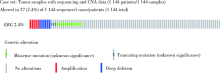
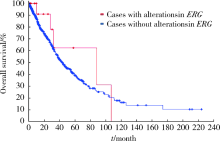
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 971-974. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.030
同时性多原发肺腺癌组织编码转录因子ERG基因相同位点突变1例报告
- 1.浙江省嘉兴市第二医院 肿瘤科,浙江嘉兴 314000
2.浙江省嘉兴市第二医院 中心实验室,浙江嘉兴 314000
Concordant point mutation of ETS-related gene (ERG) in tumor tissues from a synchronous multiple primary lung cancer: A case report
- 1. Department of Oncology, The Second Hospital of Jiaxing, Jiaxing 314000, Zhejiang, China
2. Key Laboratory, The Second Hospital of Jiaxing, Jiaxing 314000, Zhejiang, China
摘要:
中图分类号:
- R734.2
| [1] |
Kumar-Sinha C, Tomlins SA, Chinnaiyan AM. Recurrent gene fusions in prostate cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2008,8(7):497-511.
doi: 10.1038/nrc2402 pmid: 18563191 |
| [2] |
Brenner JC, Ateeq B, Li Y, et al. Mechanistic rationale for inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in ETS gene fusion-positive prostate cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2011,19(5):664-678.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.04.010 |
| [3] |
Wang X, Qiao Y, Asangani IA, et al. Development of peptidomimetic inhibitors of the ERG gene gusion product in prostate cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2017,31(4):532-548.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.02.017 pmid: 28344039 |
| [4] |
Martini N, Melamed MR. Multiple primary lung cancers[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 1975,70(4):606-612.
pmid: 170482 |
| [5] |
Kozower BD, Larner JM, Detterbeck FC. Special treatment issues in non-small cell lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines[J]. Chest, 2013,143(5 Suppl):e369S-e399S.
doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2362 pmid: 23649447 |
| [6] |
Slaughter DP, Southwick HW, Smejkal W. Field cancerization in oral stratified squamous epithelium; clinical implications of multicentric origin[J]. Cancer, 1953,6(5):963-968.
doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195309)6:5<963::aid-cncr2820060515>3.0.co;2-q pmid: 13094644 |
| [7] |
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Nature, 2014,511(7511):543-550.
doi: 10.1038/nature13385 |
| [8] |
Jamal-Hanjani M, Wilson GA, McGranahan N, et al. Tracking the evolution of non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017,376(22):2109-2121.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1616288 pmid: 28445112 |
| [9] |
Adamo P, Ladomery MR. The oncogene ERG: A key factor in prostate cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2016,35(4):403-414.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.109 pmid: 25915839 |
| [10] |
Ida K, Kobayashi S, Taki T, et al. EWS-FLI-1 and EWS-ERG chimeric mRNAs in Ewing’s sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumor[J]. Int J Cancer, 1995,63(4):500-504.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910630407 pmid: 7591257 |
| [11] |
Nagai N, Ohguchi H, Nakaki R, et al. Downregulation of ERG and FLI1 expression in endothelial cells triggers endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. PLoS Genet, 2018,14(11):e1007826.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007826 pmid: 30500808 |
| [1] | 李志存, 吴天俣, 梁磊, 范宇, 孟一森, 张骞. 穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | 刘家骏, 刘国康, 朱玉虎. 免疫相关性重症肺炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 932-937. |
| [3] | 黄教悌,胡菁,韩博. 治疗相关神经内分泌前列腺癌机制研究与靶向治疗新进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 557-561. |
| [4] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [5] | 姚凯烽,阮明健,李德润,田宇轩,陈宇珂,范宇,刘毅. 靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺对PI-RADS 4~5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [6] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [7] | 王滨帅,邱敏,张前进,田茂锋,刘磊,王国良,陆敏,田晓军,张树栋. 6例肾尤文肉瘤伴静脉瘤栓的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [8] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [9] | 舒帆,郝一昌,张展奕,邓绍晖,张洪宪,刘磊,王国良,田晓军,赵磊,马潞林,张树栋. 肾部分切除术治疗囊性肾癌的功能学和肿瘤学结果:单中心回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
| [10] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [11] | 柴晓东,孙子文,李海爽,朱靓怡,刘小旦,刘延涛,裴斐,常青. 髓母细胞瘤分子亚型中CD8+T淋巴细胞浸润的临床病理特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 512-518. |
| [12] | 林国中,马长城,吴超,司雨,杨军. 微通道技术在颈椎管肿瘤微创切除术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 318-321. |
| [13] | 俞光岩. 儿童唾液腺疾病[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 1-3. |
| [14] | 薛蔚,董樑,钱宏阳,费笑晨. 前列腺癌新辅助治疗与辅助治疗的现状及进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 775-780. |
| [15] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
|
||