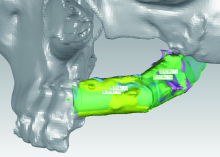
目的:研究腓骨瓣重建上颌骨术后腓骨瓣位置是否发生变化,初步分析影响腓骨瓣位置变化的因素。方法:选择2012年11月至2016年11月于北京大学口腔医院口腔颌面外科行上颌骨腓骨瓣重建的患者,根据患者修复颧上颌支柱的方式,分为钛板支柱组和骨支柱组。使用软件将术后1周与术后1年的CT进行三维重建,对齐术后1周及术后1年的上颌骨模型,获得腓骨瓣长轴的单位方向向量,根据单位方向向量坐标计算角度改变并记录位置改变方向。结果:32例患者纳入本研究。在术后1周与术后1年时,在X-Y平面上腓骨瓣长轴与X轴的夹角分别为95.65°±53.49°和95.53°±52.77°,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。在X-Z平面上的夹角分别为 96.88°±69.76°和95.33°±67.42°,差异有统计学意义(P=0.0497)。钛板支柱组和骨支柱组用于修复牙槽突的腓骨瓣长轴在X-Y平面上的角度变化分别为3.23°±3.93°、1.94°±1.78°,在X-Z平面上的角度变化分别为 6.02°±9.89°、3.27°±2.31°,两组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。在X-Y平面上用于修复前牙牙槽突、后牙牙槽突、颧上颌支柱的腓骨瓣长轴变化分别为3.13°±3.78°、2.56°±3.17°、5.51°±4.39°,后两者间差异有统计学意义(P=0.023);在X-Z平面上分别为4.94°±4.75°、5.26°±10.25°、6.69°±6.52°,两两比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。腓骨瓣主要的位置偏移方向均为向内侧、上方偏移。结论:术后1年与术后1周相比,腓骨瓣在矢状平面上的位置发生了显著性变化,在水平面上的位置变化不明显;腓骨瓣位置的改变主要以向内侧、上方偏移为主。
中图分类号:
- R782.4
| [1] |
Peng X, Mao C, Yu GY, et al. Maxillary reconstruction with the free fibula flap[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2005,115(6):1562.
doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000160691.63029.74 pmid: 15861059 |
| [2] |
Kazaoka Y, Shinohara AK, Hasegawa T. Functional reconstruction after a total maxillectomy using a fibula osteocutaneous flap with osseointegrated implants[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1999,103(4):1244-1246.
doi: 10.1097/00006534-199904040-00021 pmid: 10088513 |
| [3] |
Wijbenga JG, Schepers RH, Werker PM, et al. A systematic review of functional outcome and quality of life following reconstruction of maxillofacial defects using vascularized free fibula flaps and dental rehabilitation reveals poor data quality.[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2016,69(8):1024-1036.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2016.05.003 pmid: 27292287 |
| [4] |
Sozzi D, Novelli G, Silva R, et al. Implant rehabilitation in fibula-free flap reconstruction: A retrospective study of cases at 1-18 years following surgery[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2017,45(10):1655.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2017.06.021 pmid: 28823690 |
| [5] | Frodel JL, Funk GF, Capper DT, et al. Osseointegrated implants: A comparative study of bone thickness in four vascularized bone flaps.[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1994,32(2):456-458. |
| [6] | 王明一, 王慧珊, 杨劼, 等. 咬合引导的颌骨重建精确度分析及功能评价[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2018,16(2):162-166. |
| [7] | 沈毅, 孙坚, 李军, 等. 上颌骨功能性重建中用钛植入体重建颧上颌支柱的生物力学研究[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2011,9(3):198-203. |
| [8] | 刘尚萍, 蔡志刚, 张杰, 等. 下颌骨缺损重建术后钛板相关并发症97例临床回顾研究[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2013,48(10):586-590. |
| [9] |
Wolff J. The classic: On the inner architecture of bones and its importance for bone growth[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2010,468(4):1056.
doi: 10.1007/s11999-010-1239-2 pmid: 20162387 |
| [10] |
Frost HM. A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff’s law for clinicians[J]. Angle Orthod, 2004,74(1):3.
doi: 10.1043/0003-3219(2004)074<0003:AUOBPA>2.0.CO;2 pmid: 15038485 |
| [11] |
Wilkman T, Apajalahti S, Wilkman E, et al. A comparison of bone resorption over time: An analysis of the free scapular, iliac crest, and fibular microvascular flaps in mandibular reconstruction[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017,75(3):616-621.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.09.009 pmid: 27725102 |
| [12] |
Hölzle F, Watola A, Kesting MR, et al. Atrophy of free fibular grafts after mandibular reconstruction[J]. Plas Reconstr Surg, 2007,119(1):151.
doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000240703.02620.24 |
| [13] |
Mertens C, Decker C, Engel M, et al. Early bone resorption of free microvascular reanastomized bone grafts for mandibular reconstruction: A comparison of iliac crest and fibula grafts[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2014,42(5):e217.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2013.08.010 pmid: 24269641 |
| [14] |
Li L, Blake F, Heiland M, et al. Long-term evaluation after mandibular reconstruction with fibular grafts versus microsurgical fibular flaps[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2007,65(2):281-286.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2006.08.009 pmid: 17236934 |
| [15] |
Powell HR, Jaafar M, Bisase B, et al. Resorption of fibula bone following mandibular reconstruction for osteoradionecrosis[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014,52(4):375-378.
pmid: 24613371 |
| [16] |
Kang YF, Liang J, He Z, et al. Cortical bone resorption of fibular bone after maxillary reconstruction with a vascularized fibula free flap: A computed tomography imaging study[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2019,48:1009-1014.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2019.03.008 pmid: 30979515 |
| [1] | 黄莹,吴志远,周行红,蔡志刚,张杰. 股前外侧皮瓣修复上颌骨缺损术后面部软组织对称性感观分级[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [2] | 章文博,于尧,王洋,刘筱菁,毛驰,郭传瑸,俞光岩,彭歆. 数字化外科技术在上颌骨缺损重建中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 1-005. |
|
||