北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 235-239. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.001
• 论著 • 下一篇
基因沉默肽基精氨酸脱亚胺酶4的表达对胶原诱导关节炎小鼠肺间质病变的影响
- 内蒙古科技大学包头医学院第一附属医院风湿免疫科,内蒙古自治区自体免疫学重点实验室, 内蒙古包头 014010
Therapeutic effect of gene silencing peptidyl arginine deaminase 4 on pulmonary interstitial lesions induced by collagen-induced arthritis mice
ZHAO Kai,CHANG Zhi-fang,WANG Zhi-hua,PANG Chun-yan( ),WANG Yong-fu(
),WANG Yong-fu( )
)
- Department of Rheumatism and Immunology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Inner Monolia University of Secience and Technology, Inner Mongolia Autoimmunology Key Laboratory, Baotou 014010, Inner Mongolia, China
摘要:
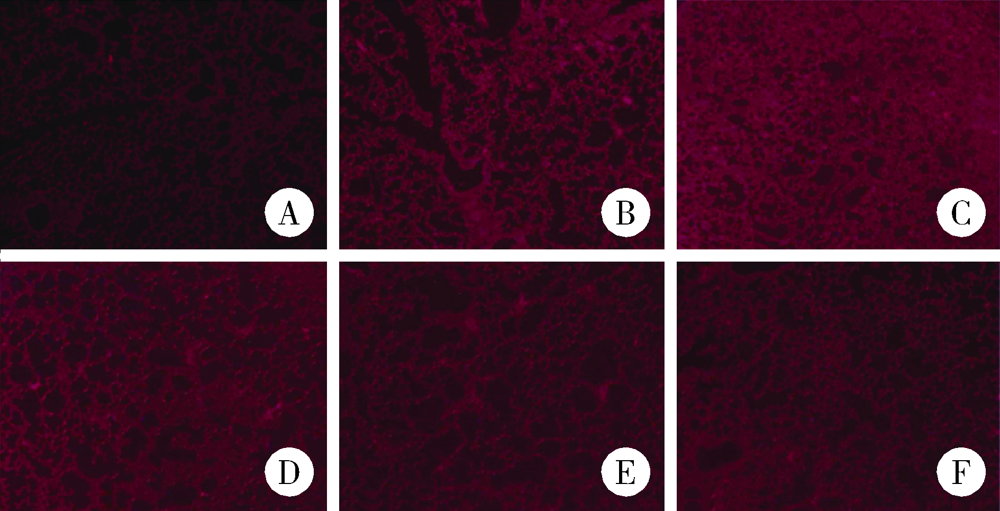
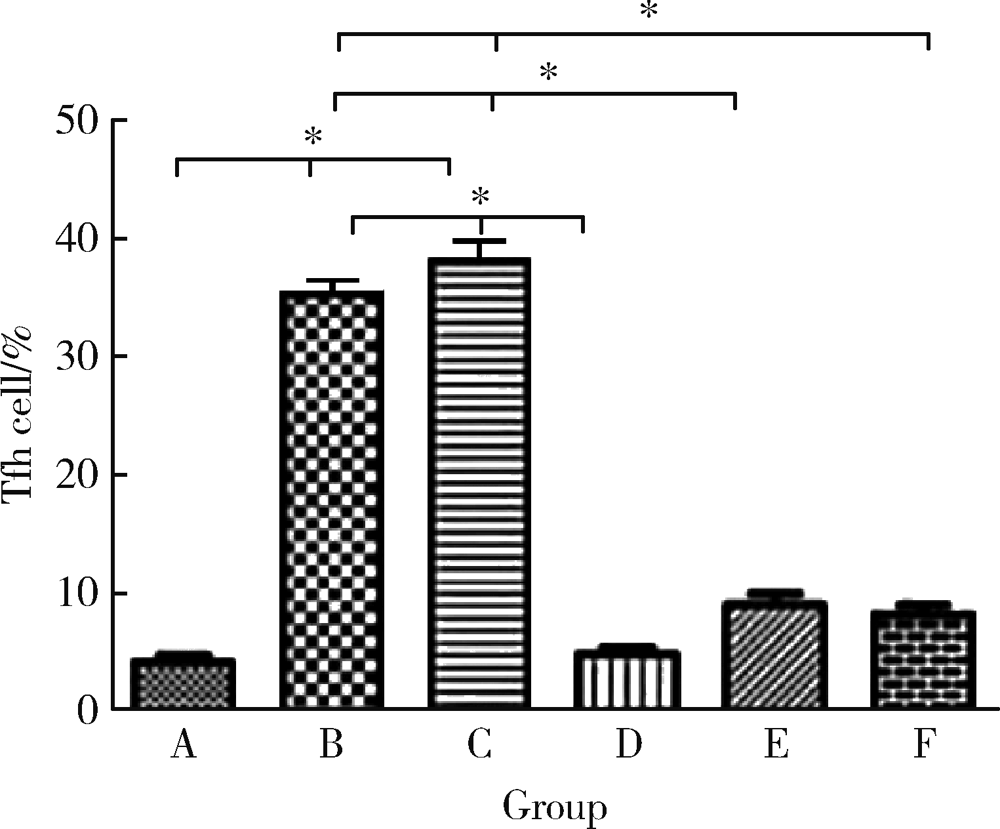
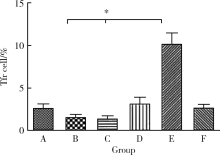
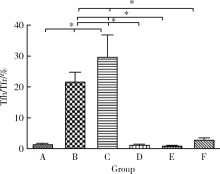
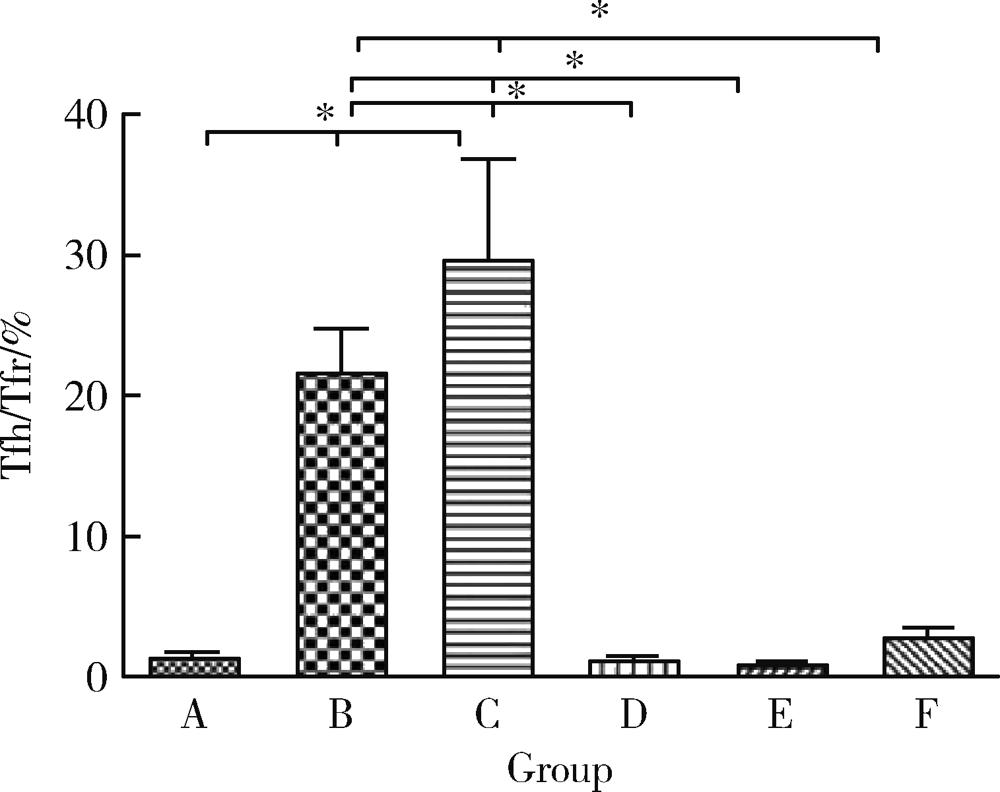
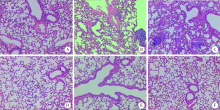
目的: 研究基因沉默肽基精氨酸脱亚胺酶 4 (peptidyl arginine deaminase 4,PAD4)的表达对胶原诱导的关节炎(collagen-induced arthritis,CIA)小鼠肺间质病变的治疗作用及可能机制。方法: DBA/1小鼠建立CIA模型,尾静脉注射PAD4-siRNA表达载体制备的病毒液,每周1次,共8次。处死小鼠,实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)法检测肺中PAD4 mRNA的表达水平;免疫组织化学法检测PAD4蛋白的表达;取脾组织进行细胞培养,流式细胞术检测Tfh细胞和Tfr细胞比例的变化;HE染色观察肺病理学的改变。结果: (1)与空白组比较,模型组小鼠肺组织PAD4 mRNA的表达水平增加,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05), PAD4-siRNA治疗后CIA小鼠肺组织中PAD4 mRNA的表达水平较模型组和阴性对照组明显减少,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);(2)空白组小鼠肺组织红色荧光较少,而模型组和阴性对照组小鼠肺组织的炎细胞浸润区和气管周围可见较多的红色荧光,PAD4-siRNA治疗后3组的红色荧光明显减少;(3)与空白组比较,模型组脾细胞中Tfh细胞比例升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),PAD4-siRNA治疗后CIA小鼠脾细胞中Tfh细胞比例较模型组和阴性对照组明显降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);与空白组比较,模型组小鼠脾细胞中Tfr细胞比例略有降低,但差异无统计学意义,PAD4-siRNA治疗后小鼠脾细胞中Tfr细胞比例升高,但只有PAD4-siRNA2组与模型组和阴性对照组比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);(4)模型组脾细胞中Tfh/Tfr值升高,与空白组比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);PAD4-siRNA治疗后3组Tfh/Tfr值均下降,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);(5)与空白组比较,模型组小鼠肺组织的肺泡壁增厚,炎性细胞浸润增加,PAD4-siRNA治疗后CIA小鼠的肺组织破坏及炎性浸润减少,纤维化程度减轻。结论: 基因沉默PAD4的表达可以降低Tfh细胞的比例,升高Tfr细胞的比例,逆转Tfh/Tfr值,减轻肺组织的间质病变程度和炎症浸润程度。
中图分类号:
- R593.22
| [1] |
Haridas V, Shetty P, Sarathkumar E, et al. Reciprocal regulation of pro-inflammatory Annexin A2 and anti-inflammatory Annexin A1 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2019,46(1):83-95.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4448-5 pmid: 30426384 |
| [2] |
Yuzhalin AE, Gordon-Weeks AN, Tognoli ML, et al. Colorectal cancer liver metastatic growth depends on PAD4-driver citrullination of the extracellular matrix[J]. Nat Commun, 2018,9(1):4783.
pmid: 30429478 |
| [3] | 郭靖, 钱龙, 李向培, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血单个核细胞肽酰基精氨酸脱亚氨酶4表达及组蛋白甲基化水平[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2013,52(11):928-931. |
| [4] |
Thanapati S, Ganu M, Giri P, et al. Impaired NK cell functiona-lity and increased TNF-α production as biomarkers of chronic chikungunya arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Hum Immunol, 2017,78(4):370-374.
pmid: 28213049 |
| [5] | 王建. Th细胞在类风湿关节炎发病作用的研究进展[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2015,35(2):263-266. |
| [6] |
Xu B, Li J, Wu C, et al. CXCL10 and TRAIL are upregulated by TXNDC5 in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes[J]. J Rheumatol, 2018,45(3):335-340.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.170170 pmid: 29247155 |
| [7] | 刘倩, 杨宇, 陈立, 等. 血小板源性生长因子及其受体在类风湿性关节炎大鼠肺组织的表达及与风湿肺关系的探讨[J]. 中国医科大学学报, 2002,31(1):11-14. |
| [8] |
Darrah E, Giles JT, Davis RL, et al. Autoantibodies to peptidylarginine deiminase 2 are associated with less severe disease in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Front Immunol, 2018,9:2696.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02696 pmid: 30515171 |
| [9] |
Apa I, Saliba D, Ponzoni M, et al. TFH-derived dopamine accelelates productive synapses in germinal centres[J]. Nature, 2017,547(7663):318-323.
doi: 10.1038/nature23013 pmid: 28700579 |
| [10] | 邹晓月, 熊御云, 张龙锋, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血滤泡辅助性T淋巴细胞百分率的变化及意义[J]. 重庆医学, 2017,46(35):4920-4922. |
| [11] | Wang X, Yang C, Xu F, et al. Imbalance of circulating Tfr/Tfh ratio in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2019,19(1):55-64. |
| [12] | Hou S, Clement RL, Diallo A, et al. FoxP3 and Ezh2 regulate Tfr cell suppressive function and transcriptional program[J]. J Exp Med, 2019,216(3):605-620. |
| [1] | 刘东武, 陈杰, 高明利, 于静. 类风湿关节炎伴发淋巴结Castleman样病理改变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [2] | 黄会娜,赵静,赵祥格,白自然,李霞,王冠. 乳酸对类风湿关节炎患者外周血CD4+T细胞亚群的调控作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [3] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [4] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [5] | 吴琦,蔡月明,何娟,黄文蒂,王庆文. 血脂异常与类风湿关节炎肺间质病变的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [6] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 体重指数与类风湿关节炎临床特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [7] | 金银姬,孙琳,赵金霞,刘湘源. 血清IgA型抗鼠科肉瘤病毒癌基因同源物B1抗体在类风湿关节炎中的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [8] | 蔡文心,李仕成,刘一鸣,梁如玉,李静,郭建萍,胡凡磊,孙晓麟,李春,刘栩,叶华,邓立宗,李茹,栗占国. 类风湿关节炎临床分层及其特征的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [9] | 程昉,杨邵英,房星星,王璇,赵福涛. CCL28-CCR10通路在类风湿关节炎单核细胞迁移中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [10] | 刘蕊,赵金霞,闫良. 类风湿关节炎合并下肢静脉血栓患者的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
| [11] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 类风湿关节炎患者生活质量与疾病活动度的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1086-1093. |
| [12] | 高超,陈立红,王莉,姚鸿,黄晓玮,贾语博,刘田. 类风湿关节炎合并纤维肌痛简易分类标准的临床验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 278-282. |
| [13] | 娄雪,廖莉,李兴珺,王楠,刘爽,崔若玫,徐健. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血TWEAK基因启动子区甲基化状态及其表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
| [14] | 钟华,徐丽玲,白明欣,苏茵. 类风湿关节炎患者趋化因子CXCL9和CXCL10在骨侵蚀中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1026-1031. |
| [15] | 罗靓,霍文岗,张钦,李春. 类风湿关节炎合并角膜溃疡的临床特点和相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1032-1036. |
|
||