北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 220-226. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.034
基于赋权形态学分析的三维面部对称参考平面构建方法
朱玉佳1,2,赵一姣1,2,郑盛文3,4,温奥楠1,2,傅湘玲3,4,Δ( ),王勇1,2,Δ(
),王勇1,2,Δ( )
)
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔医学数字化研究中心 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔修复教研室,北京 100081
3.北京邮电大学计算机学院(国家示范性软件学院),北京 100876
4.北京邮电大学可信分布式计算与服务教育部重点实验室,北京 100876
A method for constructing three-dimensional face symmetry reference plane based on weighted shape analysis algorithm
ZHU Yu-jia1,2,ZHAO Yi-jiao1,2,ZHENG Sheng-wen3,4,WEN Ao-nan1,2,FU Xiang-ling3,4,Δ( ),WANG Yong1,2,Δ(
),WANG Yong1,2,Δ( )
)
- 1. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
3. School of Computer Science, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (National Pilot Software Engineering School), Beijing 100876, China
4. Key Laboratory of Trustworthy Distributed Computing and Service, Ministry of Education, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
摘要:
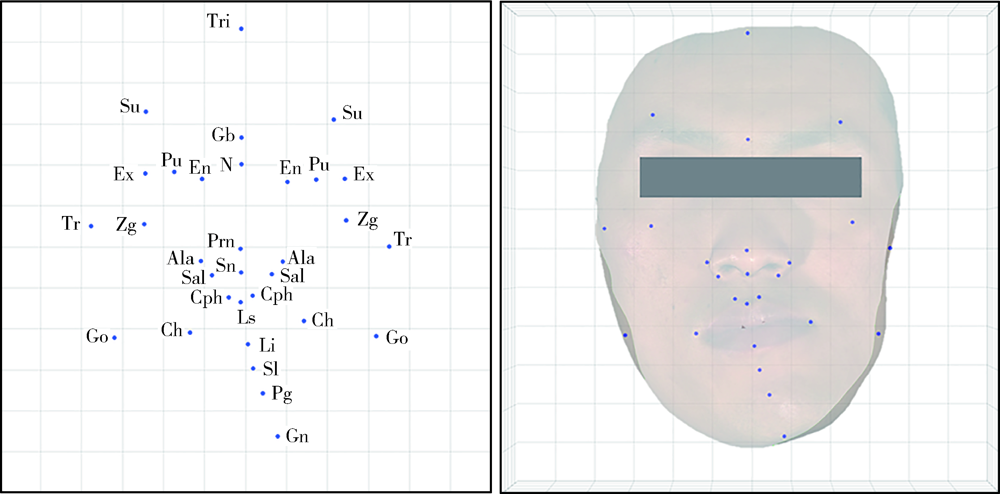
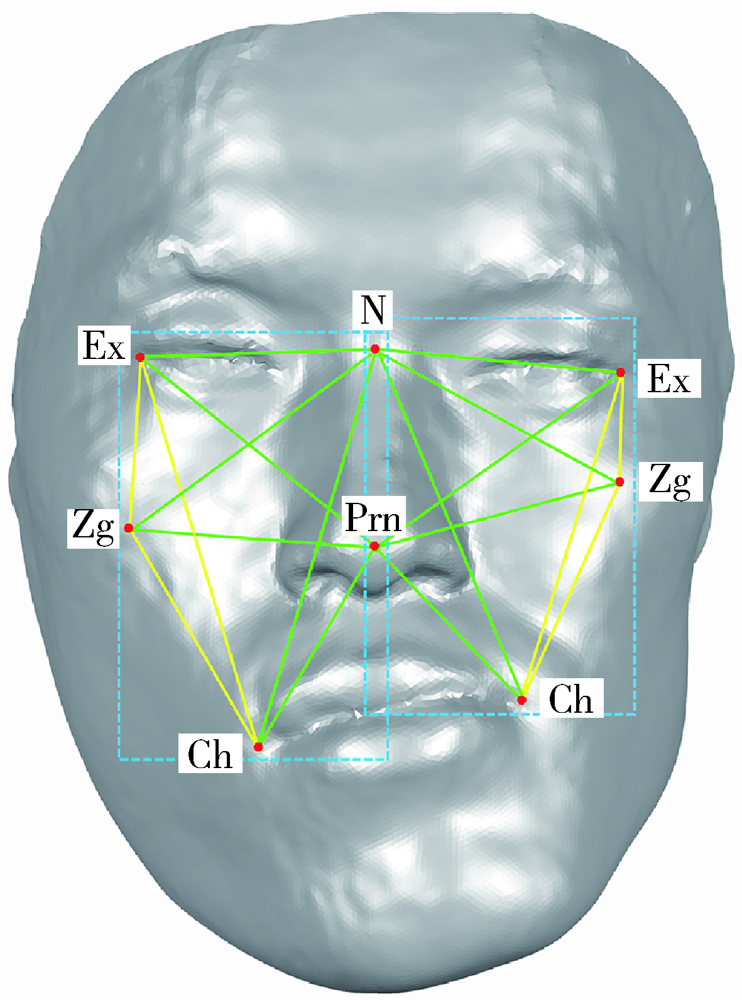
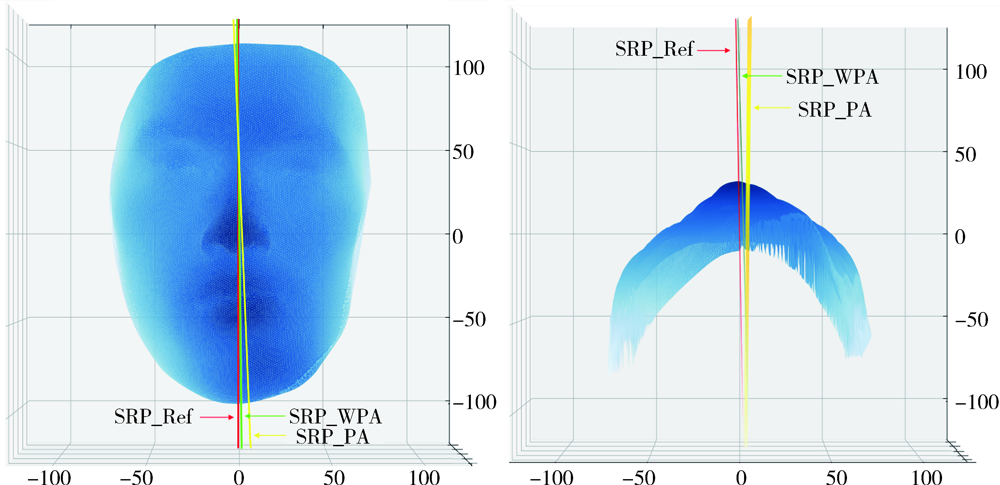
目的: 建立一种基于三维形态学分析的赋权普氏分析(weighted Procrustes analysis,WPA)方法,实现对下颌偏斜患者面部解剖标志点不对称程度量化赋权的三维面部对称参考平面自动化构建。方法: 临床收集下颌偏斜患者30例,基于本体-镜像关联法的普氏分析(Procrustes analysis,PA)算法和自主研发的WPA算法,分别构建每名患者三维面部模型的对称参考平面(实验组一和二),以专家定义的区域迭代最近点(iterative closest point,ICP)算法(选取对称性良好的区域)构建的对称参考平面为“真值平面”,作为参考组。以实验组与参考组的平面角度误差作为评价指标,分别比较两个实验组与参考组的差异,评价WPA算法构建对称参考平面的临床适用性。结果: 30例下颌偏斜患者WPA算法构建的对称参考平面与真值平面的角度误差为1.53°±0.84°,PA算法构建的对称参考平面与真值平面的角度误差为2.06°±0.86°。对于下颌偏斜大于12 mm的患者,WPA算法比PA算法的平均平面角度误差小0.86°。结论: 基于三维面部形态学分析的WPA算法对下颌偏斜面部不对称畸形患者构建三维面部对称参考平面的临床应用效果比传统PA算法有显著提高,初步达到了口腔临床专家级诊断策略的效果。
中图分类号:
- R782.2
| [1] |
Baudouin JY, Tiberghien G. Symmetry, averageness, and feature size in the facial attractiveness of women[J]. Acta Psychol (Amst), 2004,117(3):313-332.
doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2004.07.002 |
| [2] |
Ferrario VF, Sforza C, Ciusa V, et al. The effect of sex and age on facial asymmetry in healthy subjects: a cross-sectional study from adolescence to mid-adulthood[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2001,59(4):382-388.
doi: 10.1053/joms.2001.21872 pmid: 11289167 |
| [3] |
Shaner DJ, Peterson AE, Beattie OB, et al. Assessment of soft tissue facial asymmetry in medically normal and syndrome-affected individuals by analysis of landmarks and measurements[J]. Am J Med Genet, 2000,93(2):143-154.
doi: 10.1002/1096-8628(20000717)93:2<143::aid-ajmg12>3.0.co;2-q pmid: 10869118 |
| [4] |
Burke PH, Healy MJ. A serial study of normal facial asymmetry in monozygotic twins[J]. Ann Hum Biol, 1993,20(6):527-534.
doi: 10.1080/03014469300002932 pmid: 8257078 |
| [5] | 黄佳梦, 李娟, 林军. 面部不对称畸形评估的研究进展[J]. 中国医疗美容, 2019,9(6):121-128. |
| [6] |
Kim MS, Lee EJ, Song IJ, et al. The location of midfacial landmarks according to the method of establishing the midsagittal reference plane in three-dimensional computed tomography analysis of facial asymmetry[J]. Imaging Sci Dent, 2015,45(4):227-232.
doi: 10.5624/isd.2015.45.4.227 pmid: 26730370 |
| [7] |
Lee MS, Chung DH, Lee JW, et al. Assessing soft-tissue characteristics of facial asymmetry with photographs[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2010,138(1):23-31.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2008.08.029 pmid: 20620830 |
| [8] |
Haraguchi S, Iguchi Y, Takada K. Asymmetry of the face in orthodontic patients[J]. Angle Orthod, 2008,78(3):421-426.
doi: 10.2319/022107-85.1 pmid: 18416611 |
| [9] |
O’Grady KF, Antonyshyn OM. Facial asymmetry: three-dimensional analysis using laser surface scanning[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1999,104(4):928-937.
doi: 10.1097/00006534-199909040-00006 pmid: 10654730 |
| [10] |
Nur RB, Cakan DG, Arun T. Evaluation of facial hard and soft tissue asymmetry using cone-beam computed tomography[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2016,149(2):225-237.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2015.07.038 pmid: 26827979 |
| [11] |
Lee JK, Jung PK, Moon CH. Three-dimensional cone beam computed tomographic image reorientation using soft tissues as reference for facial asymmetry diagnosis[J]. Angle Orthod, 2014,84(1):38-47.
doi: 10.2319/112112-890.1 pmid: 23758600 |
| [12] |
Klingenberg CP, Barluenga M, Meyer A. Shape analysis of symmetric structures: quantifying variation among individuals and asymmetry[J]. Evolution, 2002,56(10):1909-1920.
doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2002.tb00117.x pmid: 12449478 |
| [13] |
Du S, Xu Y, Wan T, et al. Robust iterative closest point algorithm based on global reference point for rotation invariant registration[J]. PLoS One, 2017,12(11):e0188039.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188039 pmid: 29176780 |
| [14] |
Damstra J, Fourie Z, De Wit M, et al. A three-dimensional comparison of a morphometric and conventional cephalometric mid-sagittal planes for craniofacial asymmetry[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2012,16(1):285-294.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-011-0512-4 pmid: 21271348 |
| [15] |
Besl PJ, McKay ND. A method for registration of 3-D shapes[J]. IEEE T Pattern Anal, 1992,14(2):239-256.
doi: 10.1109/34.121791 |
| [16] |
Verhoeven TJ, Coppen C, Barkhuysen R, et al. Three dimensio-nal evaluation of facial asymmetry after mandibular reconstruction: validation of a new method using stereophotogrammetry[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2013,42(1):19-25.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2012.05.036 pmid: 22939875 |
| [17] |
De Momi E, Chapuis J, Pappas I, et al. Automatic extraction of the mid-facial plane for cranio-maxillofacial surgery planning[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2006,35(7):636-642.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2006.01.028 pmid: 16542822 |
| [18] |
Xiong Y, Zhao Y, Yang H, et al. Comparison between interactive closest point and procrustes analysis for determining the median sagittal plane of three-dimensional facial data[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2016,27(2):441-444.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000002376 pmid: 26825747 |
| [19] |
Richtsmeier JT, Lele S. A coordinate-free approach to the analysis of growth patterns: models and theoretical considerations[J]. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc, 1993,68(3):381-411.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1993.tb00737.x pmid: 8347767 |
| [20] |
Lele S, Richtsmeier JT. Euclidean distance matrix analysis: a coordinate-free approach for comparing biological shapes using landmark data[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol, 1991,86(3):415-421.
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330860307 pmid: 1746646 |
| [21] |
Verhoeven TJ, Nolte JW, Maal TJ, et al. Unilateral condylar hyperplasia: a 3-dimensional quantification of asymmetry[J]. PLoS One, 2013,8(3):e59391.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059391 pmid: 23544063 |
| [22] |
Gateno J, Jajoo A, Nicol M, et al. The primal sagittal plane of the head: a new concept[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2016,45(3):399-405.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2015.11.013 pmid: 26708049 |
| [23] |
Chetverikov D, Stepanov D, Krsek P. Robust Euclidean alignment of 3D point sets: the trimmed iterative closest point algorithm[J]. Image Vision Comput, 2005,23(3):299-309.
doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2004.05.007 |
| [24] | Zelditch ML, Swiderski DL, Sheets DH, et al. Geometric morphometrics for biologists: A primer [M]. San Diego: Elsevier Academic Press, 2004: 293-319. |
| [25] |
Walters M, Claes P, Kakulas E, et al. Robust and regional 3D facial asymmetry assessment in hemimandibular hyperplasia and hemimandibular elongation anomalies[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2013,42(1):36-42.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2012.05.021 pmid: 22749574 |
| [26] |
Claes P, Walters M, Clement J. Improved facial outcome assessment using a 3D anthropometric mask[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2012,41(3):324-330.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2011.10.019 pmid: 22103995 |
| [27] |
Claes P, Walters M, Vandermeulen D, et al. Spatially-dense 3D facial asymmetry assessment in both typical and disordered growth[J]. J Anat, 2011,219(4):444-455.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2011.01411.x |
| [28] |
Wu J, Heike C, Birgfeld C, et al. Measuring symmetry in children with unrepaired cleft lip: defining a standard for the three-dimensional midfacial reference plane[J]. Cleft Palate Craniofac J, 2016,53(6):695-704.
doi: 10.1597/15-053 pmid: 26752127 |
| [29] |
Perlyn CA, DeLeon VB, Babbs C, et al. The craniofacial phenotype of the Crouzon mouse: analysis of a model for syndromic craniosynostosis using three-dimensional MicroCT[J]. Cleft Palate Craniofac J, 2006,43(6):740-748.
doi: 10.1597/05-212 pmid: 17105336 |
| [30] |
Richtsmeier JT, Cole TR, Krovitz G, et al. Preoperative mor-phology and development in sagittal synostosis[J]. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol, 1998,18(2):64-78.
pmid: 9672839 |
| [31] |
Richtsmeier JT, Lele S. Analysis of craniofacial growth in Crouzon syndrome using landmark data[J]. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol, 1990,10(1):39-62.
pmid: 2373755 |
| [32] |
Dufresne C, Richtsmeier JT. Interaction of craniofacial dysmorphology, growth, and prediction of surgical outcome[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 1995,6(4):270-281.
doi: 10.1097/00001665-199507000-00003 pmid: 9020701 |
| [33] | Ferrario VF, Sforza C, Pizzini G, et al. Sexual dimorphism in the human face assessed by Euclidean distance matrix analysis[J]. J Anat, 1993,183(Pt 3):593-600. |
| [34] |
Ferrario VF, Sforza C, Miani AJ, et al. Maxillary versus mandi-bular arch form differences in human permanent dentition assessed by Euclidean-distance matrix analysis[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 1994,39(2):135-139.
doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(94)90108-2 pmid: 8185498 |
| [35] |
Ferrario VF, Sforza C, Miani AJ, et al. Human dental arch shape evaluated by Euclidean-distance matrix analysis[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol, 1993,90(4):445-453.
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330900405 pmid: 8476003 |
| [36] |
Ferrario VF, Sforza C, Miani AJ, et al. Dental arch asymmetry in young healthy human subjects evaluated by Euclidean distance matrix analysis[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 1993,38(3):189-194.
doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(93)90027-j pmid: 8489412 |
| [37] | 聂琼, 林久祥. Angle Ⅱ1与正常牙合牙弓形态差异——应用欧几里德距离矩阵分析法[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2005,21(5):659-662. |
| [1] | 邱淑婷,朱玉佳,王时敏,王飞龙,叶红强,赵一姣,刘云松,王勇,周永胜. 姿势微笑位口唇对称参考平面的数字化构建及初步应用验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 193-199. |
| [2] | 朱玉佳,许晴,赵一姣,张磊,付子旺,温奥楠,高梓翔,张昀,傅湘玲,王勇. 深度学习算法辅助构建三维颜面正中矢状平面[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 134-139. |
| [3] | 熊玉雪, 杨慧芳, 赵一姣, 王勇. 两种评价面部三维表面数据不对称度方法的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(2): 340-343. |
| [4] | 张晓芸, 许天民. 应用锥束计算机体层摄影术评价颅颌面的不对称[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(1): 156-161. |
|
||